Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters claim breach of Resecurity; firm asserts only honeypot was accessed
Published on: 2026-01-03
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Hackers claim Resecurity hack firm says it was a honeypot
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
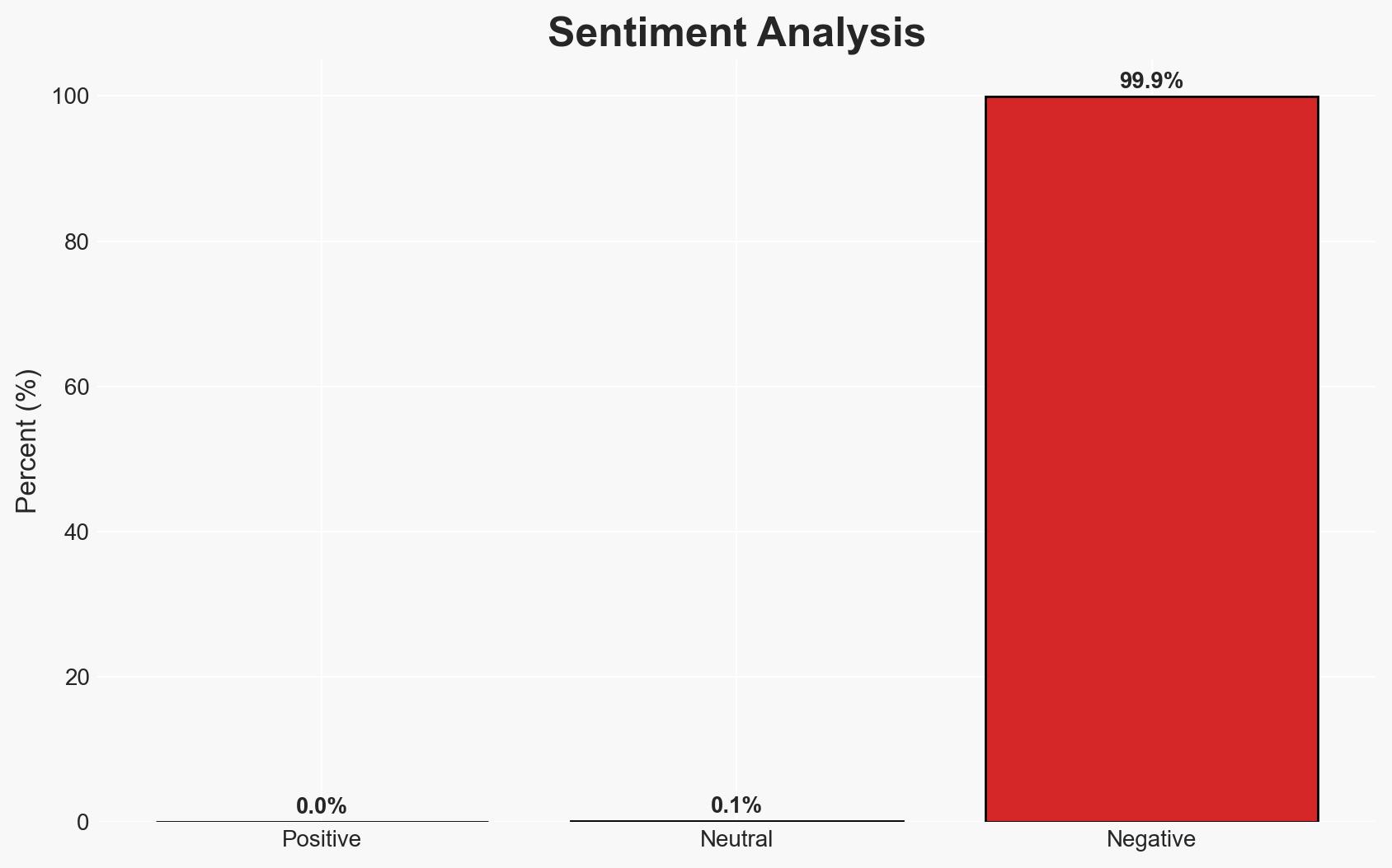
The incident involving Resecurity and the Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters highlights a potential breach or a sophisticated deception operation. The most likely hypothesis is that Resecurity’s systems were not genuinely compromised, but rather, the attackers interacted with a honeypot. This situation affects cybersecurity firms and their clients, with moderate confidence in this assessment.
