Security Affairs newsletter Round 538 by Pierluigi Paganini INTERNATIONAL EDITION – Securityaffairs.com
Published on: 2025-08-24
Intelligence Report: Security Affairs newsletter Round 538 by Pierluigi Paganini INTERNATIONAL EDITION – Securityaffairs.com
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The most supported hypothesis suggests an increasing sophistication and coordination in cyber threats targeting critical infrastructure and financial systems globally, with a focus on exploiting vulnerabilities in emerging markets like Africa. Confidence level is moderate due to the complexity and evolving nature of cyber threats. Recommended action includes enhancing international cooperation on cybersecurity measures and investing in advanced threat detection technologies.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The surge in cyber incidents, including ransomware and data breaches, indicates a coordinated effort by state-sponsored actors to destabilize economic and critical infrastructure globally, with a focus on exploiting vulnerabilities in less prepared regions like Africa.
Hypothesis 2: The increase in cyber threats is primarily driven by independent cybercriminal groups motivated by financial gain, leveraging advanced tools and techniques to exploit vulnerabilities across various sectors, with no direct state sponsorship.
Using the Analysis of Competing Hypotheses (ACH) 2.0, Hypothesis 1 is better supported by the involvement of sophisticated ransomware groups and the targeting of critical infrastructure, which often aligns with state-sponsored objectives. However, Hypothesis 2 cannot be entirely dismissed due to the financial motivations evident in many attacks.