Russia Sidelined In New Middle East After Trump’s Israel-Gaza Deal – Globalsecurity.org
Published on: 2025-10-21
Intelligence Report: Russia Sidelined In New Middle East After Trump’s Israel-Gaza Deal – Globalsecurity.org
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
Russia’s influence in the Middle East is perceived to be waning, particularly in light of its absence from a significant diplomatic summit in Egypt. The most supported hypothesis is that Russia’s strategic focus on Ukraine has led to a reduction in its diplomatic and military engagement in the Middle East. Confidence Level: Moderate. Recommended action includes monitoring Russia’s strategic shifts and potential realignment efforts in the region.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **Hypothesis A**: Russia’s diminished presence at the Egypt summit and its sidelining in the Middle East are primarily due to its strategic focus on the Ukraine conflict, which has diverted resources and attention away from the region.
2. **Hypothesis B**: Russia’s absence is a temporary diplomatic setback rather than a long-term strategic shift, with Moscow likely to reassert its influence through alternative diplomatic channels and military partnerships, particularly with Iran.
Using ACH 2.0, Hypothesis A is better supported by the evidence of Russia’s resource constraints and shifting priorities towards Ukraine. Hypothesis B lacks immediate supporting evidence of Russia’s active re-engagement in the Middle East.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**: Hypothesis A assumes Russia’s strategic priorities are static and heavily focused on Ukraine. Hypothesis B assumes Russia has the capability and intent to re-engage in the Middle East despite current setbacks.
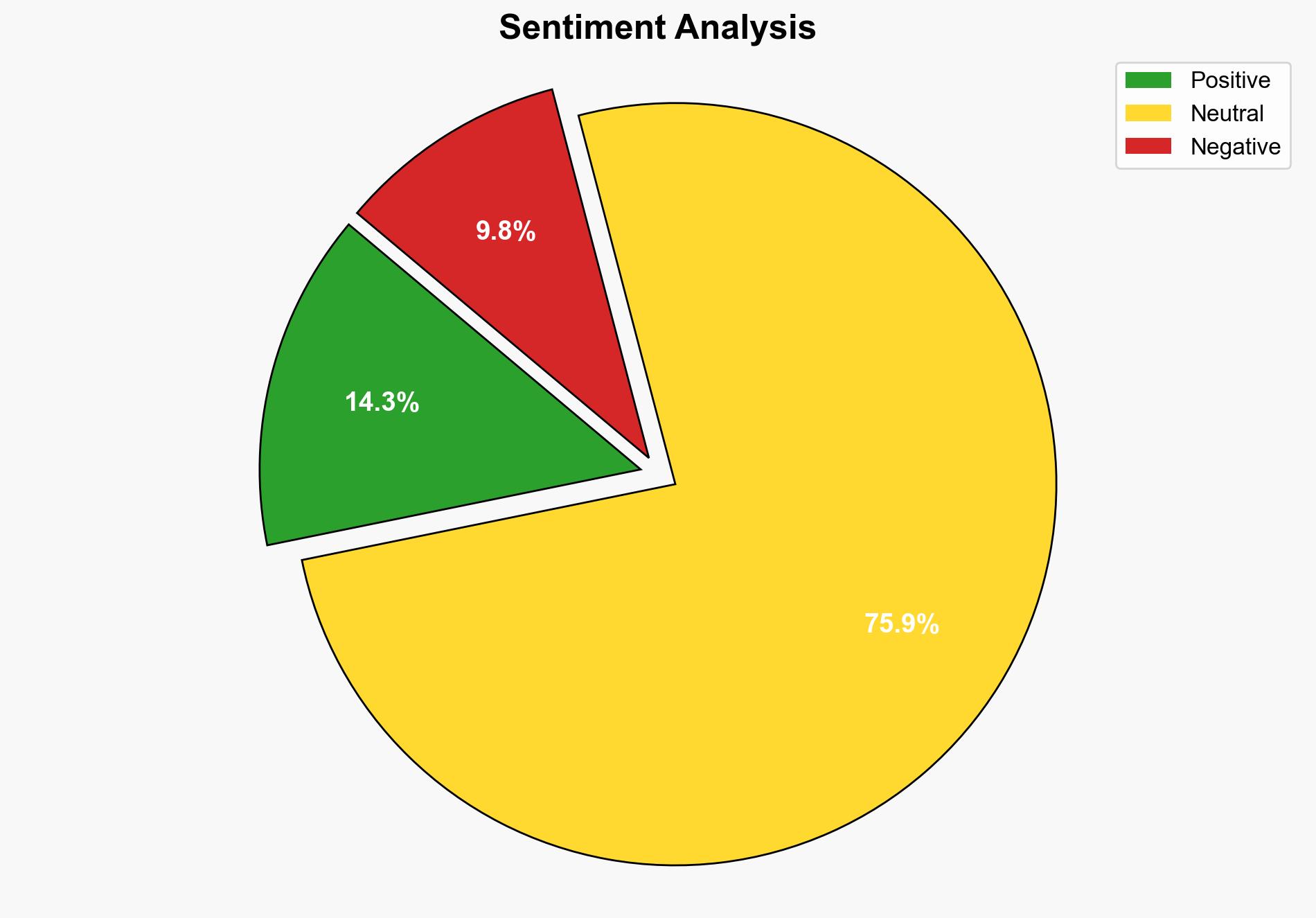
– **Red Flags**: The absence of Russian and Chinese roles at the summit could indicate broader geopolitical shifts. The reliance on unnamed sources and anonymous European officials introduces potential bias.
