Saudi Arabia and UAE’s Yemen Conflict Highlights Deepening Regional Divisions and Shifting Alliances
Published on: 2026-01-12
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Saudi-UAE bust-up over Yemen was only a matter of time and reflects wider rift over vision for the region
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
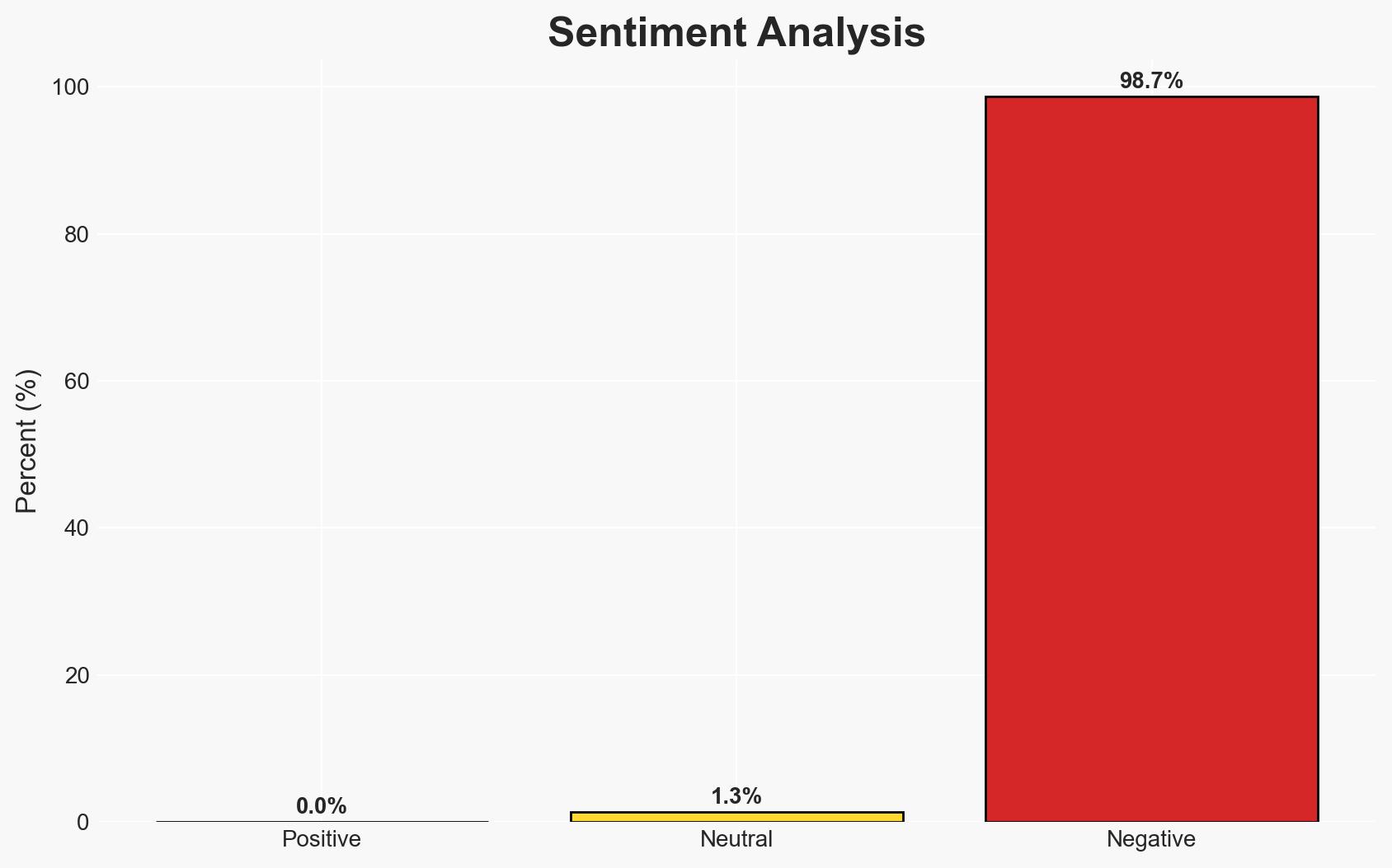
The recent escalation of tensions between Saudi Arabia and the UAE over Yemen highlights a significant fracture in their regional alliance, with Saudi actions against UAE-backed separatists marking a shift in the geopolitical landscape. This development could destabilize the anti-Houthi coalition and exacerbate regional power struggles, with moderate confidence in the assessment that Saudi Arabia is asserting dominance over Yemen policy. The situation affects regional stability and could have broader implications for Middle Eastern geopolitics.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Saudi Arabia’s actions are primarily driven by a desire to consolidate control over the Yemen conflict and counter perceived Iranian influence via the Houthis. This is supported by the recent military actions and political maneuvers against UAE-backed entities. However, the extent of Iranian influence and Saudi’s capacity to maintain long-term control remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The Saudi-UAE rift is a broader strategic divergence over regional influence, with Yemen being a focal point. The UAE’s backing of separatists reflects its strategic interest in countering Islamist groups and securing influence in southern Yemen. Contradictory evidence includes the historical alignment on regional issues, though recent actions suggest a strategic recalibration.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the immediate military and political actions taken by Saudi Arabia, indicating a prioritization of consolidating control over Yemen. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in UAE’s regional alliances or Saudi’s diplomatic engagements with Iran.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Saudi Arabia views the Houthis as an existential threat; the UAE’s primary interest in Yemen is countering Islamist groups; regional alliances are fluid and subject to rapid change.