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions include the belief that state-sponsored actors have the capability and intent to conduct such widespread cyber operations. A red flag is the potential underestimation of the capabilities of independent cybercriminal groups. There is also a lack of detailed attribution data, which complicates definitive conclusions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The implications of these cyber threats include potential disruptions to global supply chains, financial markets, and public trust in digital systems. Strategic risks involve the escalation of cyber warfare tactics and potential retaliatory measures by affected states, leading to broader geopolitical tensions.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Enhance international collaboration on cybersecurity intelligence sharing and joint response strategies.
- Invest in advanced cybersecurity infrastructure, particularly in vulnerable regions like Africa.
- Scenario-based projections:
- Best Case: Successful international cooperation leads to a significant reduction in cyber incidents.
- Worst Case: Continued escalation of cyber threats results in major disruptions to critical infrastructure.
- Most Likely: Ongoing cyber threats with periodic high-impact incidents, necessitating continuous adaptation of defense strategies.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Entities involved include Warlock ransomware group, Scatter Spider hackers, and Qilin ransomware. Europol is noted for its role in dismantling a cybercrime network.
7. Thematic Tags
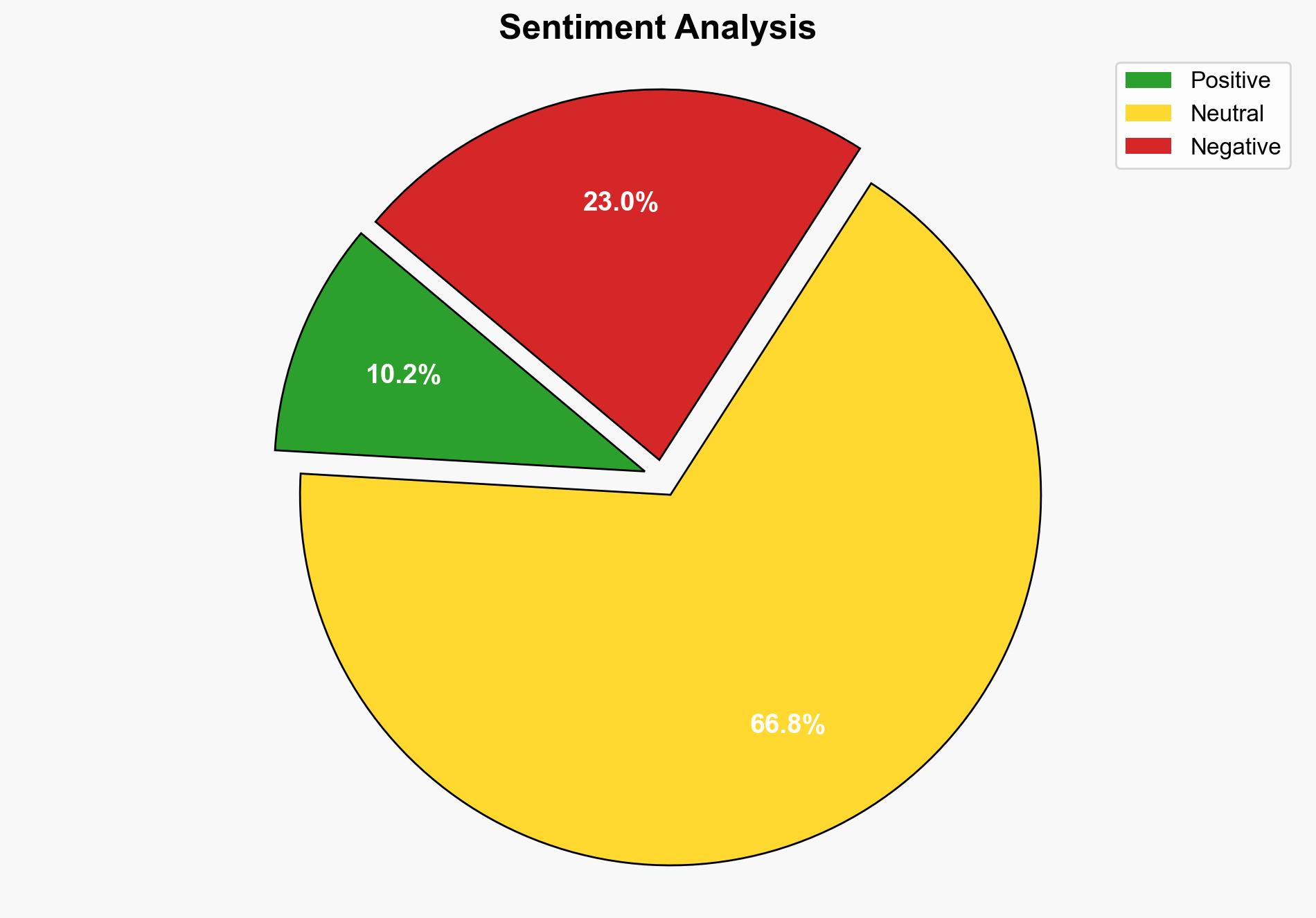
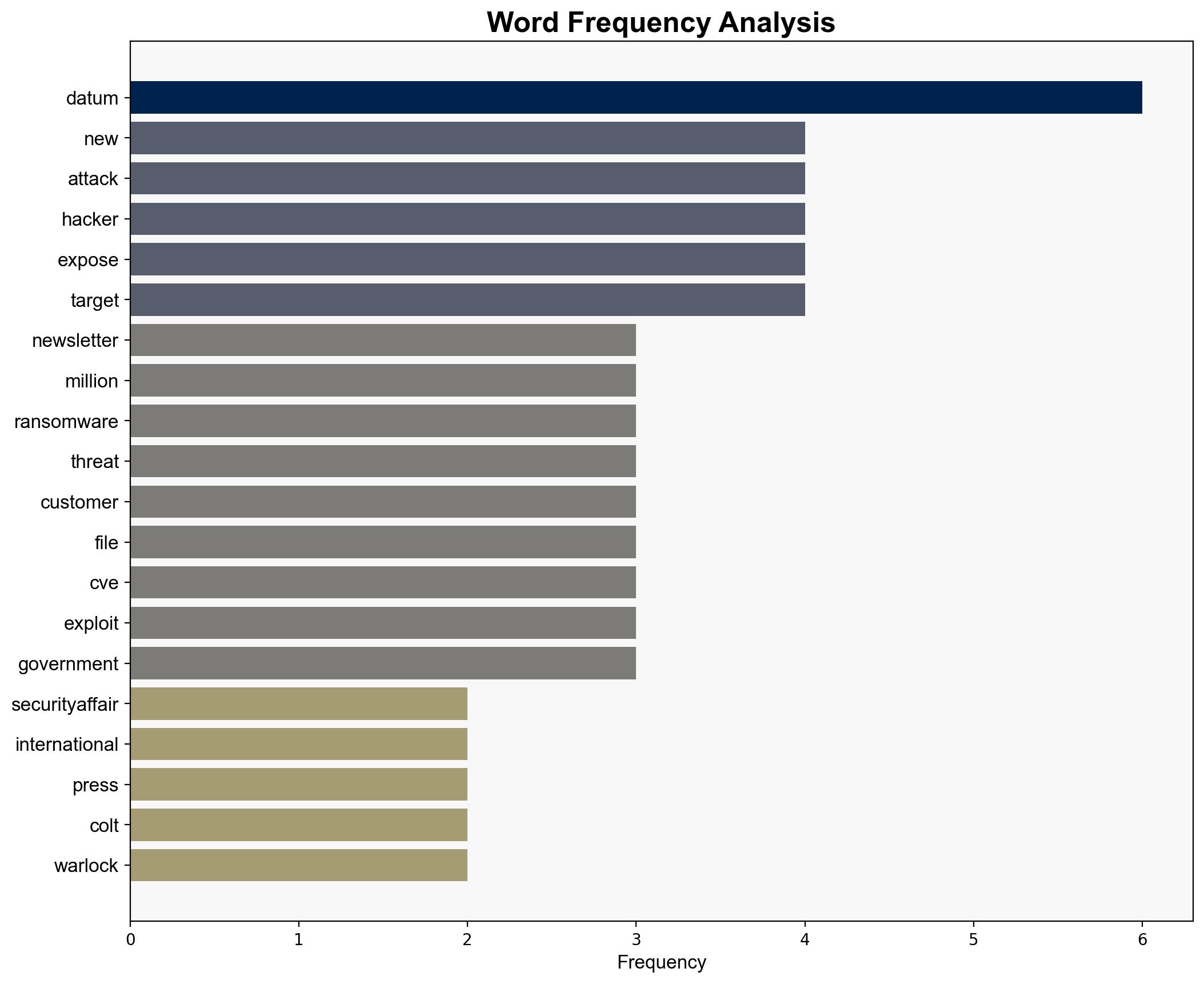
national security threats, cybersecurity, counter-terrorism, regional focus