Redis CVE-2025-49844 Use-After-Free may lead to remote code execution – Redis.io
Published on: 2025-10-07
Intelligence Report: Redis CVE-2025-49844 Use-After-Free may lead to remote code execution – Redis.io
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
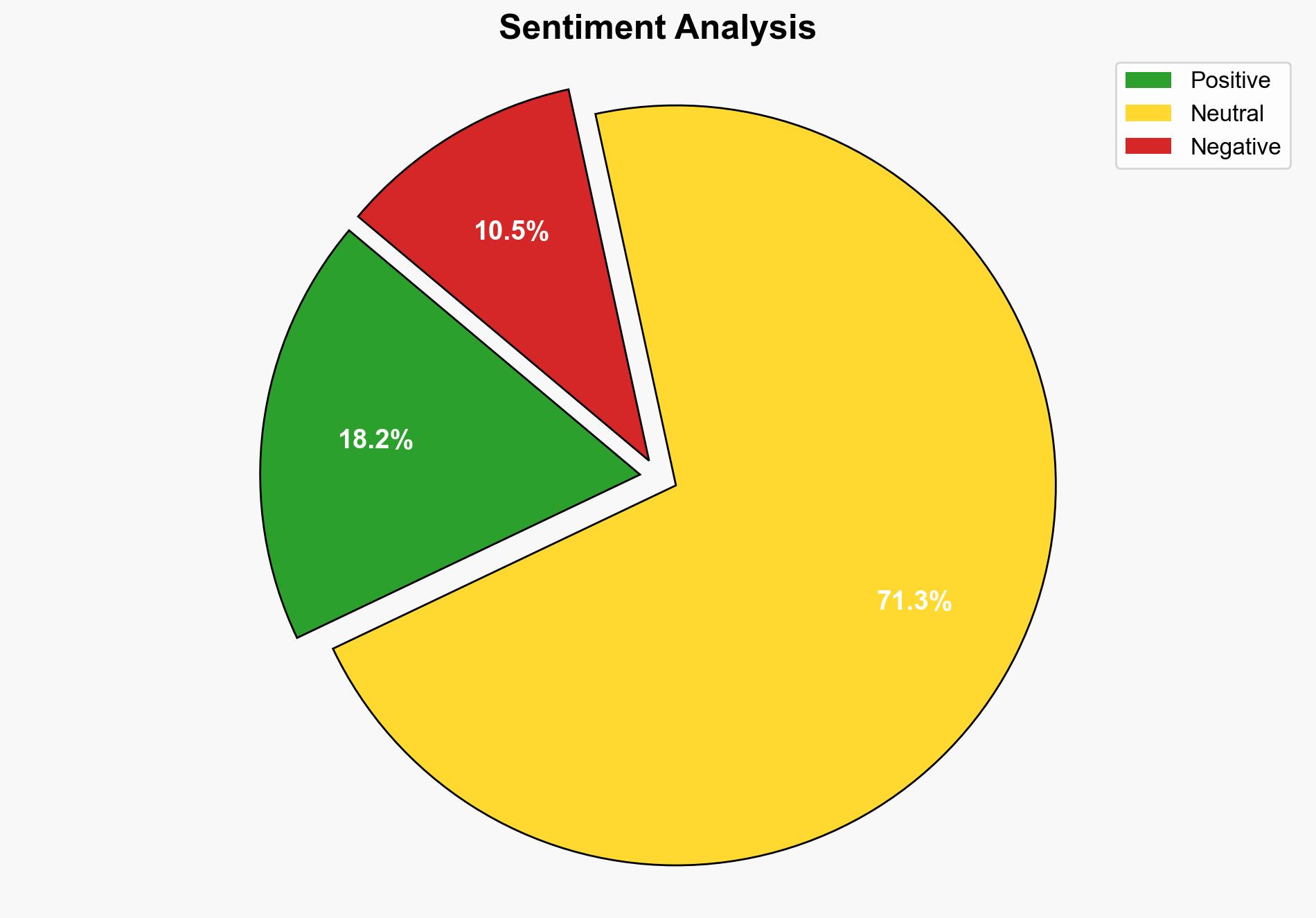
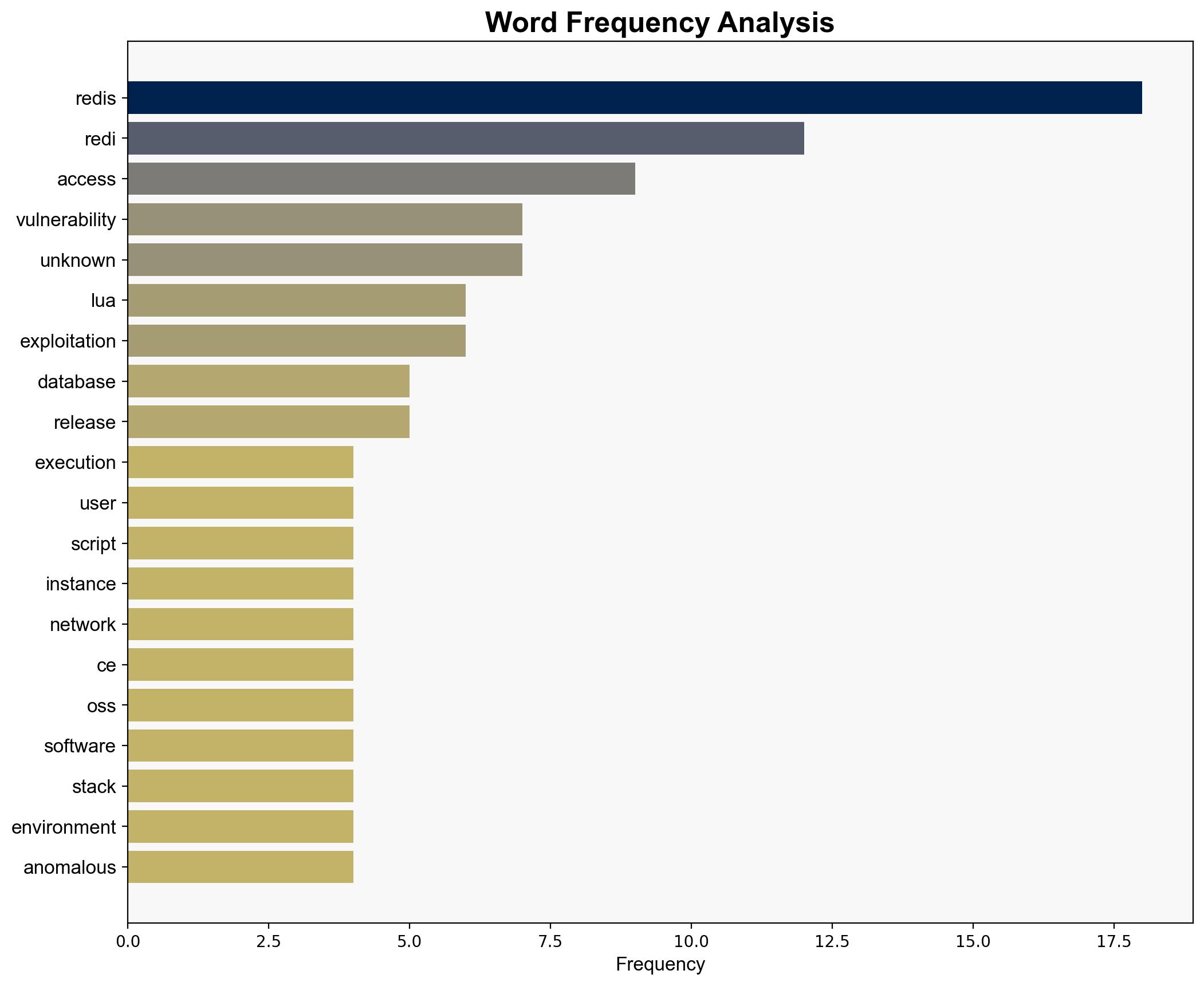
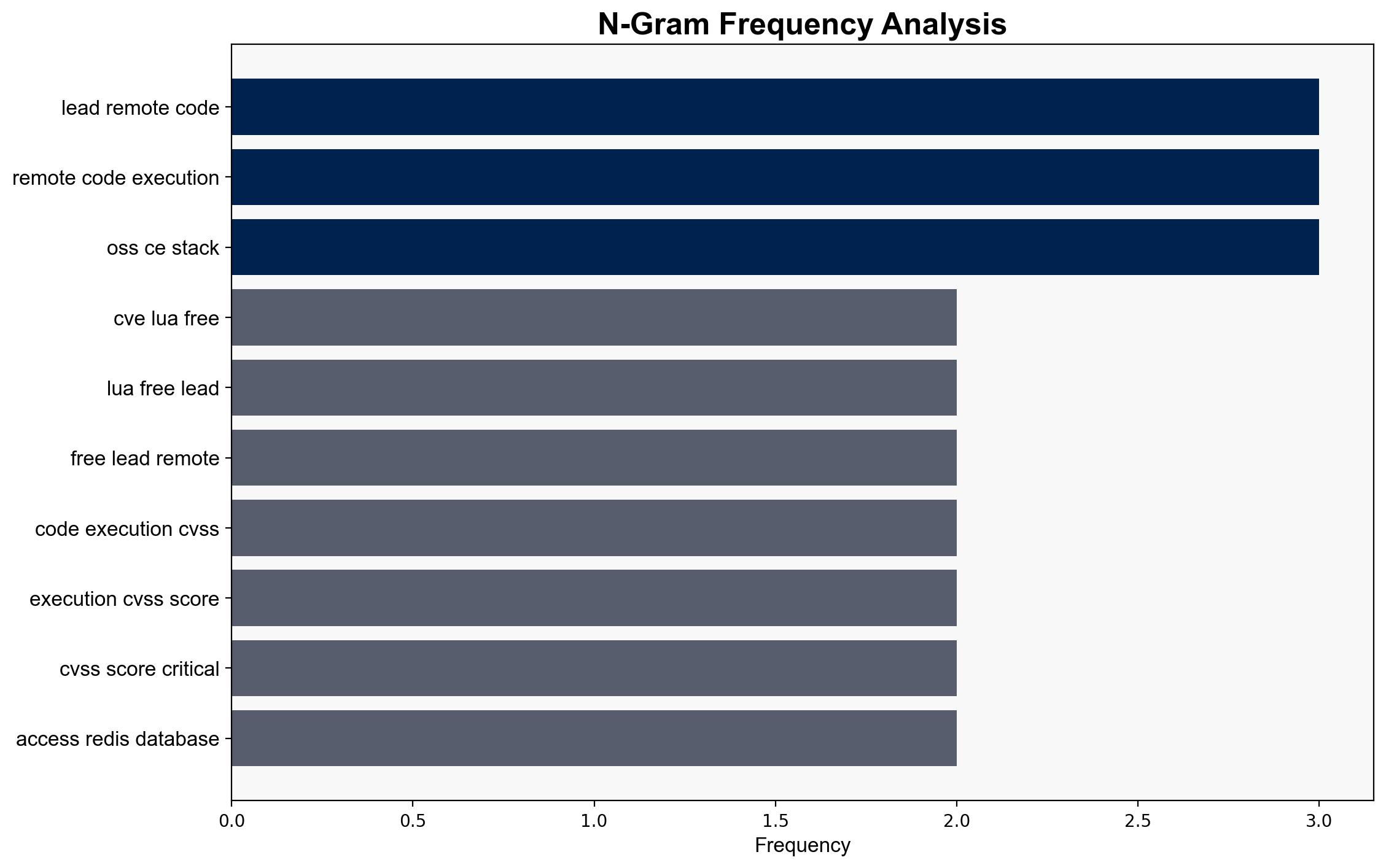
The vulnerability CVE-2025-49844 in Redis poses a critical threat due to its potential for remote code execution through a use-after-free flaw. The most supported hypothesis is that this vulnerability, if exploited, could lead to significant unauthorized access and control over affected systems. Immediate patching and strict access controls are recommended. Confidence Level: High.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The vulnerability will be exploited primarily by sophisticated threat actors targeting high-value systems due to the requirement of authenticated access.
Hypothesis 2: The vulnerability will see widespread exploitation by various threat actors, including less sophisticated ones, due to potential lapses in security practices and authentication measures.
