Russian GRU Hackers Shift Tactics to Target Western Firms Through Misconfigured Edge Devices, Amazon Reports
Published on: 2025-12-16
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Amazon Warns Russian GRU Hackers Target Western Firms via Edge Devices
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
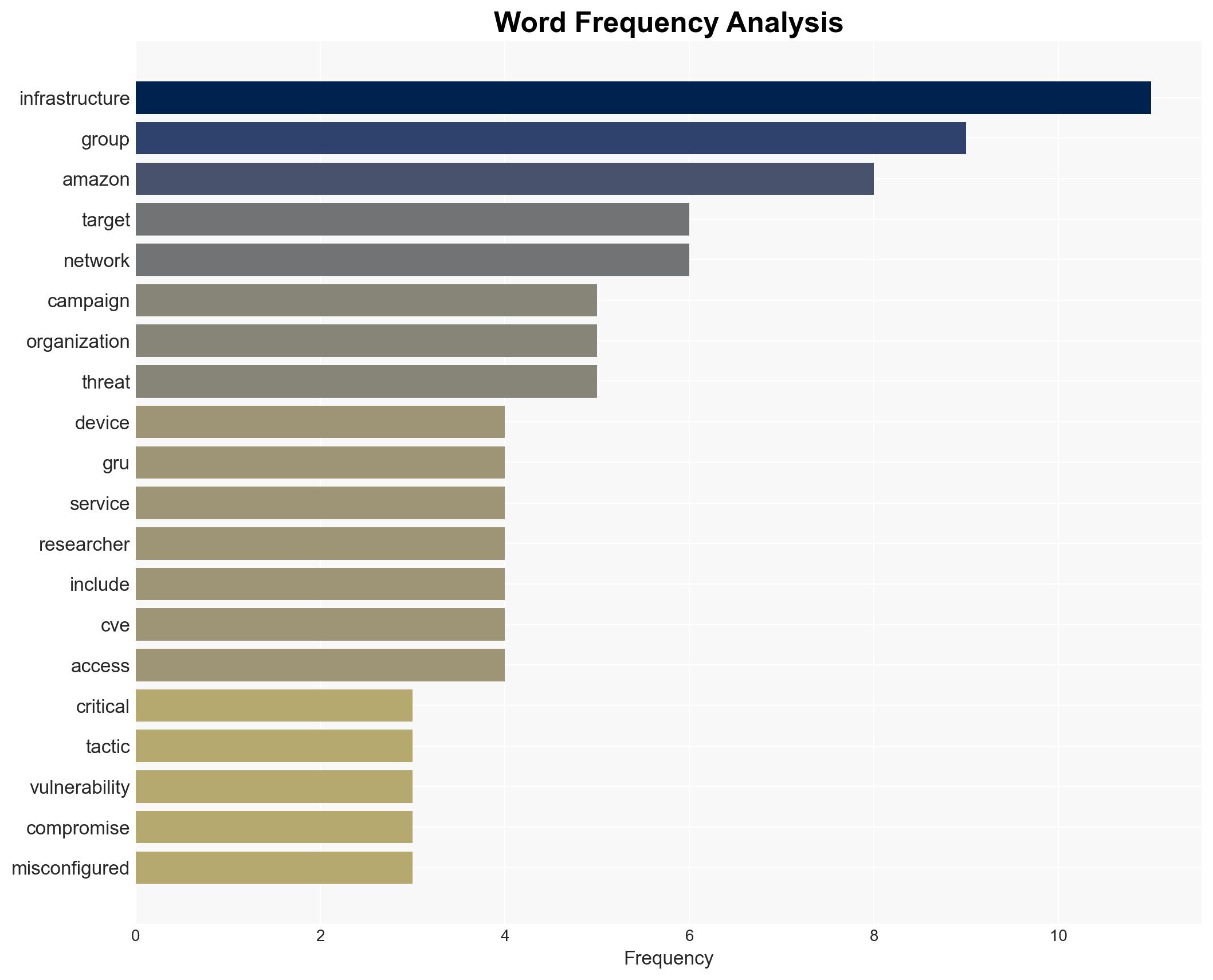
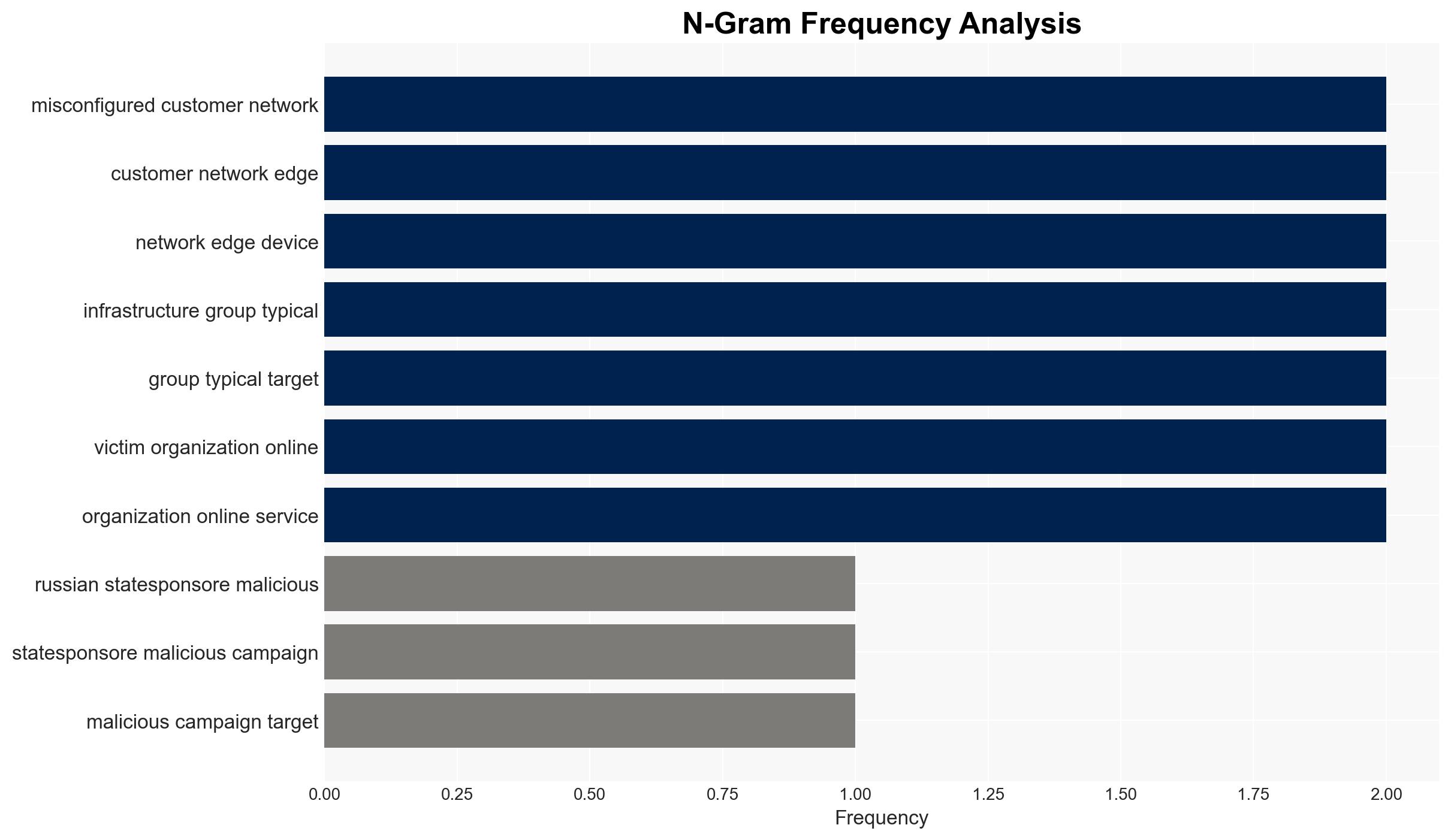
Amazon has attributed a cyber campaign targeting Western critical infrastructure to the Russian GRU, focusing on exploiting misconfigured network edge devices. This shift in tactics aims to reduce exposure while maintaining operational effectiveness. The campaign poses a significant threat to energy and infrastructure sectors across North America and Europe. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the attribution challenges and evolving tactics.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The campaign is a GRU operation targeting Western infrastructure, supported by infrastructure overlaps with known GRU-linked groups like Sandworm. However, the lack of direct attribution evidence and reliance on infrastructure patterns introduce uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: The campaign could be conducted by a non-state actor or another state-sponsored group mimicking GRU tactics to obscure their identity. This is less supported due to the consistent targeting of strategic sectors aligned with Russian interests.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the infrastructure overlaps and historical GRU targeting patterns. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include new evidence of alternative actors or changes in targeting patterns.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The GRU has the capability and intent to target Western infrastructure; infrastructure overlaps are a reliable indicator of attribution; misconfigured devices are a viable entry point for cyber operations.
- Information Gaps: Direct evidence linking the GRU to the current campaign; detailed technical data on the specific misconfigurations exploited.
