Russian Hackers Target Hospitality Sector with Phishing Emails and Malware Delivery via Fake BSODs
Published on: 2026-01-07
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Fake Bookingcom emails and BSODs used to infect hospitality staff
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
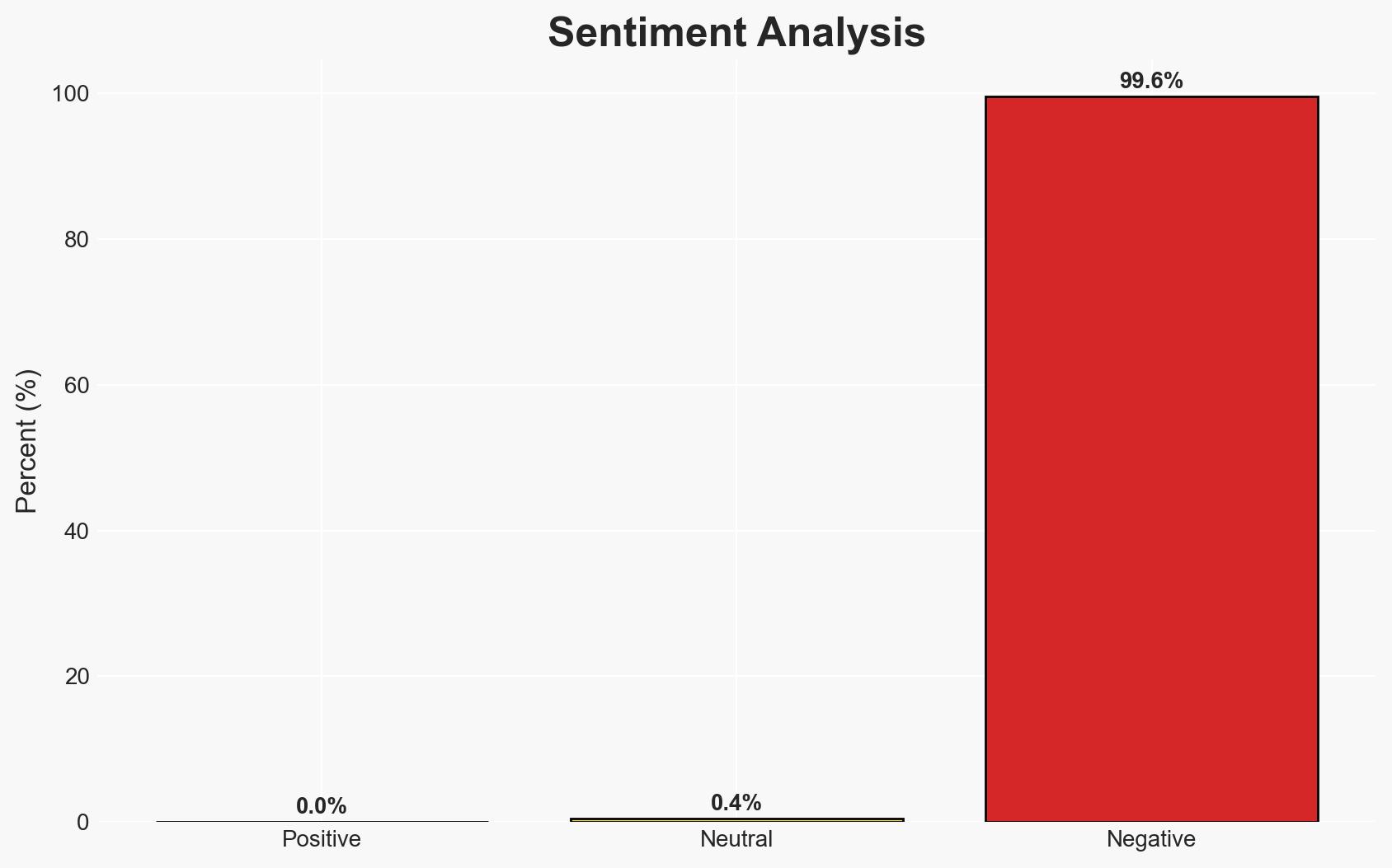
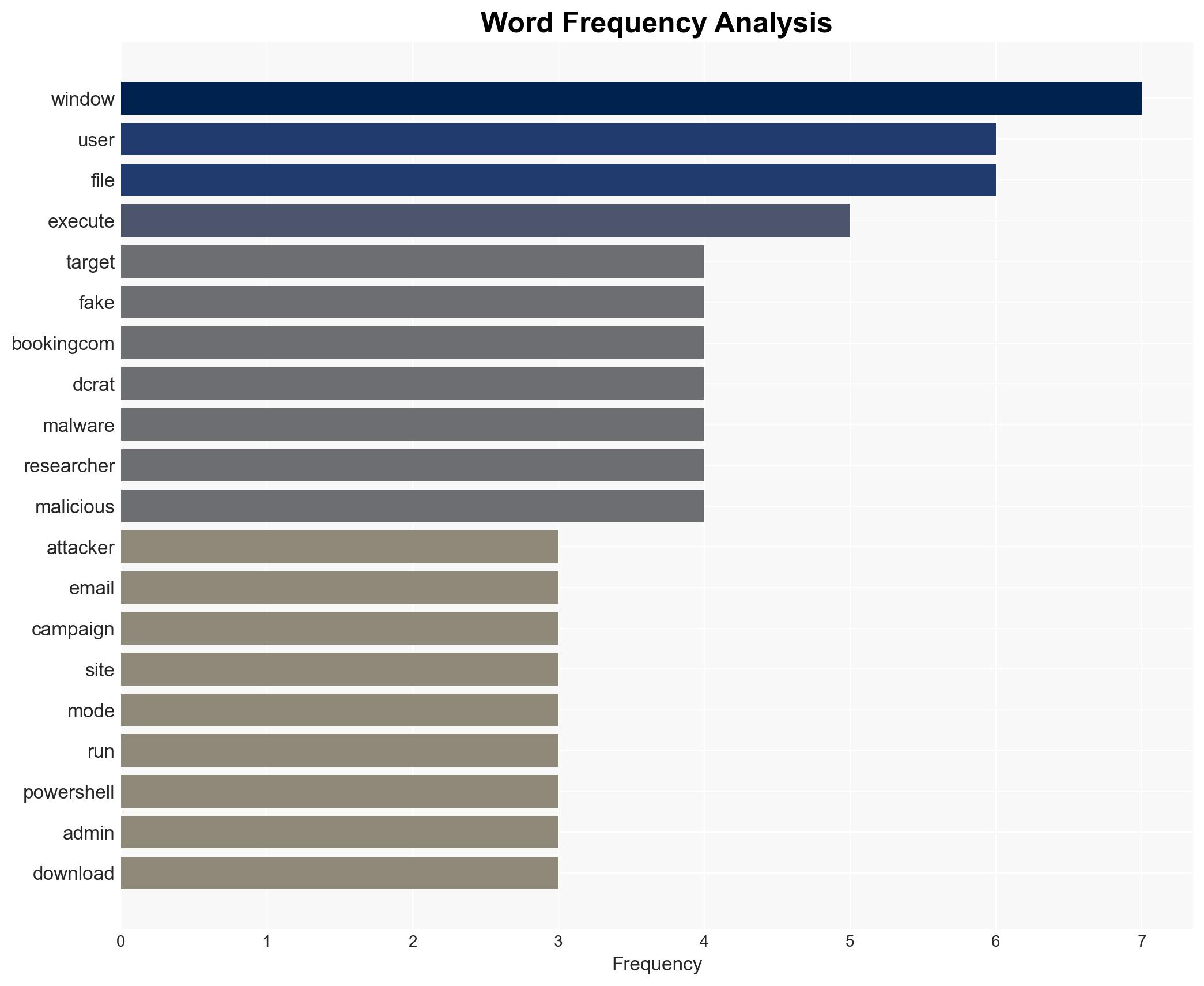
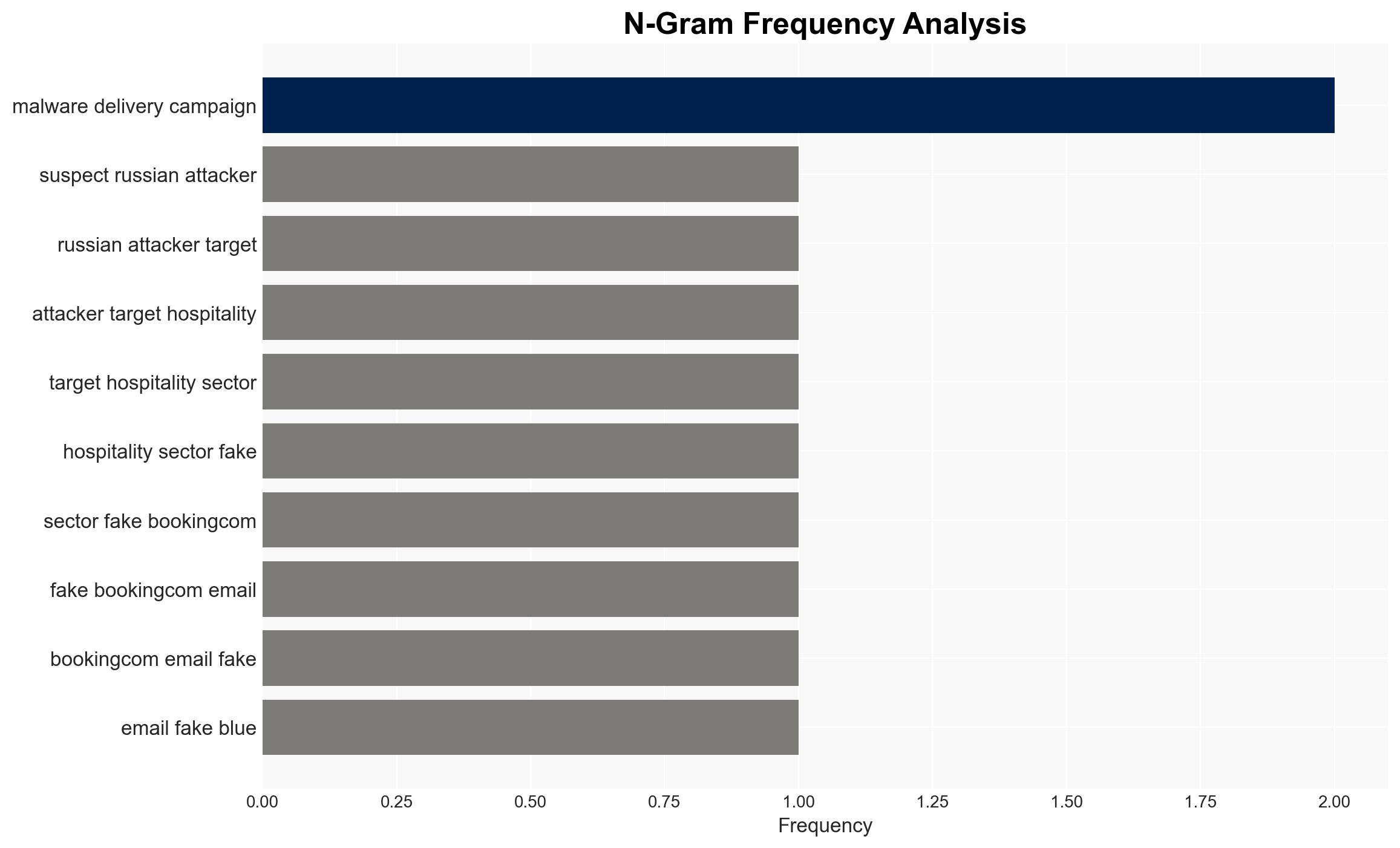
Suspected Russian cyber actors are targeting the European hospitality sector using sophisticated phishing techniques to deliver DCRat malware. The campaign exploits fake Booking.com emails and a fake “Blue Screen of Death” to deceive users. This threat poses significant risks to the targeted sector and potentially beyond, with moderate confidence in the assessment based on current evidence.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The campaign is primarily aimed at the European hospitality sector as a precursor to broader cyber operations. Evidence includes the use of euros in phishing emails and the adaptability of the campaign to other industries. However, the specific strategic intent remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The campaign is part of a broader effort to compromise various sectors globally, using the hospitality industry as an initial testbed. This is supported by the attackers’ capability to adapt the campaign but lacks direct evidence of targeting beyond Europe.