Research Reveals Vulnerabilities in Major Cloud Password Managers to Password Recovery Attacks
Published on: 2026-02-16
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Study Uncovers 25 Password Recovery Attacks in Major Cloud Password Managers
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
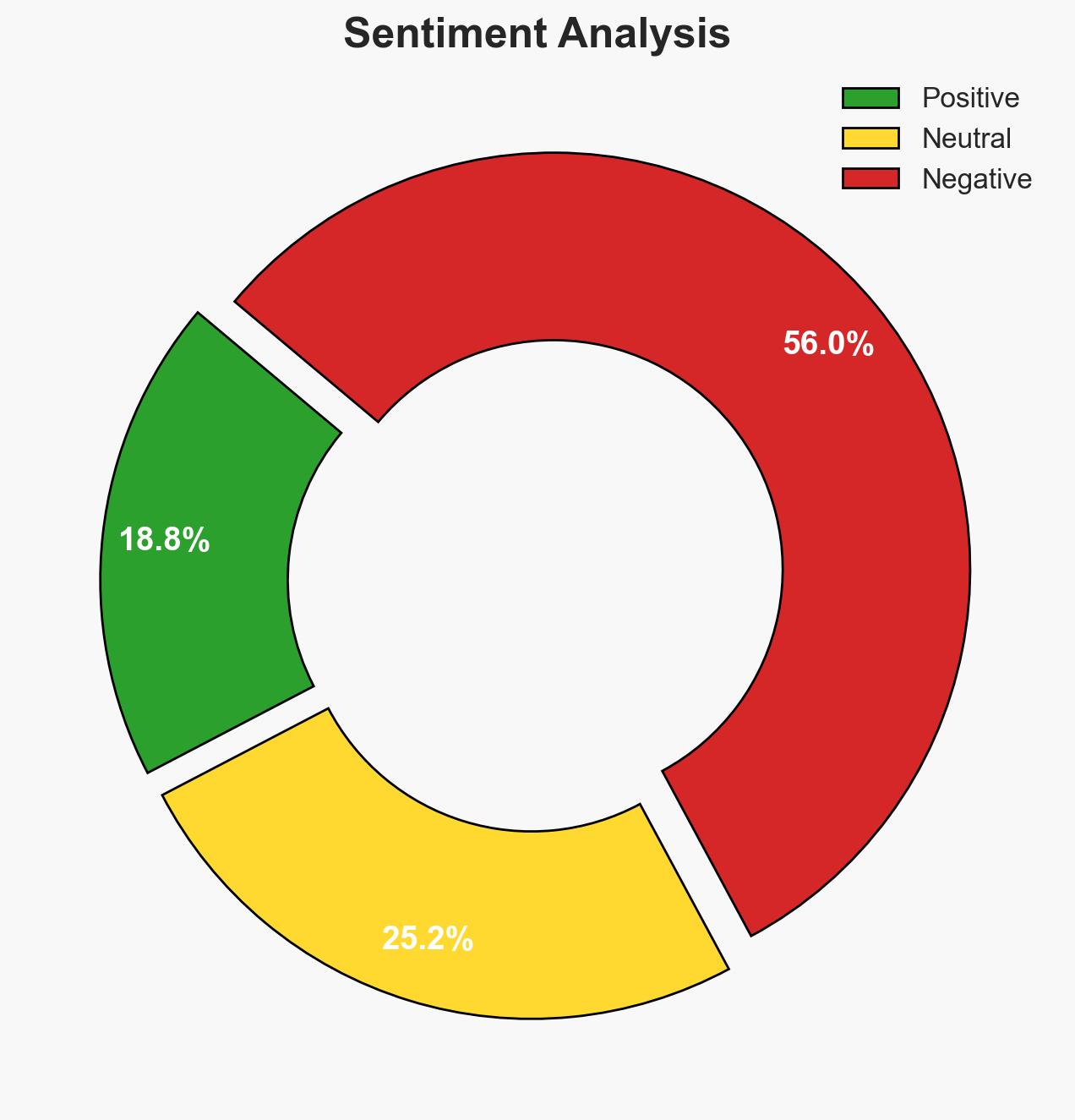
The recent study identifies significant vulnerabilities in major cloud-based password managers, affecting over 60 million users and 125,000 businesses. The most likely hypothesis is that these vulnerabilities stem from design flaws and cryptographic misconceptions, with moderate confidence. This poses a substantial risk to user data integrity and confidentiality.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The vulnerabilities are primarily due to inherent design flaws and cryptographic misconceptions in the password managers. Supporting evidence includes the identification of common design anti-patterns and specific attacks exploiting these flaws. Key uncertainties involve the extent to which these vulnerabilities are actively being exploited.
- Hypothesis B: The vulnerabilities are exaggerated or misrepresented by the researchers, potentially due to biases or errors in the study. Contradicting evidence includes the detailed categorization of attacks and the involvement of reputable academic institutions. However, the absence of real-world exploitation data weakens this hypothesis.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the detailed technical findings and the credibility of the research institutions. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of active exploitation or vendor responses addressing the vulnerabilities.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The study’s findings accurately reflect the vulnerabilities present in the password managers. The vendors are unaware of these vulnerabilities or have not yet addressed them. The research methodology is sound and unbiased.
- Information Gaps: Data on whether these vulnerabilities have been exploited in real-world scenarios. Vendor responses or patches addressing the identified vulnerabilities.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential for cognitive bias in interpreting the study’s findings as more severe than they are. Source bias due to the study being conducted by specific academic institutions with potential vested interests.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The discovery of these vulnerabilities could lead to increased scrutiny of cloud-based password managers and pressure on vendors to enhance security measures. This development may also influence user trust and adoption rates.
- Political / Geopolitical: Limited direct implications, but potential for increased regulatory scrutiny on data protection standards.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information, potentially impacting organizational security.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for exploitation by cybercriminals, leading to data leaks and compromised accounts.
- Economic / Social: Possible economic impact on vendors due to loss of consumer trust and potential legal liabilities.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor vendor responses and updates. Encourage users to implement additional security measures, such as two-factor authentication.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms to enhance password manager security. Advocate for industry-wide standards on cryptographic practices.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best-case: Vendors address vulnerabilities promptly, restoring user trust.
- Worst-case: Widespread exploitation of vulnerabilities leads to significant data breaches.
- Most-likely: Gradual improvements in security practices with moderate impact on user trust.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Bitwarden
- Dashlane
- LastPass
- 1Password
- ETH Zurich
- Università della Svizzera italiana
- Jacob DePriest
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, data protection, cryptographic vulnerabilities, password management, cloud security, user privacy, information security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us