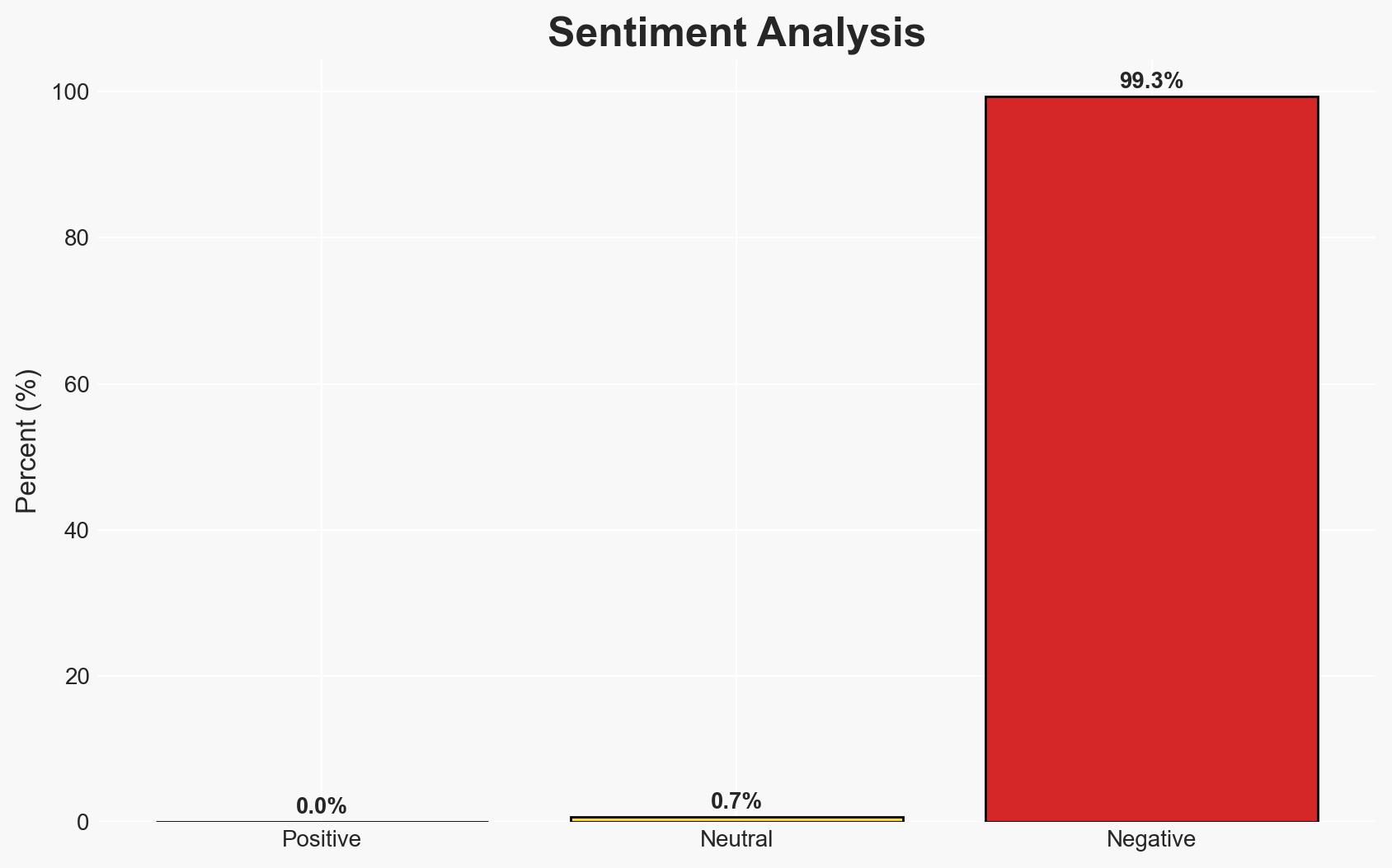
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential confirmation bias in attributing to the GRU based on historical patterns; risk of adversaries using false flags to mislead attribution efforts.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased tensions between Russia and Western nations, potentially escalating cyber conflict. The adaptation in tactics may inspire similar approaches by other threat actors, complicating defensive measures.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for diplomatic confrontations and sanctions against Russia, increasing geopolitical tensions.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment for critical infrastructure, requiring enhanced security measures.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased focus on securing edge devices and addressing misconfigurations; potential for misinformation campaigns exploiting the situation.
- Economic / Social: Disruptions in energy and infrastructure sectors could impact economic stability and public confidence.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of network edge devices for misconfigurations; increase information sharing among affected sectors.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for critical infrastructure; strengthen international partnerships for cyber defense.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Improved defenses deter further attacks, leading to reduced threat levels.
- Worst: Escalation of cyber operations results in significant infrastructure disruptions.
- Most-Likely: Continued low-level cyber operations with periodic disruptions, prompting ongoing defensive measures.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, cyber-espionage, critical infrastructure, Russian GRU, cyber defense, network security, geopolitical tensions
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us