Ransomware Threats Evolve in Manufacturing, Highlighting New Vulnerabilities and Security Gaps
Published on: 2025-12-15
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Manufacturing is becoming a test bed for ransomware shifts
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
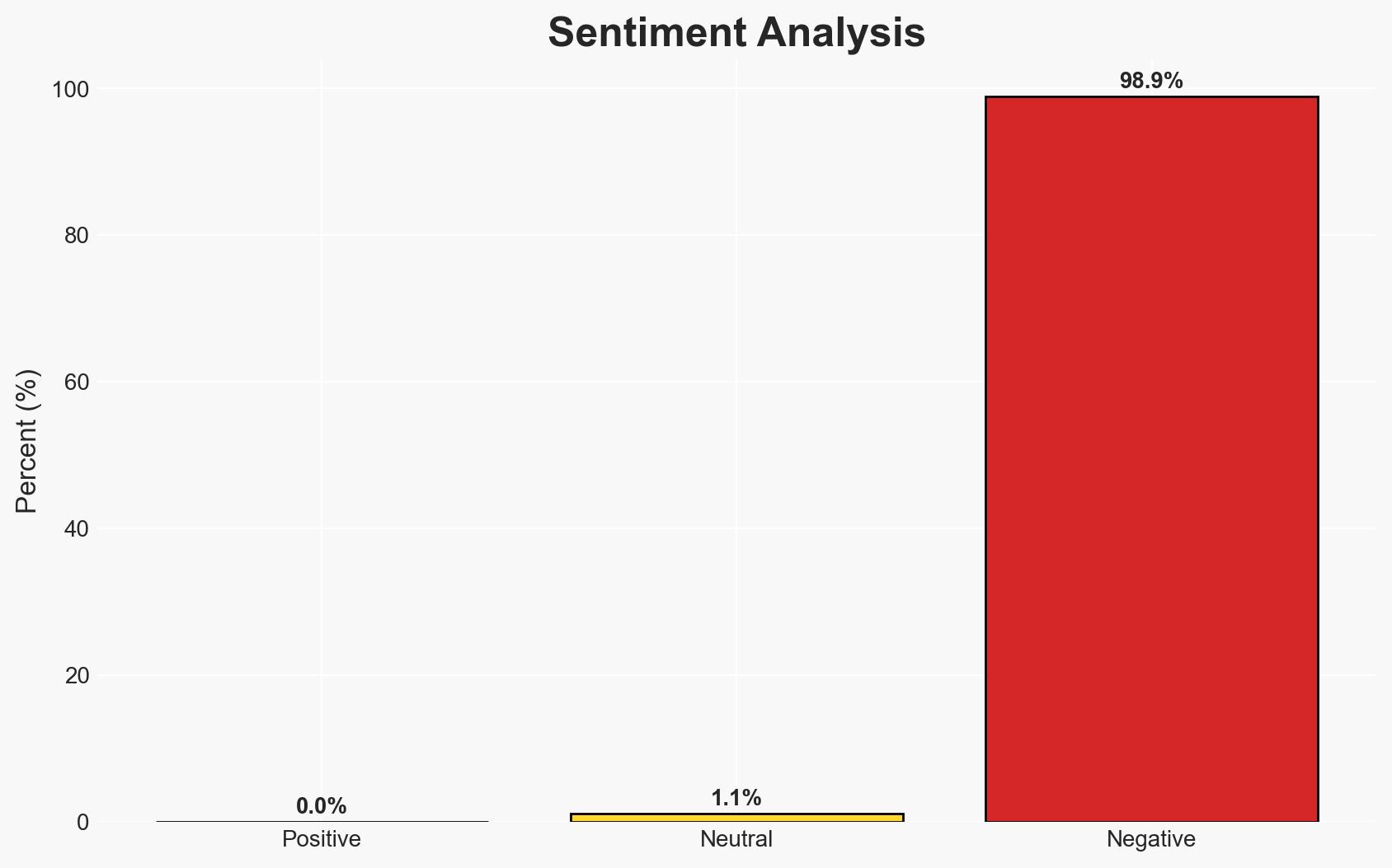
The manufacturing sector is experiencing a shift in ransomware tactics, with attackers increasingly leveraging data theft and extortion over encryption. This shift is driven by the high value of intellectual property and the critical nature of manufacturing operations. The overall confidence level in this assessment is moderate, given the evolving nature of threats and the reliance on survey data.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Attackers are shifting tactics from data encryption to data theft and extortion due to the high value of intellectual property and operational disruption in manufacturing. This is supported by the reported decrease in encryption rates and increased extortion cases. However, the reliance on survey data introduces uncertainty about the representativeness of these findings.
- Hypothesis B: The observed shift is temporary and attackers will revert to encryption as the primary tactic once defenses against data theft improve. This is contradicted by the current trend of reduced encryption rates and increased extortion demands, but remains a possibility if organizations enhance their data protection measures.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the consistent pattern of reduced encryption and increased extortion reported in the survey. Indicators such as a resurgence in encryption tactics or significant improvements in data protection could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Attackers prioritize financial gain over disruption, manufacturing systems remain vulnerable, survey data accurately reflects broader trends, organizations will continue to improve defenses.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on specific vulnerabilities exploited, attacker motivations, and the full scope of financial impacts on victims.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in survey responses, selective reporting by companies, and the possibility of attackers intentionally misleading about tactics.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The shift in ransomware tactics could lead to increased financial and operational risks for the manufacturing sector, with broader implications for supply chain stability and economic performance.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regulatory scrutiny and international cooperation on cybersecurity standards.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened focus on protecting critical infrastructure and industrial systems from cyber threats.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased demand for advanced cybersecurity solutions and threat intelligence capabilities.
- Economic / Social: Potential disruptions to supply chains and increased costs for manufacturers, impacting economic stability and employment.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of ransomware activities, conduct vulnerability assessments, and update incident response plans.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Invest in cybersecurity training, strengthen partnerships with cybersecurity firms, and develop robust data protection strategies.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Improved defenses lead to a decline in successful attacks; triggers include widespread adoption of advanced security measures.
- Worst Case: Attackers develop more sophisticated tactics, leading to increased financial losses; triggers include stagnation in cybersecurity innovation.
- Most-Likely: Continued adaptation by attackers and defenders, with a gradual reduction in successful attacks; triggers include ongoing investment in cybersecurity.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Alexandra Rose, Director of Threat Research, Sophos Counter Threat Unit
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, ransomware, manufacturing, data theft, extortion, supply chain, intellectual property
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us