Rising Antisemitism: The Urgent Need for Education and Accountability Following Hanukkah Tragedy in Australia
Published on: 2025-12-15
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
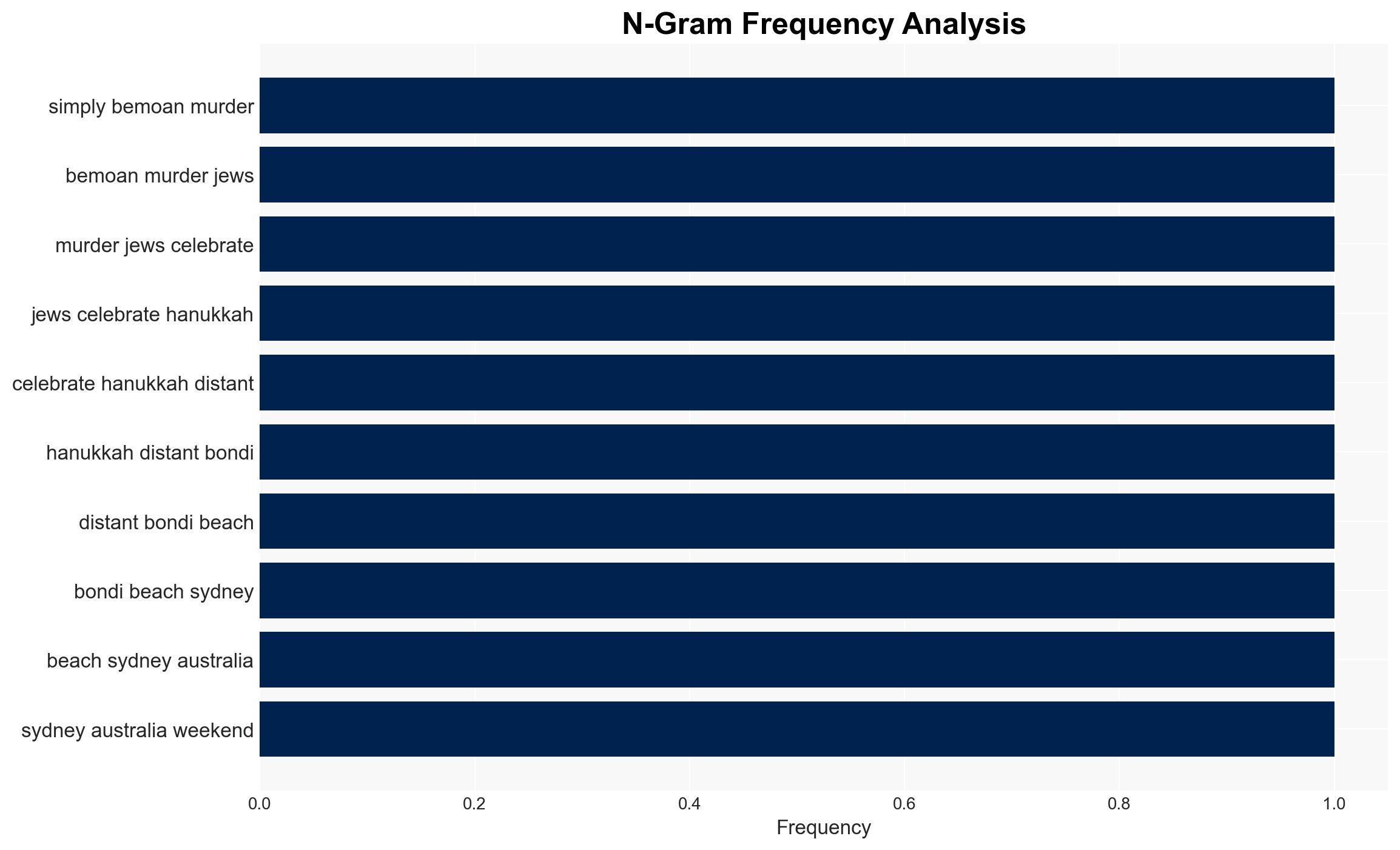
Intelligence Report: After the Mass Murder of Jews on Hanukkah Half a World Away Education and Accountability
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
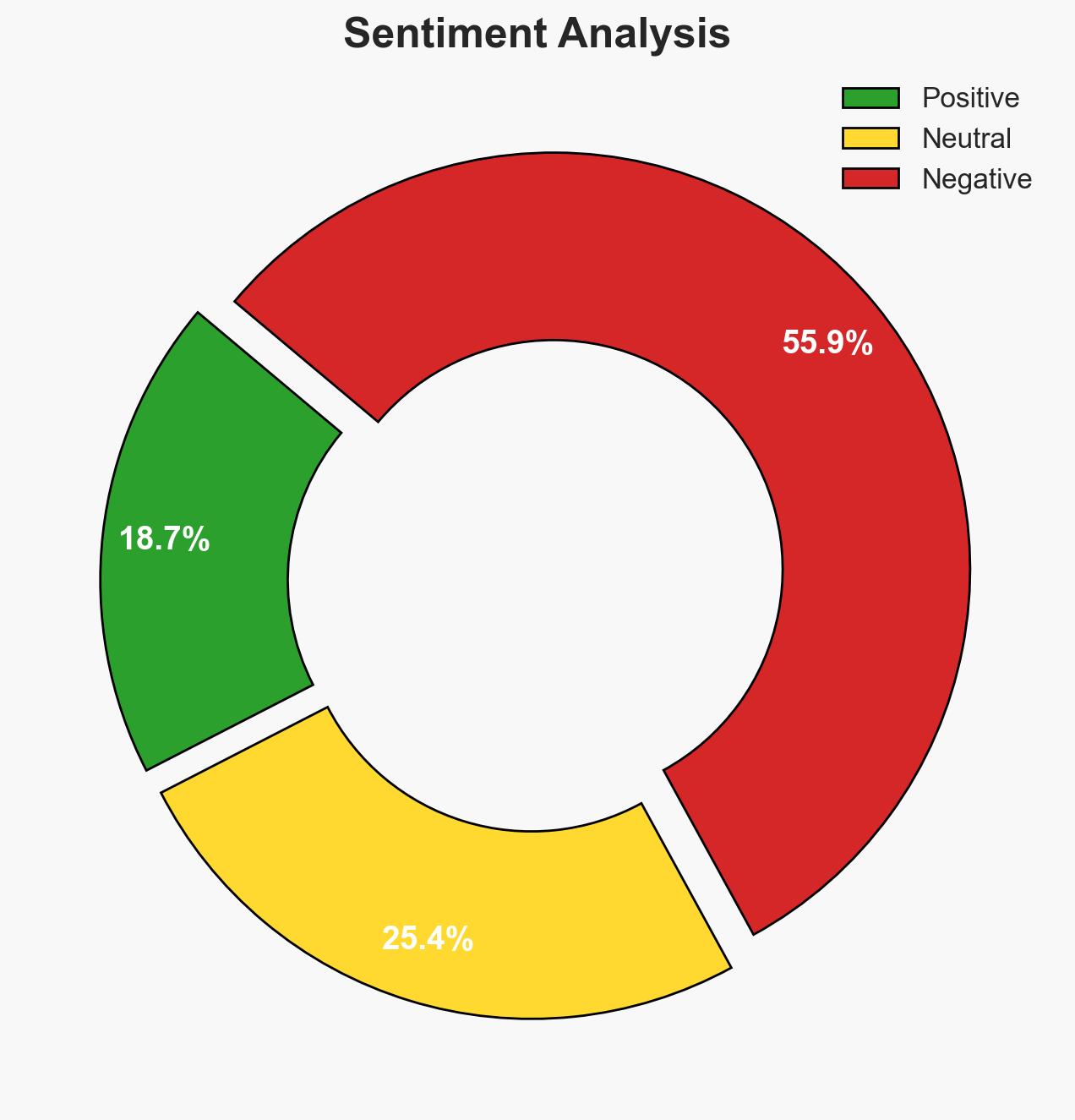
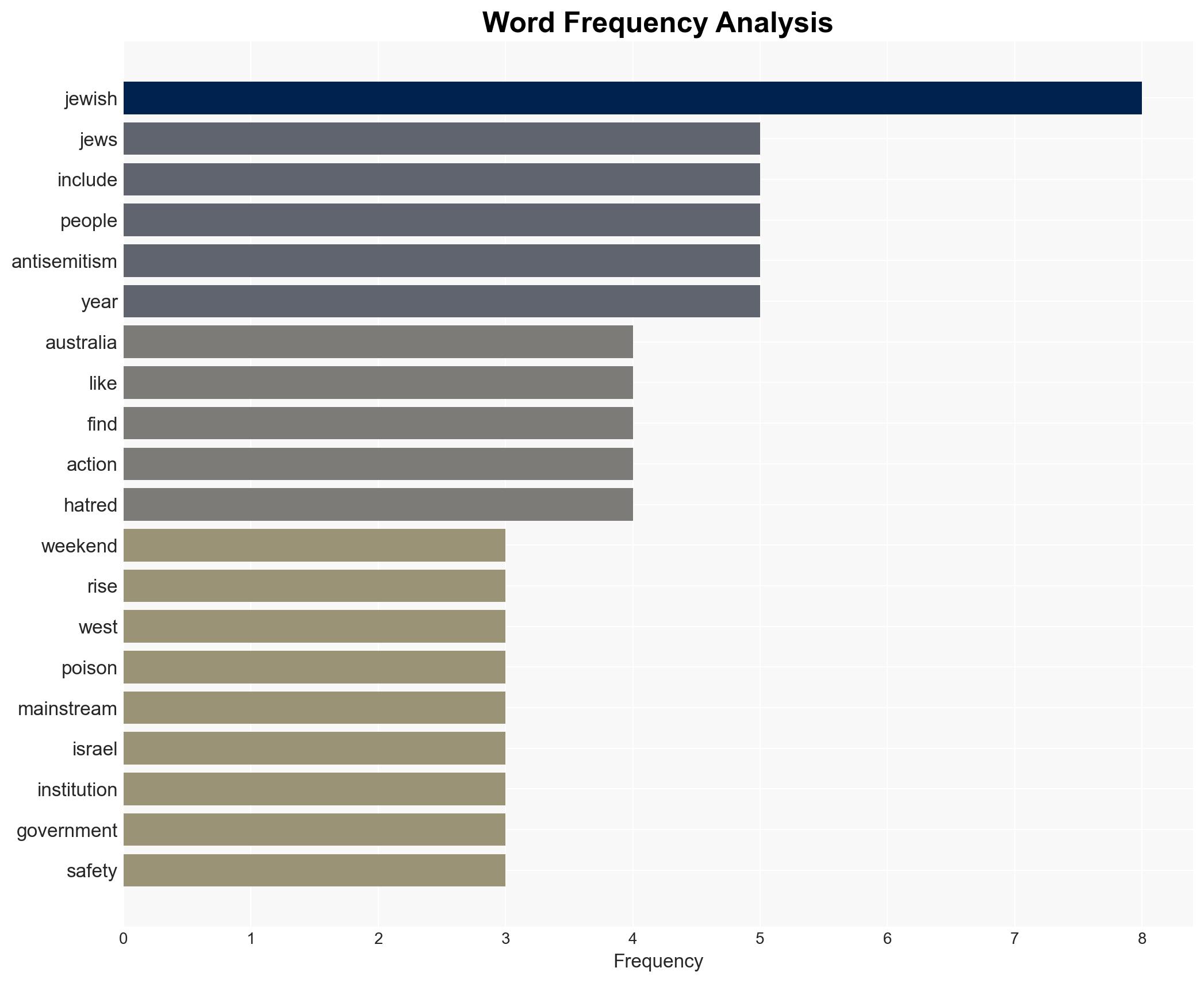
The recent murder of 15 Jews in Sydney, Australia, highlights a significant rise in antisemitic violence across the Western world, exacerbated by geopolitical tensions. This trend poses a growing threat to societal cohesion and security. The most likely hypothesis is that antisemitism is increasingly mainstreamed, with moderate confidence in this assessment due to corroborative incidents and reports.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The rise in antisemitic incidents is primarily driven by geopolitical tensions, particularly those involving Israel and Middle Eastern conflicts. Supporting evidence includes the timing of increased incidents following the Hamas attack on Israel. However, this hypothesis assumes a direct causation that may not account for all variables.
- Hypothesis B: Antisemitism is becoming more mainstream in Western societies due to broader social and political dynamics, independent of specific geopolitical events. Evidence includes the widespread nature of incidents across different countries and contexts. This hypothesis is contradicted by the lack of a single unifying cause.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the pervasive and varied nature of antisemitic incidents across multiple Western countries. