Revolutionizing Cybersecurity: Embedding Protection Directly into Hardware Solutions
Published on: 2026-01-07
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Inside the Chip Rethinking Cybersecurity from the Ground Up
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
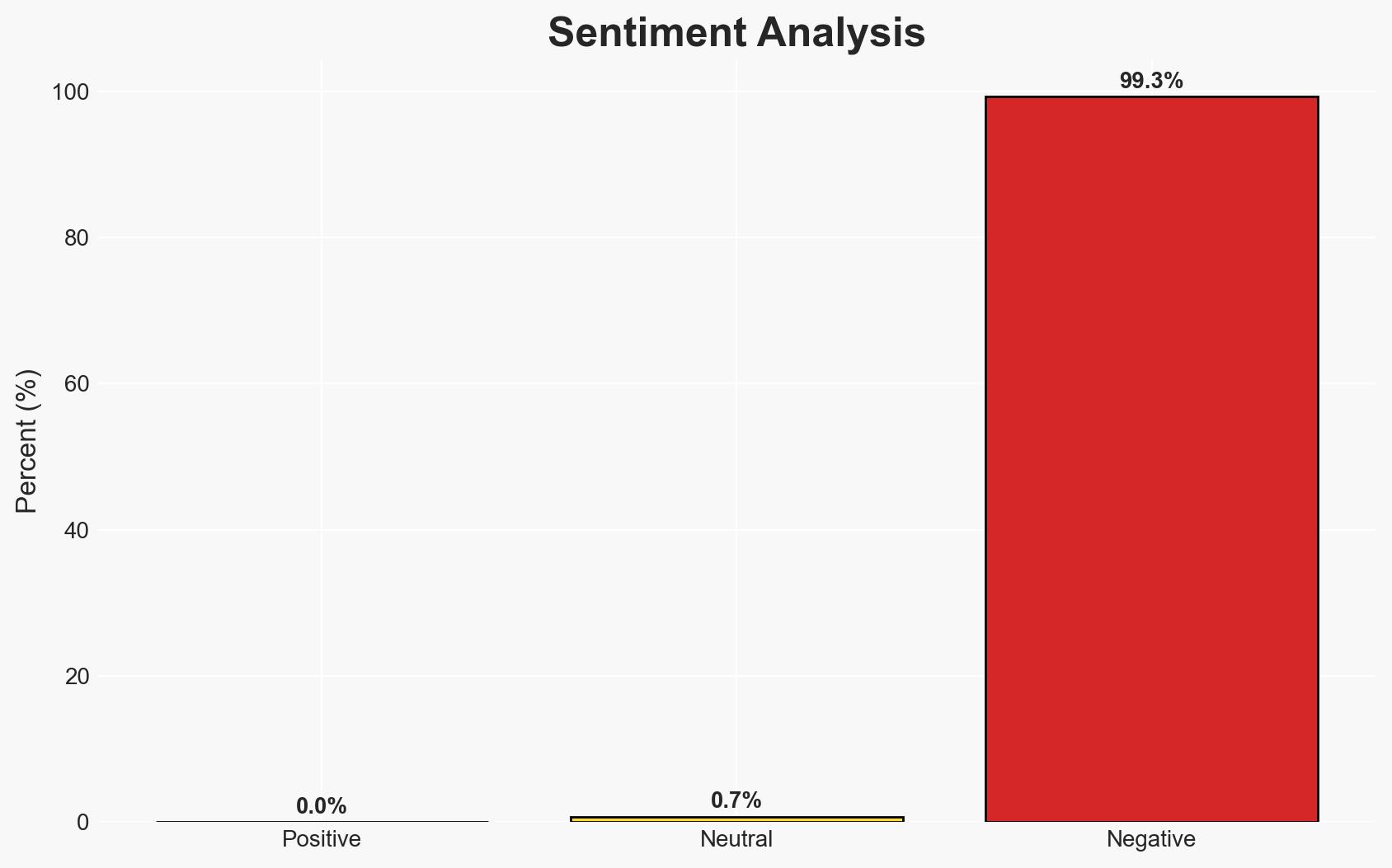
The shift towards hardware-based cybersecurity, specifically through Hardware Root of Trust (HRoT), represents a proactive strategy to mitigate deeply embedded cyber threats. This approach is likely to enhance system integrity and trust, impacting sectors reliant on digital infrastructure. Overall, there is moderate confidence in the effectiveness of this shift, contingent on technological advancements and adoption rates.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Hardware-based security, particularly HRoT, will significantly reduce cyber vulnerabilities by providing a proactive defense mechanism. This is supported by the inherent difficulty in compromising hardware compared to software. However, uncertainties remain regarding the integration costs and the time required for widespread adoption.
- Hypothesis B: Despite the potential of HRoT, attackers will adapt, finding new methods to exploit hardware vulnerabilities, thus maintaining the status quo of cyber threats. This is supported by historical patterns of adversaries evolving tactics. Contradicting evidence includes the current lack of known methods to effectively bypass HRoT.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the proactive nature of HRoT and its ability to validate system integrity independently of software. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include the discovery of new hardware vulnerabilities or significant delays in HRoT implementation.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: HRoT can be effectively integrated into existing systems; attackers will not immediately develop methods to bypass HRoT; organizations will prioritize hardware-based security investments.