– **Blind Spots**: The analysis does not fully consider the potential for Russia to leverage non-traditional alliances or economic partnerships to regain influence.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
– **Geopolitical**: A sustained reduction in Russian influence could shift power dynamics in the Middle East, potentially increasing Western influence and altering alliances.
– **Economic**: Russia’s economic ties with Iran and Gulf nations could be strained, affecting energy markets and regional stability.
– **Cyber and Psychological**: Russia may increase cyber operations or information campaigns to compensate for its reduced physical presence.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Monitor Russia’s military and diplomatic activities in the Middle East for signs of re-engagement or further withdrawal.
- Engage with regional partners to assess shifts in alliances and prepare for potential power vacuums.
- Scenario Projections:
- Best Case: Russia rebalances its focus, maintaining influence through strategic partnerships without escalating conflicts.
- Worst Case: Russia’s absence leads to increased instability and conflict in the region, with opportunistic actions by other powers.
- Most Likely: Russia continues to prioritize Ukraine, with limited engagement in the Middle East, leading to a gradual decline in influence.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– Vladimir Putin
– Sergei Lavrov
– Donald Trump
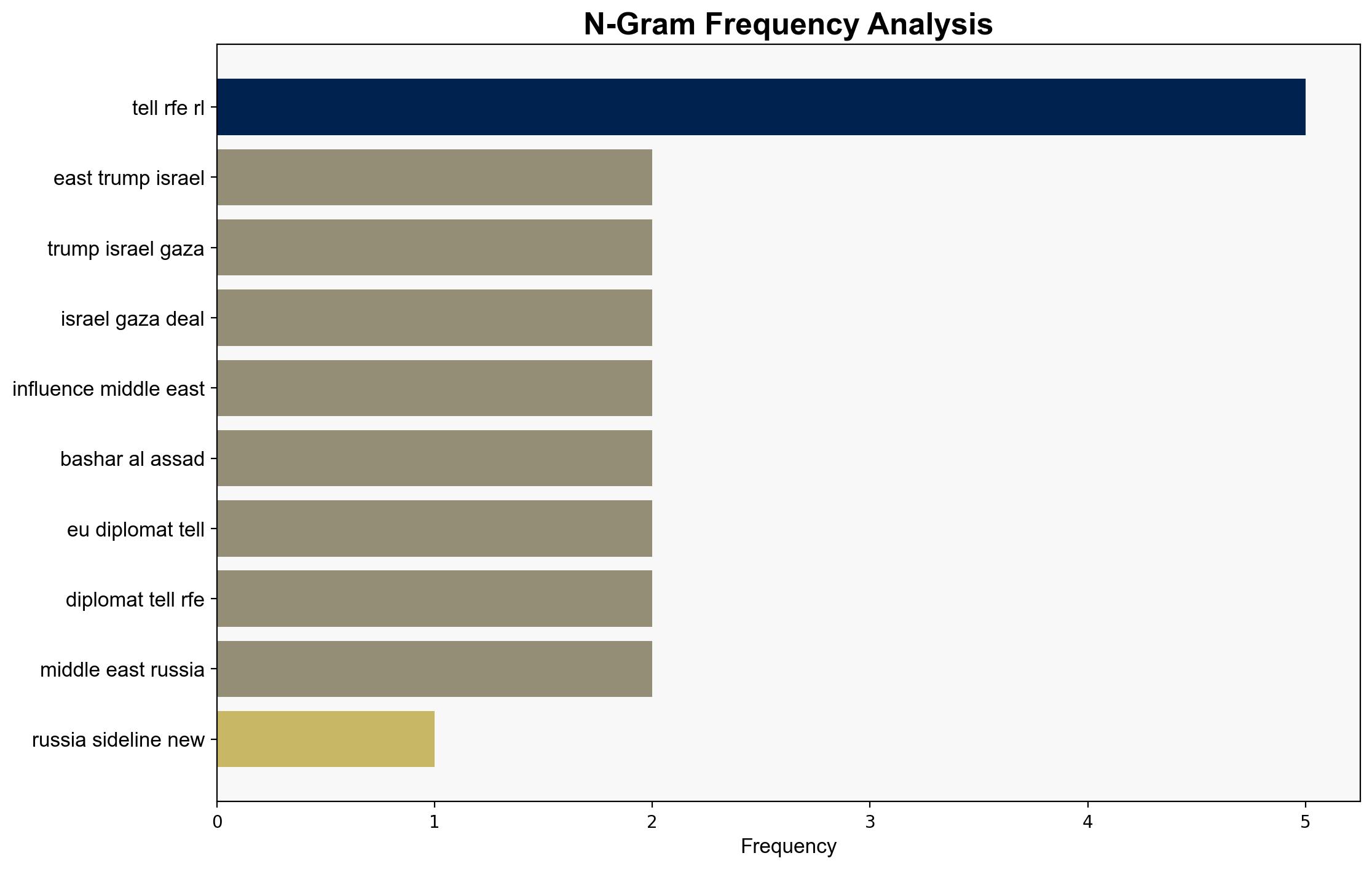
– Bashar al-Assad
– Hanna Notte
7. Thematic Tags
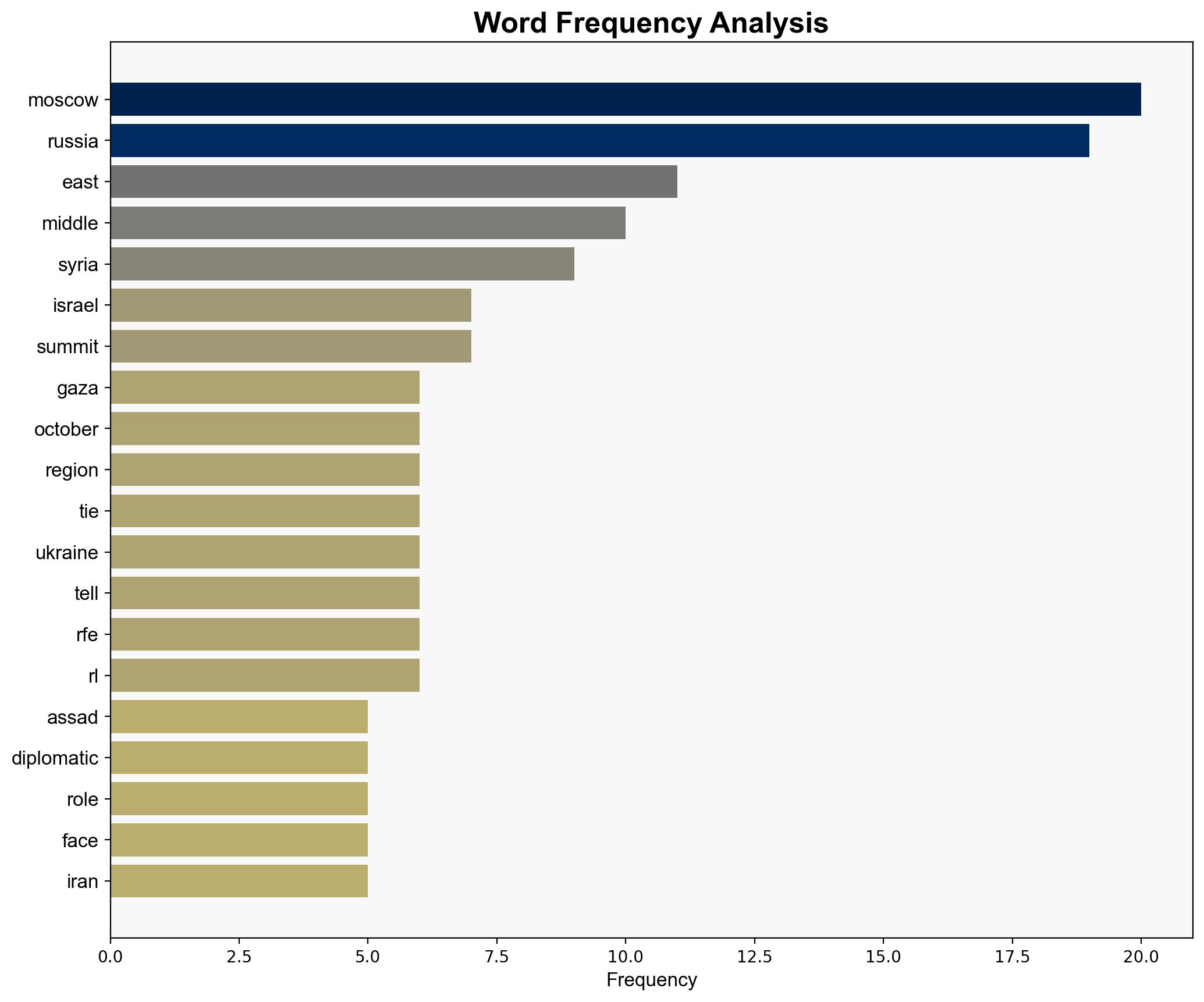
national security threats, geopolitical shifts, regional focus, strategic realignment