- Information Gaps: Detailed intelligence on the extent of UAE’s current support for separatist groups; internal Saudi and UAE strategic deliberations; Iran’s actual influence over the Houthis.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential for source bias in reporting from Saudi or UAE-affiliated media; risk of strategic deception by regional actors to manipulate international perceptions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to a prolonged conflict in Yemen, further destabilizing the region and complicating international diplomatic efforts. The fracture in the Saudi-UAE alliance may embolden other regional actors to assert influence, potentially leading to a realignment of regional power structures.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased Iranian influence if the anti-Houthi coalition weakens; risk of new alliances forming among Gulf states.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Possible resurgence of extremist groups exploiting the power vacuum; increased threat to maritime security in the Red Sea.
- Cyber / Information Space: Likely increase in cyber operations targeting critical infrastructure and information warfare to shape narratives.
- Economic / Social: Disruption of trade routes and economic instability in the region; humanitarian crisis in Yemen exacerbating social tensions.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase intelligence collection on Saudi and UAE military and diplomatic activities; engage in diplomatic dialogues with both parties to de-escalate tensions.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen regional alliances and partnerships to mitigate instability; enhance counter-terrorism cooperation with regional allies.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Diplomatic resolution leading to a unified approach against the Houthis.
- Worst: Escalation into a broader regional conflict with increased Iranian involvement.
- Most-Likely: Continued low-intensity conflict with intermittent diplomatic efforts.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
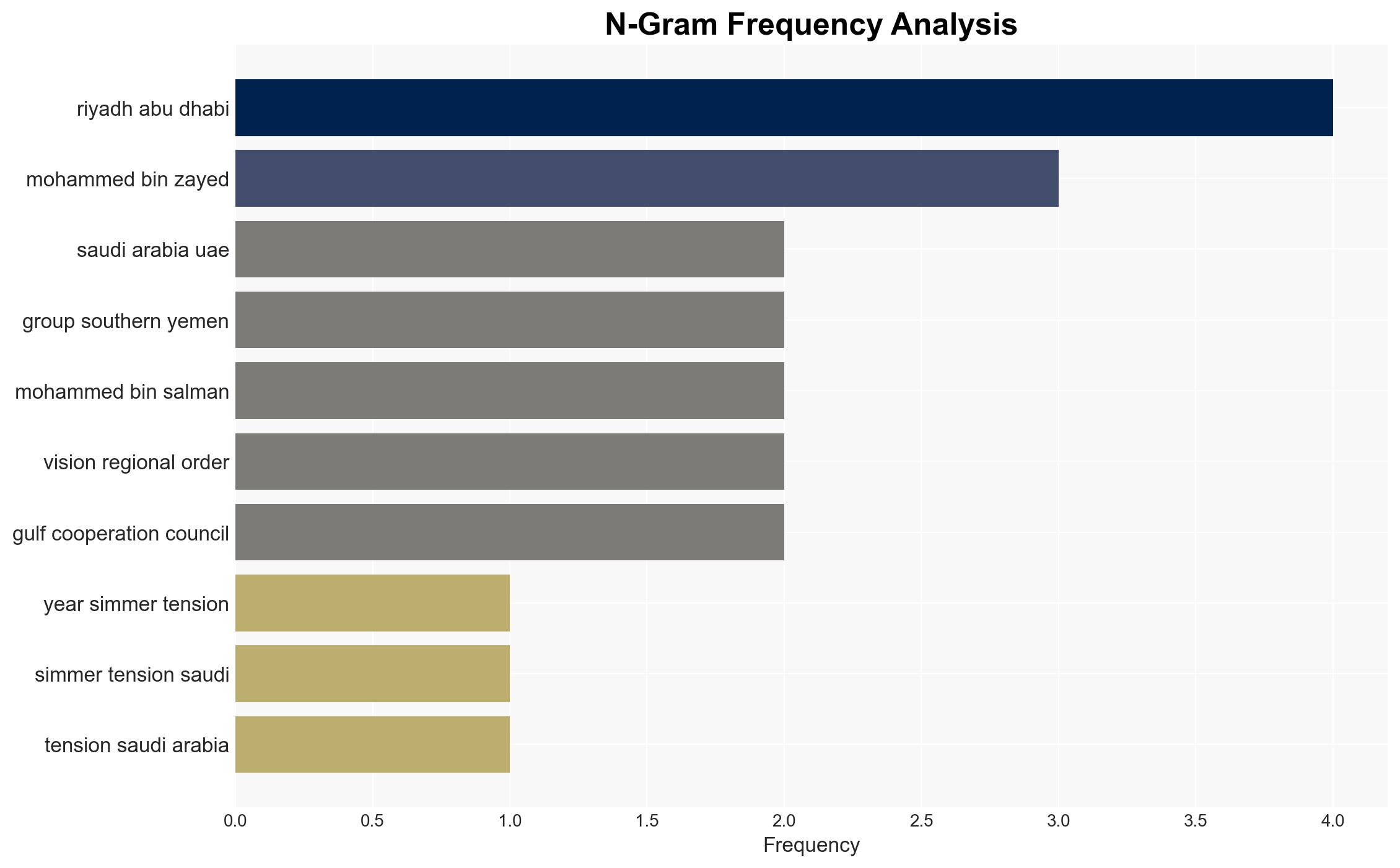
- Mohammed bin Salman (Saudi Crown Prince)
- Mohammed bin Zayed (UAE President)
- Aidarous al-Zubaidi (Former STC Leader)
- Southern Transitional Council (STC)
- Houthi Rebels
7. Thematic Tags
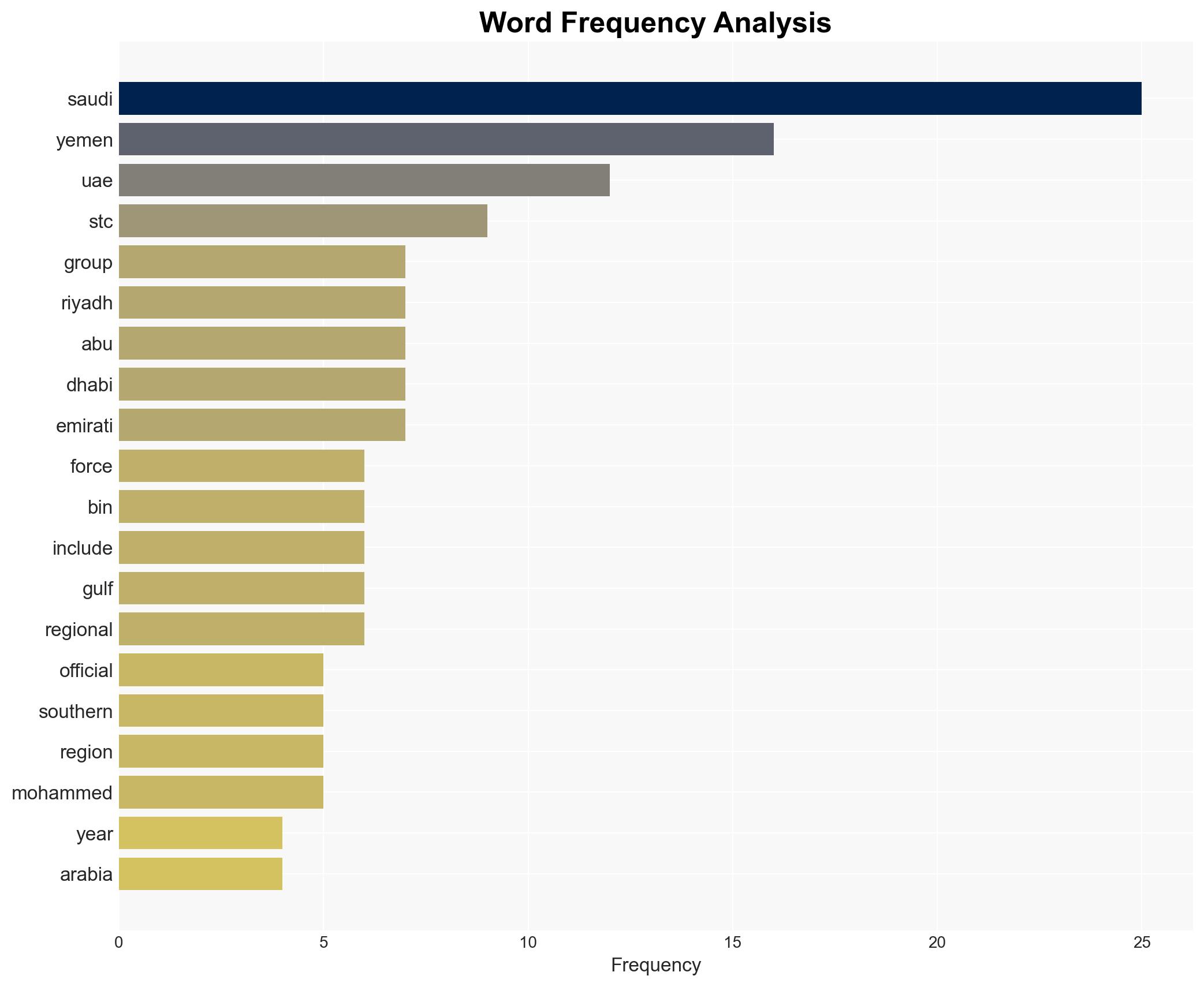
regional conflicts, regional stability, Saudi-UAE relations, Yemen conflict, separatist movements, Iranian influence, Gulf geopolitics, counter-terrorism
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us