- Information Gaps: Detailed cost analysis of HRoT implementation; empirical data on HRoT effectiveness in real-world scenarios.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential over-reliance on vendor claims about HRoT capabilities; confirmation bias towards hardware solutions due to current software limitations.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The adoption of HRoT could redefine cybersecurity paradigms, influencing both defensive strategies and adversarial tactics.
- Political / Geopolitical: Nations may prioritize domestic HRoT development to reduce reliance on foreign technology, potentially leading to tech sovereignty initiatives.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced security postures could deter state-sponsored cyber operations, shifting focus to other asymmetric tactics.
- Cyber / Information Space: A move towards hardware-based security may alter the cyber threat landscape, reducing the efficacy of current attack vectors.
- Economic / Social: Initial high costs of HRoT implementation could impact smaller organizations, potentially widening the security gap between large and small entities.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Initiate pilot programs to test HRoT integration; enhance monitoring of hardware security developments.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with hardware manufacturers; invest in training for hardware security expertise.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Widespread HRoT adoption reduces cyber incidents. Worst: New vulnerabilities in HRoT are exploited. Most-Likely: Gradual adoption with mixed results, necessitating continued software defenses.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
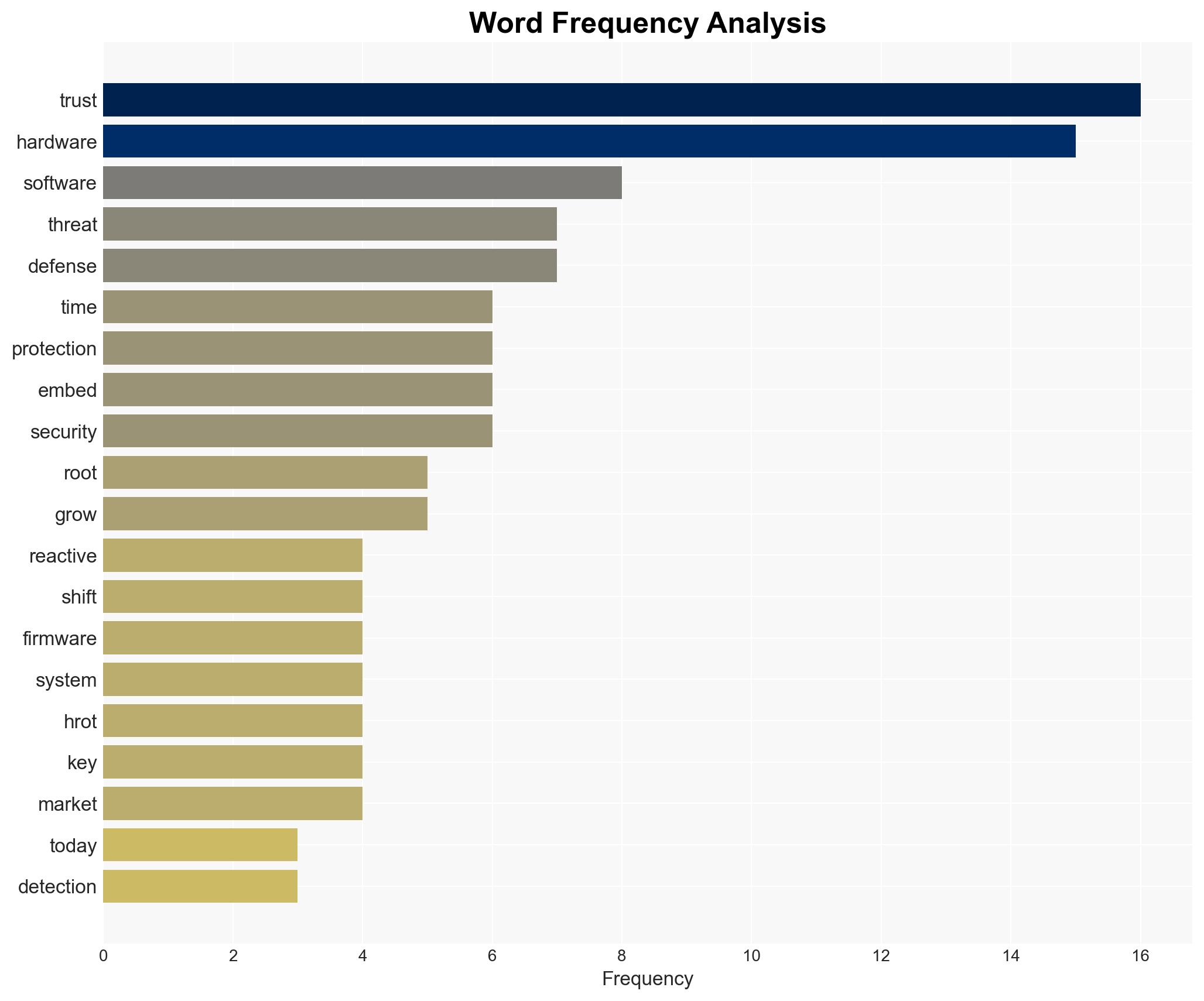
cybersecurity, hardware security, Hardware Root of Trust, cyber threats, proactive defense, digital infrastructure
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us