Using the Analysis of Competing Hypotheses (ACH) 2.0, Hypothesis 1 is better supported. The requirement for authenticated access suggests that only actors with significant resources or insider access are likely to exploit this vulnerability effectively.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions include the belief that most Redis instances are secured with strong authentication, which may not hold true universally. A red flag is the lack of detailed reporting on actual exploitation incidents, which could indicate underreporting or detection challenges. The assumption that all users will promptly update to the patched version is optimistic and may not reflect real-world behavior.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The vulnerability could lead to cascading threats, such as data breaches or service disruptions, particularly in environments where Redis is used as a backend for critical applications. Economically, organizations could face significant costs related to incident response and system downtime. Geopolitically, state-sponsored actors might exploit this vulnerability to gain strategic advantages.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate patching of Redis instances to the latest version is critical.
- Implement strict network access controls and authentication measures.
- Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing to identify potential vulnerabilities.
- Scenario Projections:
- Best Case: Rapid patch adoption and improved security practices prevent exploitation.
- Worst Case: Widespread exploitation leads to significant data breaches and operational disruptions.
- Most Likely: Targeted attacks by sophisticated actors with some incidents of less skilled exploitation.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Benny Isaacs, Nir Brakha, and Sagi Tzadik are noted for identifying and reporting the vulnerability. Their work is crucial in understanding the threat landscape and guiding mitigation efforts.
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, cybersecurity, counter-terrorism, regional focus