Resecurity refutes ShinyHunters’ breach allegations, cites use of synthetic honeypot for deception.
Published on: 2026-01-05
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Resecurity denies ShinyHunters breach claim says attackers hit synthetic honeypot
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
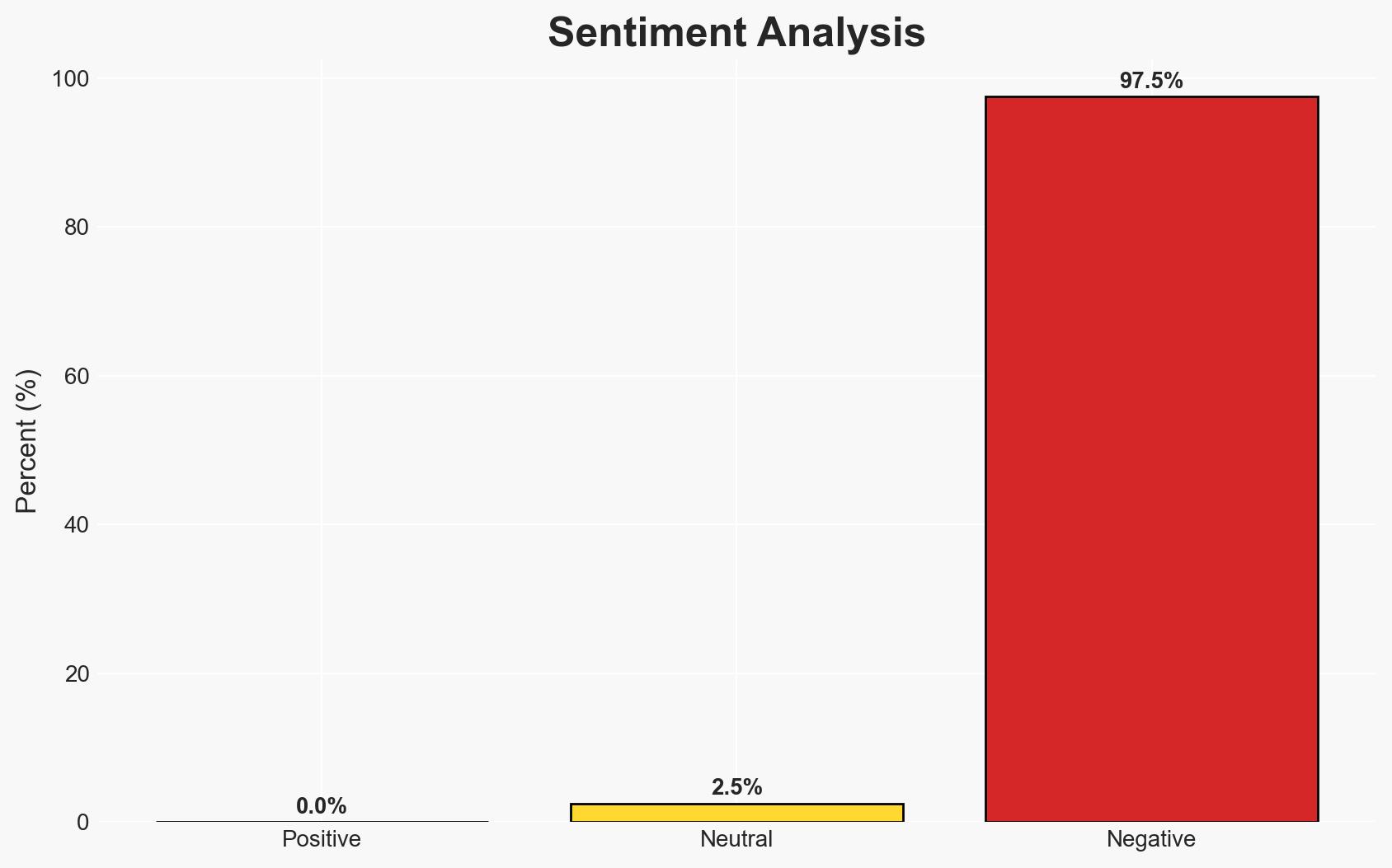
Resecurity Inc. claims that the alleged breach by ShinyHunters was a result of a deception operation involving a synthetic honeypot, not an actual compromise of their systems. This suggests a sophisticated use of active cyber defense techniques. The most likely hypothesis is that the attackers were indeed deceived by the honeypot, with moderate confidence in this assessment due to the lack of contradictory evidence. This incident affects cybersecurity stakeholders and highlights the evolving tactics in cyber defense.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: ShinyHunters successfully breached Resecurity’s systems and accessed sensitive data. Supporting evidence includes the attackers’ claims of accessing internal data. Contradicting evidence includes Resecurity’s detailed explanation of the honeypot setup and the synthetic nature of the data accessed.
- Hypothesis B: The attackers were deceived by a honeypot containing synthetic data, as claimed by Resecurity. Supporting evidence includes Resecurity’s proactive disclosure and explanation of their deception techniques. The lack of independent verification of the breach supports this hypothesis.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to Resecurity’s detailed account of the honeypot operation and the absence of evidence proving a real breach. Indicators that could shift this judgment include independent verification of the breach or new evidence from credible sources.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Resecurity’s account of the honeypot operation is accurate; the data accessed was entirely synthetic; ShinyHunters’ claims are not independently verified.
- Information Gaps: Lack of independent verification of the breach; absence of third-party analysis of the alleged data breach.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in Resecurity’s self-reporting; possible deception by ShinyHunters to inflate their capabilities or reputation.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development underscores the increasing sophistication of cyber defense strategies and the potential for misinformation in cyber threat reporting. It could influence how organizations approach threat intelligence and cyber defense.
- Political / Geopolitical: May affect international perceptions of cybersecurity capabilities and influence cyber policy discussions.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Highlights the need for advanced deception techniques in countering cyber threats.
- Cyber / Information Space: Demonstrates the role of honeypots in gathering intelligence on threat actors and the potential for misinformation in cyber claims.
- Economic / Social: Limited direct economic impact, but could affect trust in cybersecurity firms and influence market dynamics.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Verify claims through independent cybersecurity audits; enhance monitoring of threat actor communications for corroborative evidence.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms for shared intelligence; invest in deception-based cyber defense capabilities.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Confirmation of honeypot success strengthens cyber defense strategies. Worst: Verification of a real breach damages Resecurity’s credibility. Most-Likely: Continued uncertainty with gradual clarification through third-party analysis.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Resecurity Inc.
- ShinyHunters
- LAPSUS$
- Scattered Spider
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, honeypot, cyber defense, threat intelligence, deception techniques, cyber claims, misinformation
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us