Rising Espionage Threats and Internal Security Challenges in India Amidst Geopolitical Tensions
Published on: 2026-01-02
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Indias internal security Big shifts rising spy ring threats
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
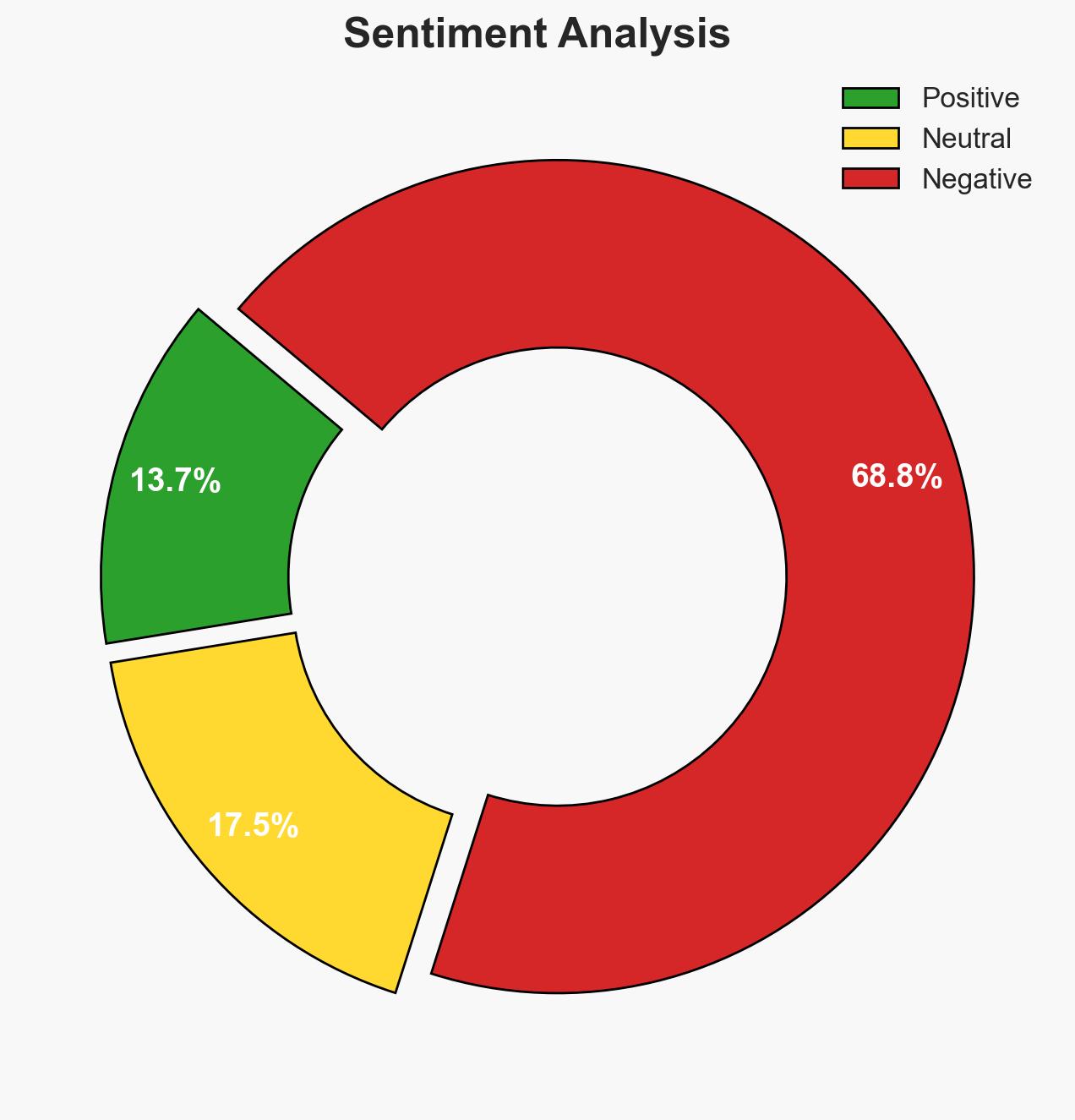
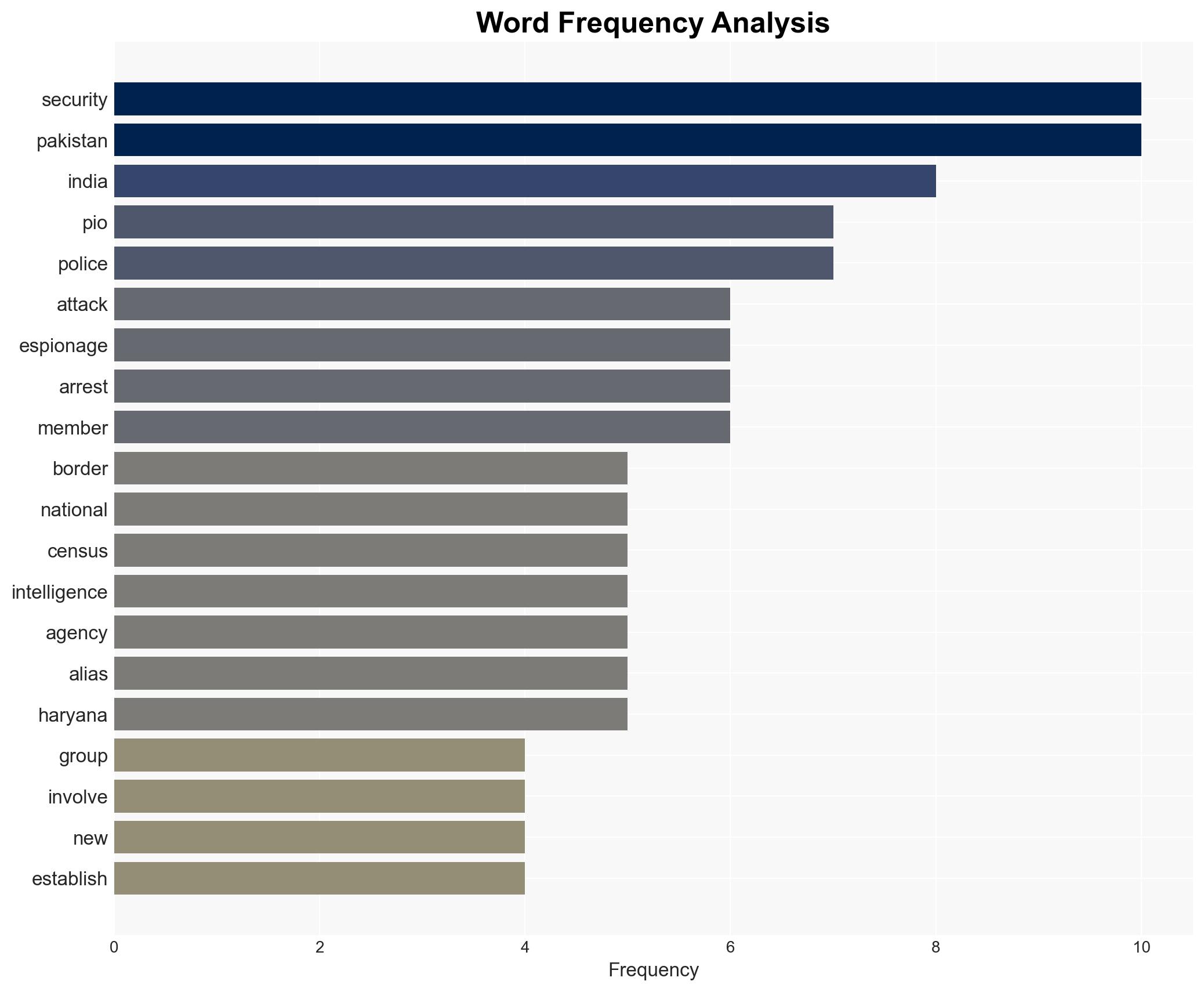
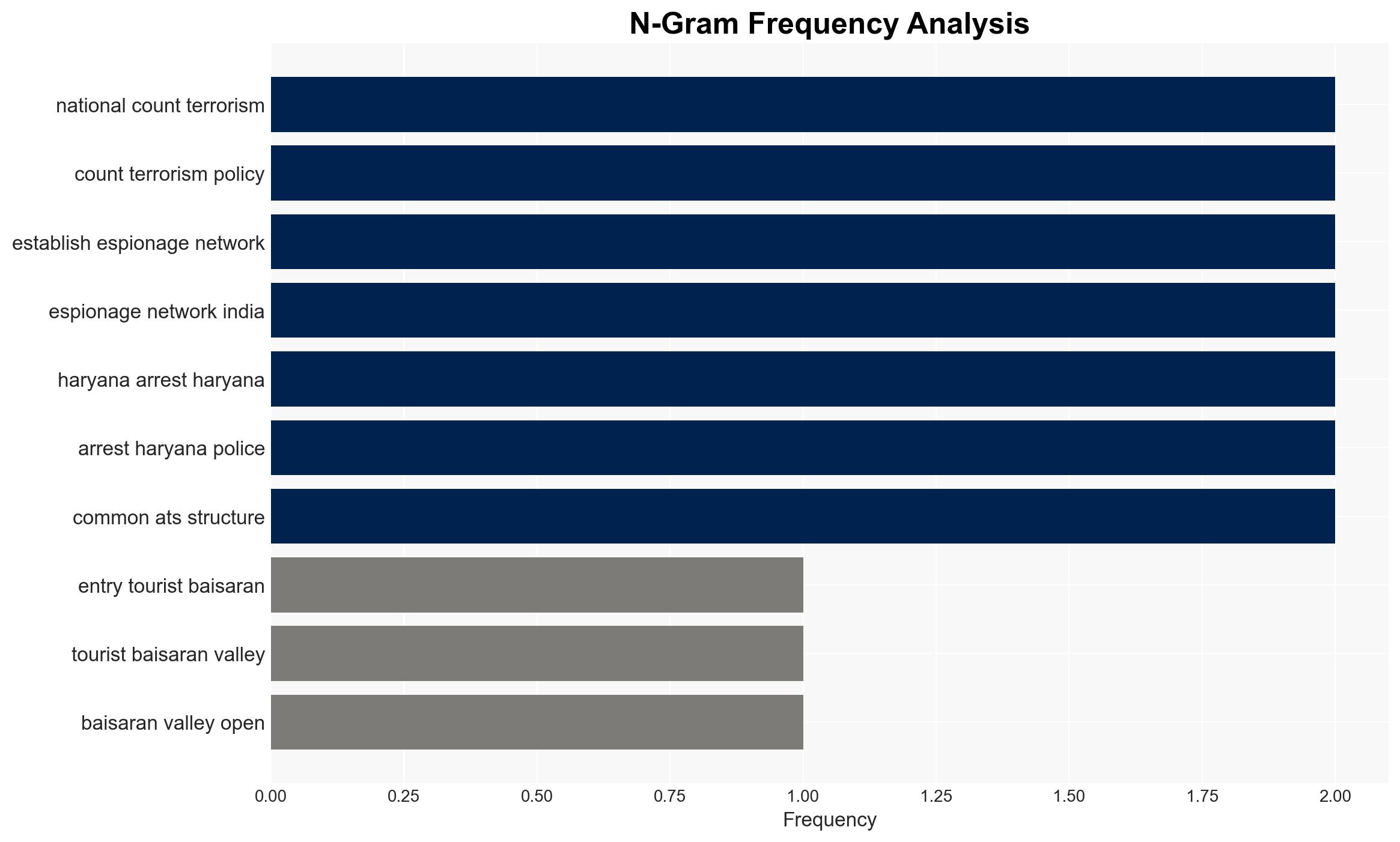
The recent terrorist attacks in India highlight a sophisticated espionage network linked to Pakistan’s ISI, exploiting vulnerabilities within India. The most likely hypothesis is that these networks are actively gathering intelligence to destabilize India’s security environment, with moderate confidence. This situation affects national security, law enforcement, and regional stability.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The espionage networks are primarily driven by Pakistan’s ISI to gather intelligence on India’s military and strategic assets. This is supported by the rapid dissemination of information about Baisaran valley and the involvement of individuals like Jyoti Malhotra. Key uncertainties include the full extent of the network and its penetration into Indian institutions.
- Hypothesis B: The espionage activities are part of a broader, decentralized effort by various non-state actors and rogue elements within Pakistan, not directly controlled by ISI. While some evidence suggests ISI involvement, the decentralized nature of communication and operations could indicate a more fragmented threat landscape.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the structured nature of operations and direct links to ISI operatives. