Rising Cybersecurity Threats Amid Manufacturers’ Shift to AI and Cloud Technologies
Published on: 2026-01-05
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Cyber risks grow as manufacturers turn to AI and cloud systems
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The rapid adoption of AI and cloud systems in the manufacturing sector has significantly increased cyber vulnerabilities, making it the most-attacked industry for four consecutive years. This trend poses substantial risks to production stability and economic performance, as evidenced by recent high-profile cyber incidents. The current assessment is made with moderate confidence, given the available data and identified information gaps.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The increase in cyberattacks on manufacturers is primarily due to the rapid integration of AI and cloud systems without adequate cybersecurity measures. Supporting evidence includes the high incidence of attacks and expert opinions highlighting connectivity as a vulnerability. Key uncertainties include the actual extent of cybersecurity measures in place across different manufacturers.
- Hypothesis B: The rise in cyberattacks is driven by increased geopolitical tensions and targeted economic sabotage rather than solely technological vulnerabilities. This hypothesis is less supported due to the lack of specific evidence linking attacks to geopolitical motives in the provided data.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported by the evidence, particularly expert analyses and the documented increase in attacks following technological integration. Future indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of state-sponsored attacks or changes in geopolitical dynamics.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Manufacturers are not uniformly implementing cybersecurity measures; AI and cloud systems inherently increase cyber vulnerability; cyberattacks will continue to target the most technologically advanced sectors.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on cybersecurity investments by manufacturers; specific attribution of recent cyberattacks to particular threat actors; comprehensive impact assessments of cyber incidents on global supply chains.
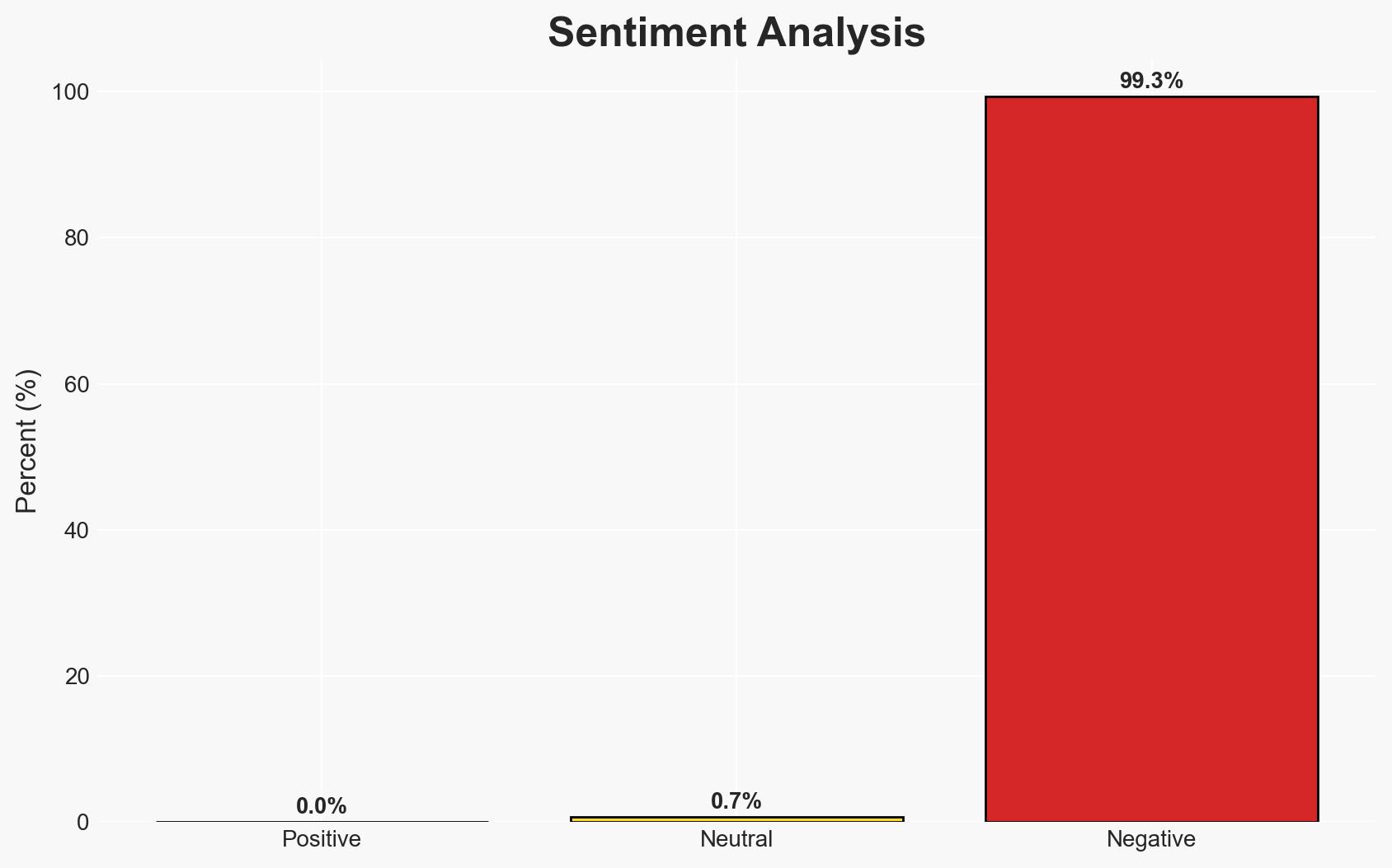
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in expert opinions favoring technological explanations; risk of underreporting due to reputational concerns; possible manipulation of incident data by affected companies to minimize perceived impact.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The ongoing integration of AI and cloud systems in manufacturing could exacerbate existing vulnerabilities, leading to more frequent and severe cyber incidents. This trend may influence broader economic and security dynamics.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased cyber incidents could strain international relations, particularly if state-sponsored attacks are suspected.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened cyber threats may necessitate enhanced security protocols and international cooperation to mitigate risks.
