Saudi Arabia Launches Airstrikes in Yemen, Issues Stern Warning to UAE Over Military Shipment Concerns
Published on: 2025-12-31
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Explained Why Saudi Arabia bombed Yemen and issued a warning to the UAE
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
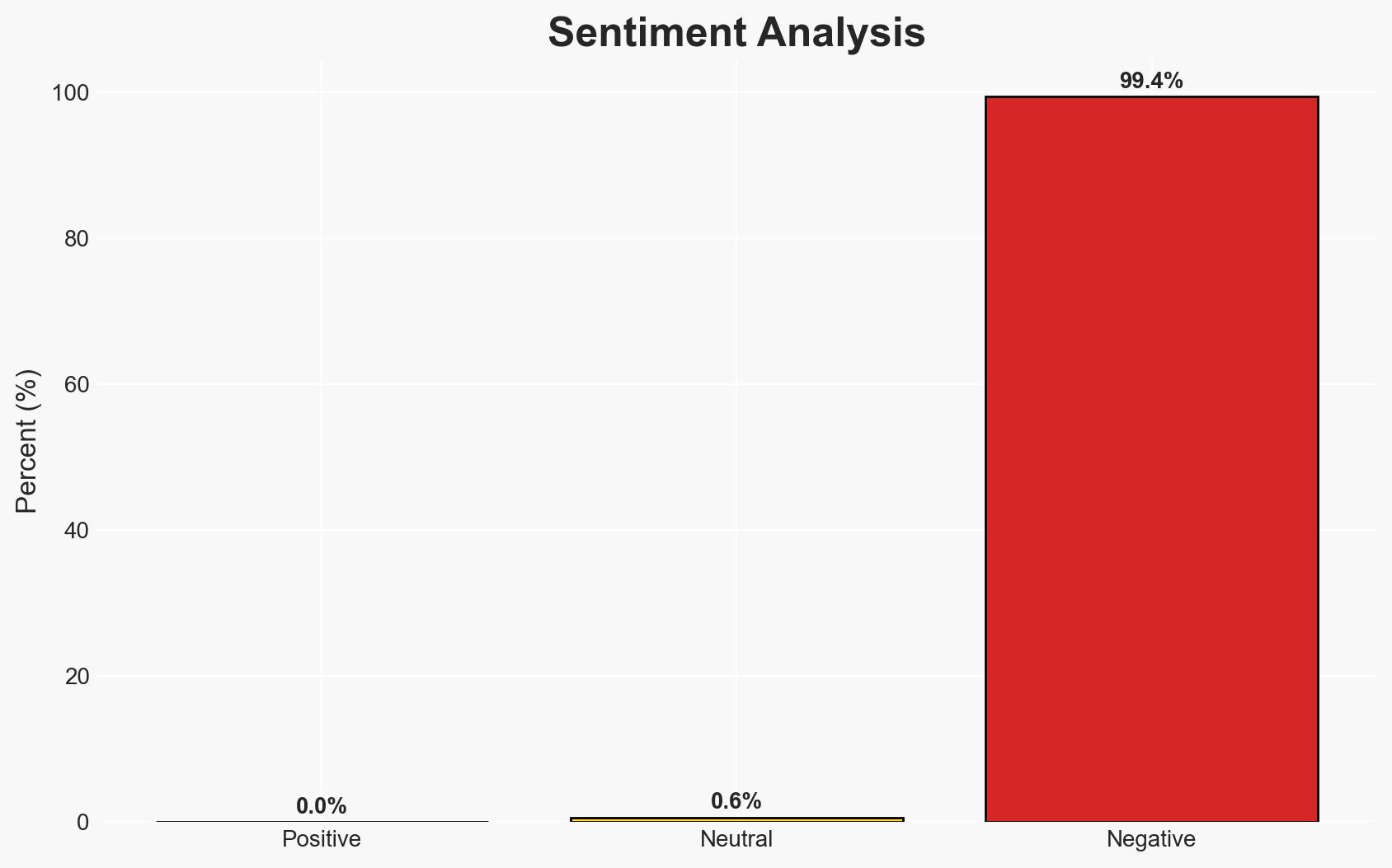
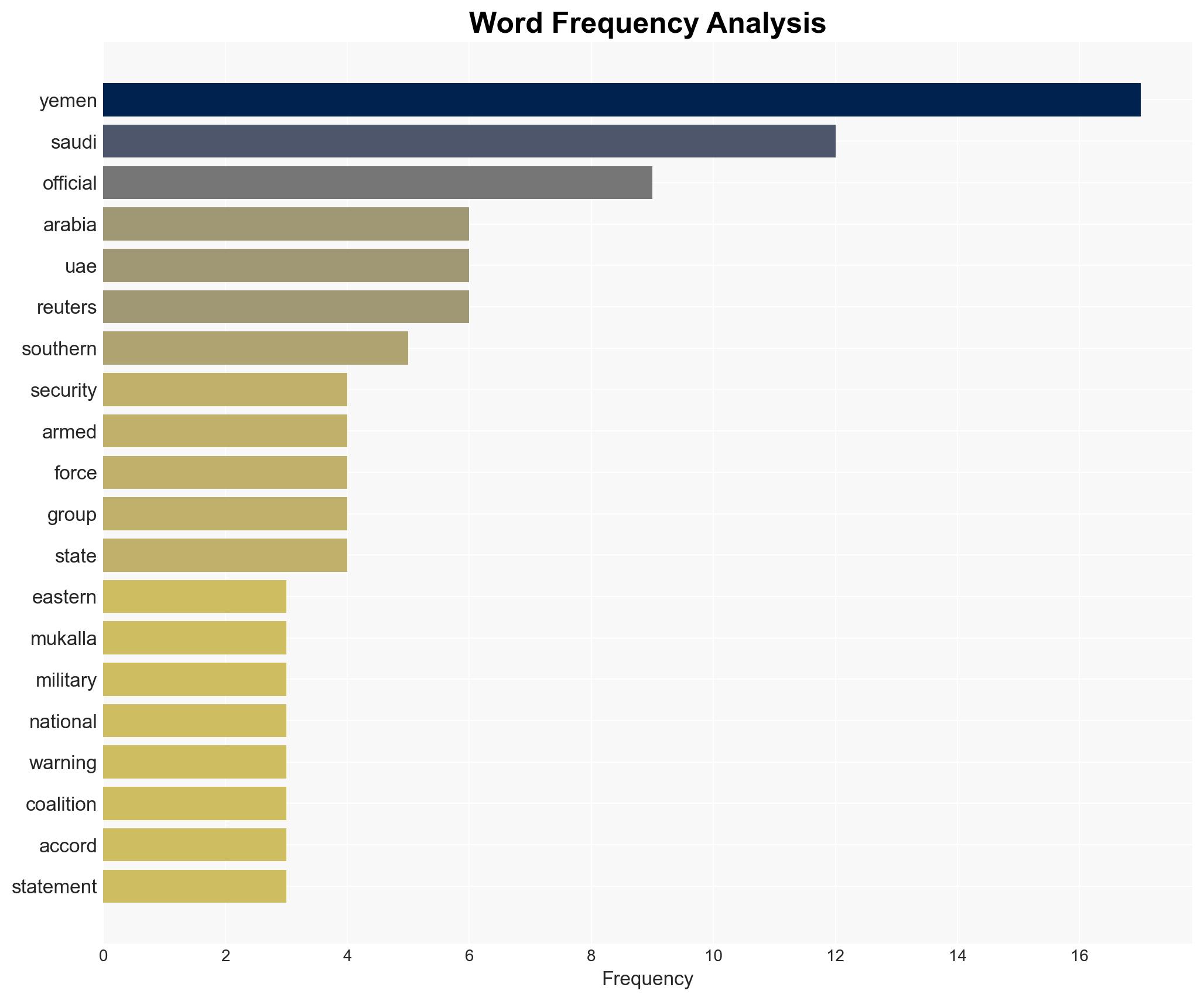
Saudi Arabia’s airstrikes on Yemen’s Mukalla and subsequent warning to the UAE highlight escalating tensions between the two Gulf allies over Yemen’s stability. The most likely hypothesis is that Saudi Arabia perceives the UAE’s actions as undermining its strategic interests in Yemen, particularly concerning separatist movements. This situation affects regional stability and the dynamics within the Saudi-led coalition. Overall confidence in this judgment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Saudi Arabia’s airstrikes and warnings are primarily driven by genuine security concerns over unauthorized military shipments that threaten its national security. Supporting evidence includes Saudi statements about red lines and regional stability. Contradicting evidence is the UAE’s denial of destabilizing actions.
- Hypothesis B: The actions are motivated by broader geopolitical competition between Saudi Arabia and the UAE over influence in Yemen, with Saudi Arabia using the airstrikes to assert dominance. Supporting evidence includes the UAE’s military withdrawal and repositioning efforts, which may indicate strategic recalibration.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to explicit Saudi statements regarding national security threats. However, ongoing UAE repositioning and diplomatic efforts could shift this assessment if further evidence of geopolitical competition emerges.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Saudi Arabia’s primary concern is national security; the UAE’s actions are not coordinated with Saudi interests; the STC is a significant factor in regional stability.