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the specific targeting indicators (e.g., euros in emails) and the known adaptability of the campaign. Future evidence of targeting outside Europe could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The attackers are Russian-affiliated; the campaign is primarily targeting the hospitality sector; the use of MSBuild is a deliberate evasion tactic; the campaign can be adapted to other sectors.
- Information Gaps: Exact attribution to specific Russian groups; full scope of targeted sectors; detailed impact assessment on affected organizations.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential confirmation bias in attributing the attack to Russian actors; deception indicators in the campaign’s adaptability claims.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased cyber threats across sectors, leveraging sophisticated evasion techniques. The campaign’s success in the hospitality sector may embolden actors to target other industries.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential escalation in cyber tensions between Russia and European nations.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased threat to critical infrastructure and potential for data breaches.
- Cyber / Information Space: Enhanced use of “Living off the Land” techniques may challenge current cybersecurity defenses.
- Economic / Social: Disruption in the hospitality sector could have cascading effects on tourism and related industries.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of phishing campaigns, update cybersecurity protocols, and conduct awareness training for hospitality staff.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for intelligence sharing, invest in advanced threat detection technologies, and strengthen cross-sector resilience measures.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Effective mitigation limits campaign impact, and no further sectors are targeted.
- Worst: Campaign expands to critical infrastructure, causing significant disruptions.
- Most-Likely: Continued targeting of the hospitality sector with gradual expansion to other industries.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, phishing, malware, Russian cyber operations, hospitality sector, cyber-espionage, information security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us