- Cyber / Information Space: The manufacturing sector may become a primary target for cyber espionage and sabotage, requiring robust cybersecurity frameworks.
- Economic / Social: Disruptions in manufacturing could lead to economic instability, job losses, and social unrest, particularly in regions heavily reliant on manufacturing.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a comprehensive audit of cybersecurity measures in the manufacturing sector; increase monitoring of cyber threats targeting manufacturers.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships between government and industry to enhance cybersecurity resilience; invest in cybersecurity training and infrastructure upgrades.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Manufacturers successfully integrate cybersecurity with technological advancements, reducing vulnerability.
- Worst: Cyber incidents lead to significant economic disruptions and geopolitical tensions.
- Most-Likely: Continued cyber threats with gradual improvements in cybersecurity measures as awareness increases.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Jaguar Land Rover
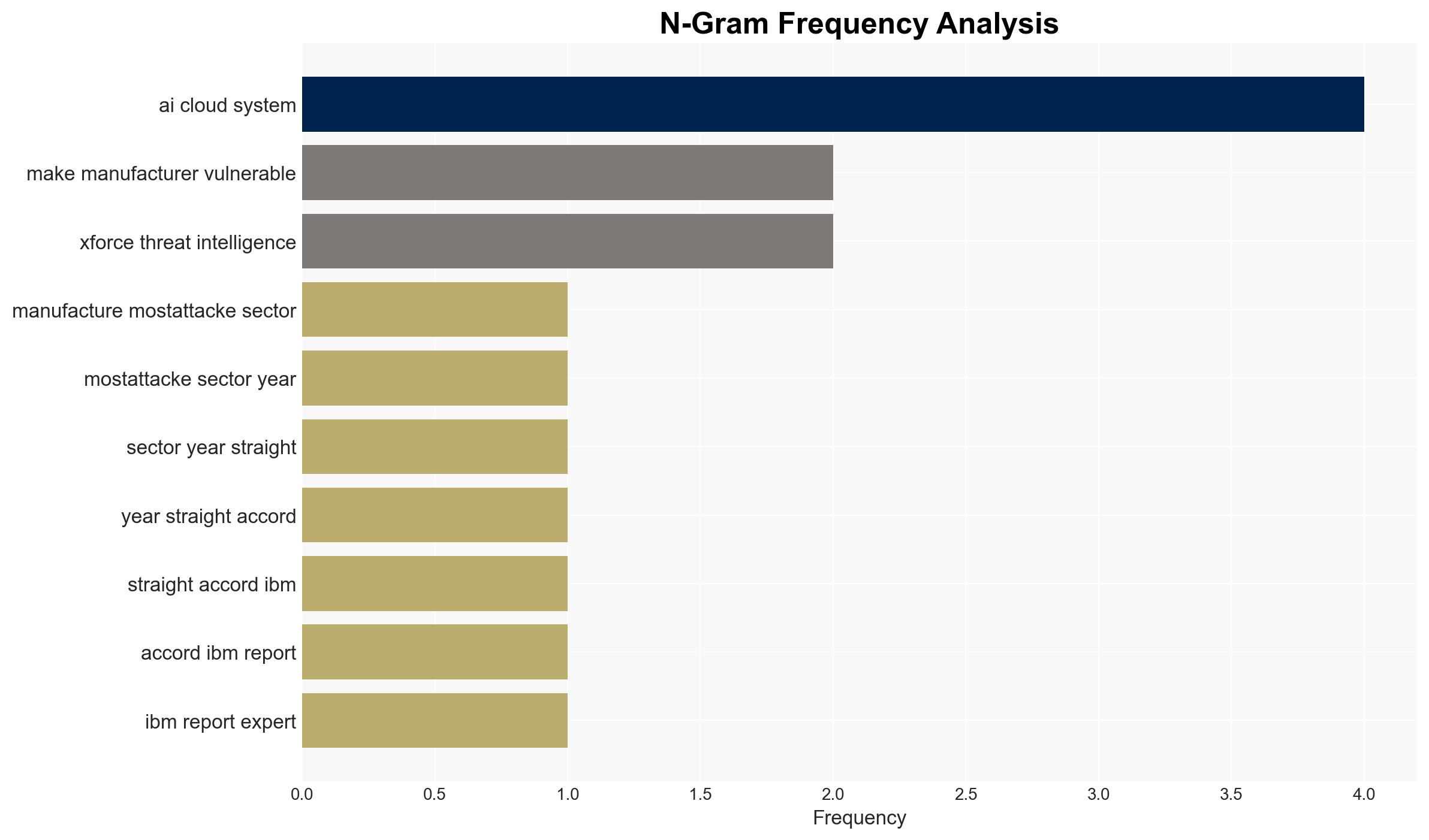
- Nick Nolen, VP of Cybersecurity Strategy and Operations at Redpoint Cyber
- Todd Moore, VP of Encryption at Thales
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
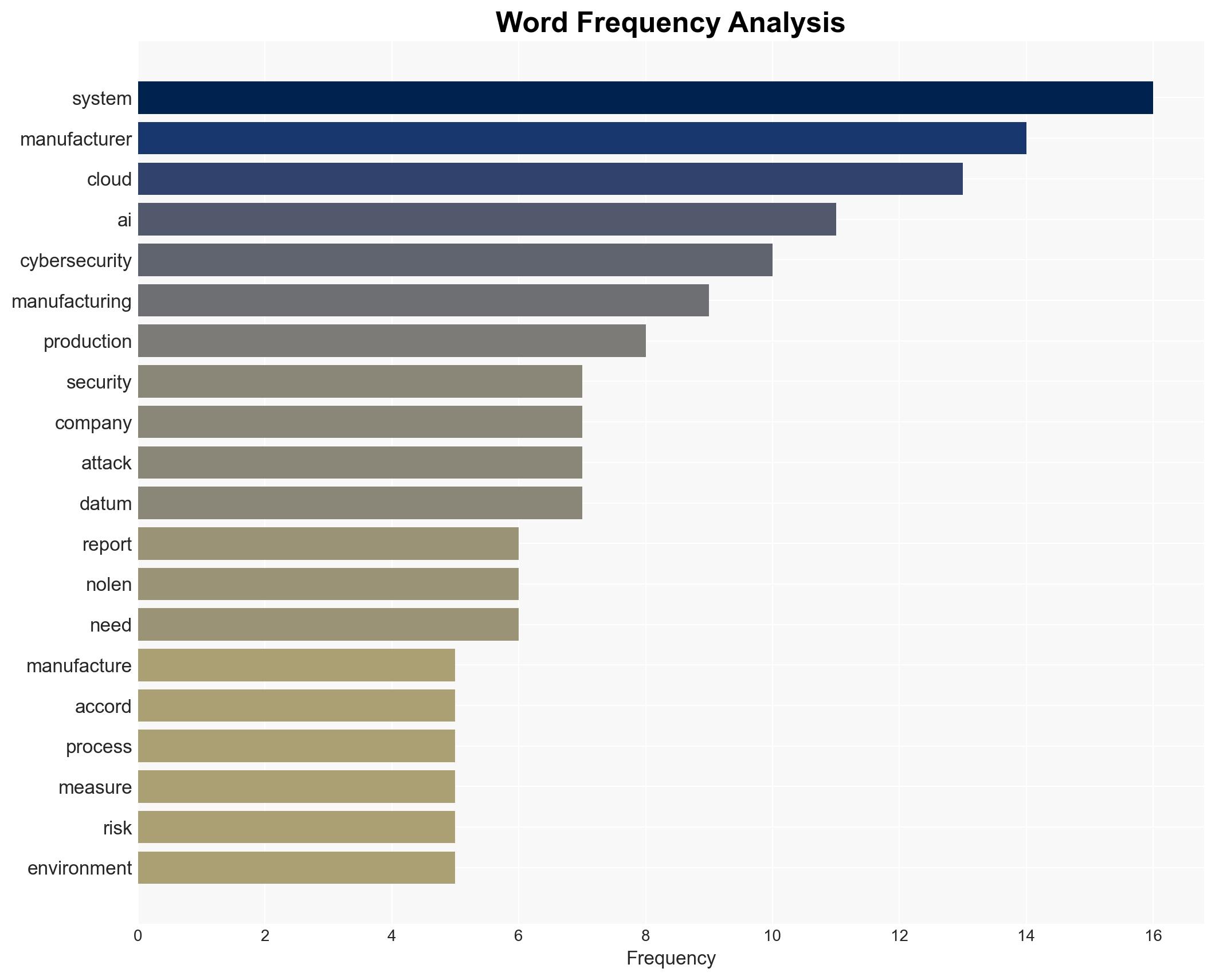
cybersecurity, manufacturing, AI integration, cloud systems, economic impact, supply chain disruption, cyber threats
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us