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in geopolitical tensions or significant policy shifts in affected countries.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Antisemitic incidents are accurately reported and documented; geopolitical tensions have a direct impact on domestic antisemitic sentiments; Western governments have the capacity to address rising antisemitism effectively.
- Information Gaps: Detailed motivations of the perpetrators in recent incidents; comprehensive data on antisemitic trends in non-Western countries; effectiveness of current government interventions.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in media reporting and advocacy group data; risk of over-attributing incidents to geopolitical causes without sufficient evidence; manipulation by extremist groups to exploit tensions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The rise in antisemitism could lead to increased polarization and societal division, impacting social cohesion and national security. If unchecked, this trend may embolden extremist groups and lead to further violence.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for strained diplomatic relations between Western countries and Israel; increased pressure on governments to address domestic extremism.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment for Jewish communities; potential for increased security measures and resource allocation.
- Cyber / Information Space: Possible exploitation of antisemitic narratives by foreign adversaries to destabilize Western societies; increased online hate speech and misinformation.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impacts from increased security costs and decreased social trust; risk of social unrest and community fragmentation.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of antisemitic incidents; increase security measures for vulnerable communities; initiate public awareness campaigns.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures through community engagement; strengthen international partnerships to combat hate speech; invest in educational programs addressing antisemitism.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Successful reduction in antisemitic incidents through coordinated policy and community efforts.
- Worst: Escalation of violence and societal division, leading to widespread instability.
- Most-Likely: Continued rise in incidents with incremental policy responses and societal adaptation.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Anti-Defamation League
- Debra Messing
- Gal Gadot
- Ted Cruz
- John Fetterman
- Zohran Mamdani
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
Counter-Terrorism, antisemitism, national security, geopolitical tensions, societal cohesion, extremism, public policy, community resilience
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- ACH 2.0: Reconstruct likely threat actor intentions via hypothesis testing and structured refutation.
- Indicators Development: Track radicalization signals and propaganda patterns to anticipate operational planning.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Analyze spread/adaptation of ideological narratives for recruitment/incitement signals.
Explore more:
Counter-Terrorism Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us