- Information Gaps: Details on the specific nature of the military equipment and its intended use; internal UAE decision-making processes regarding Yemen.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in Saudi and UAE official statements; risk of misinterpretation of military movements as aggressive rather than defensive.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could exacerbate tensions within the Saudi-led coalition and influence the broader regional power dynamics. The situation may lead to increased fragmentation in Yemen, complicating peace efforts.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for diplomatic rifts between Saudi Arabia and the UAE, affecting Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) cohesion.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of armed confrontations in eastern Yemen, potentially empowering extremist groups.
- Cyber / Information Space: Possible increase in information operations to shape narratives and influence regional perceptions.
- Economic / Social: Disruption of trade routes and humanitarian efforts in Yemen, affecting local economies and social stability.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance intelligence-sharing mechanisms between Saudi Arabia and the UAE; monitor military movements and communications in Yemen.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen diplomatic channels to mediate Saudi-UAE tensions; support initiatives for Yemen’s political stabilization.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Saudi-UAE reconciliation and coordinated efforts in Yemen; Worst: Escalation of military confrontations; Most-Likely: Continued diplomatic tensions with periodic military incidents.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Saudi-led coalition
- United Arab Emirates (UAE)
- Southern Transitional Council (STC)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
regional conflicts, regional stability, Saudi-UAE relations, Yemen conflict, military operations, geopolitical tensions, counter-terrorism, coalition dynamics
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us