2. Competing Hypotheses
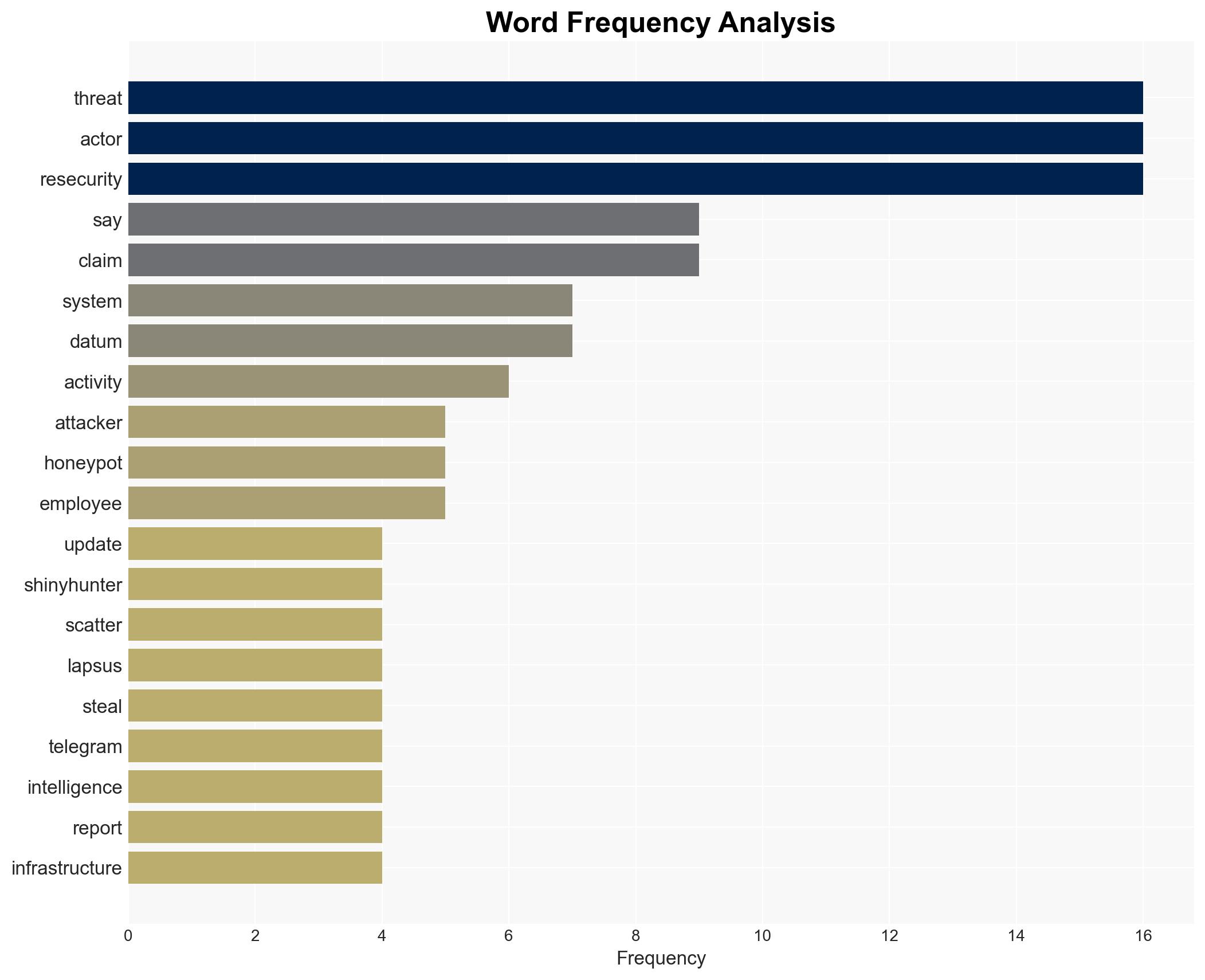
- Hypothesis A: The Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters successfully breached Resecurity’s systems and stole sensitive data. Supporting evidence includes the screenshots and claims of data theft. Contradicting evidence includes Resecurity’s assertion that the systems were a honeypot.
- Hypothesis B: Resecurity’s systems were not breached, and the attackers only accessed a honeypot with fake data. Supporting evidence includes Resecurity’s detailed account of deploying a honeypot and monitoring the attackers. The lack of independent verification of the data’s authenticity contradicts this hypothesis.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to Resecurity’s proactive measures and the absence of verified data leaks. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include independent validation of the data’s authenticity and further disclosures from the attackers.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The honeypot was effectively isolated from Resecurity’s production systems; the attackers’ claims are not independently verified; Resecurity’s account is accurate and truthful.
- Information Gaps: Verification of the authenticity of the allegedly stolen data; detailed technical analysis of the breach claims; motivations and capabilities of the Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias from Resecurity in portraying the incident as a honeypot operation; deception risks from the attackers in exaggerating their success.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could influence the cybersecurity landscape by highlighting the effectiveness or vulnerability of honeypot strategies. It may also affect the credibility of cybersecurity firms and their client trust.
- Political / Geopolitical: Escalation in cyber tensions between private cybersecurity entities and hacker groups.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Potential increase in retaliatory cyber activities by hacker groups against perceived adversaries.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased scrutiny on cybersecurity practices and the use of honeypots as a defensive measure.
- Economic / Social: Potential impact on client trust and business operations for cybersecurity firms involved in similar incidents.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a thorough forensic analysis of the incident; engage with independent cybersecurity experts for data verification; enhance monitoring of threat actor communications.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen honeypot and deception capabilities; build partnerships with other cybersecurity firms for intelligence sharing; enhance public communication strategies to manage reputational risks.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Incident is confirmed as a honeypot operation, enhancing Resecurity’s reputation for cybersecurity innovation.
- Worst: Data is verified as authentic, leading to significant reputational damage and client loss.
- Most-Likely: Incident remains ambiguous, with ongoing debates about the effectiveness of honeypot strategies.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Resecurity
- Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters
- ShinyHunters
- Lapsus$
- Scattered Spider
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, honeypot, data breach, threat actors, cyber deception, information security, cyber operations
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us