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of independent operations by non-state actors or a lack of centralized coordination.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The ISI is the primary orchestrator of these espionage activities; the espionage network has significant reach within India; financial and ideological vulnerabilities are effectively exploited.
- Information Gaps: The complete structure and hierarchy of the espionage network; the extent of infiltration into Indian security agencies; the role of other foreign entities.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential over-reliance on intelligence from sources with vested interests; possibility of false-flag operations designed to mislead Indian authorities.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The espionage activities could lead to increased tensions between India and Pakistan, potentially escalating into military confrontations. The internal security dynamics may shift, affecting counter-terrorism efforts and public trust in security institutions.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for diplomatic fallout and increased military posturing between India and Pakistan.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment requiring enhanced counter-intelligence operations.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased risk of cyber-espionage and information warfare targeting critical infrastructure.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic disruptions due to increased security measures and public fear, affecting social cohesion.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Intensify surveillance and counter-intelligence operations; enhance border security; engage in diplomatic channels to address the issue with Pakistan.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen intelligence-sharing with allies; develop resilience against espionage tactics; invest in cyber defense capabilities.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Diplomatic resolution and dismantling of espionage networks.
- Worst: Escalation into armed conflict and widespread internal destabilization.
- Most-Likely: Continued espionage activities with periodic security incidents, requiring sustained counter-intelligence efforts.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Jyoti Rani (alias Jyoti Malhotra)
- Ehsan-ur-Rahim (alias Danish)
- Nauman Ilahi
- Pakistan’s ISI
- Pakistani Intelligence Officers (PIOs)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
Counter-Terrorism, espionage, India-Pakistan relations, ISI, national security, cyber-espionage, internal security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- ACH 2.0: Reconstruct likely threat actor intentions via hypothesis testing and structured refutation.
- Indicators Development: Track radicalization signals and propaganda patterns to anticipate operational planning.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Analyze spread/adaptation of ideological narratives for recruitment/incitement signals.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
Explore more:
Counter-Terrorism Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us