Security Flaw Found in Thousands of AI Android Apps Exposes User Data Risks
Published on: 2026-02-02
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Millions of Android AI Apps Hide a Dangerous Secretand Researchers Just Exposed It
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
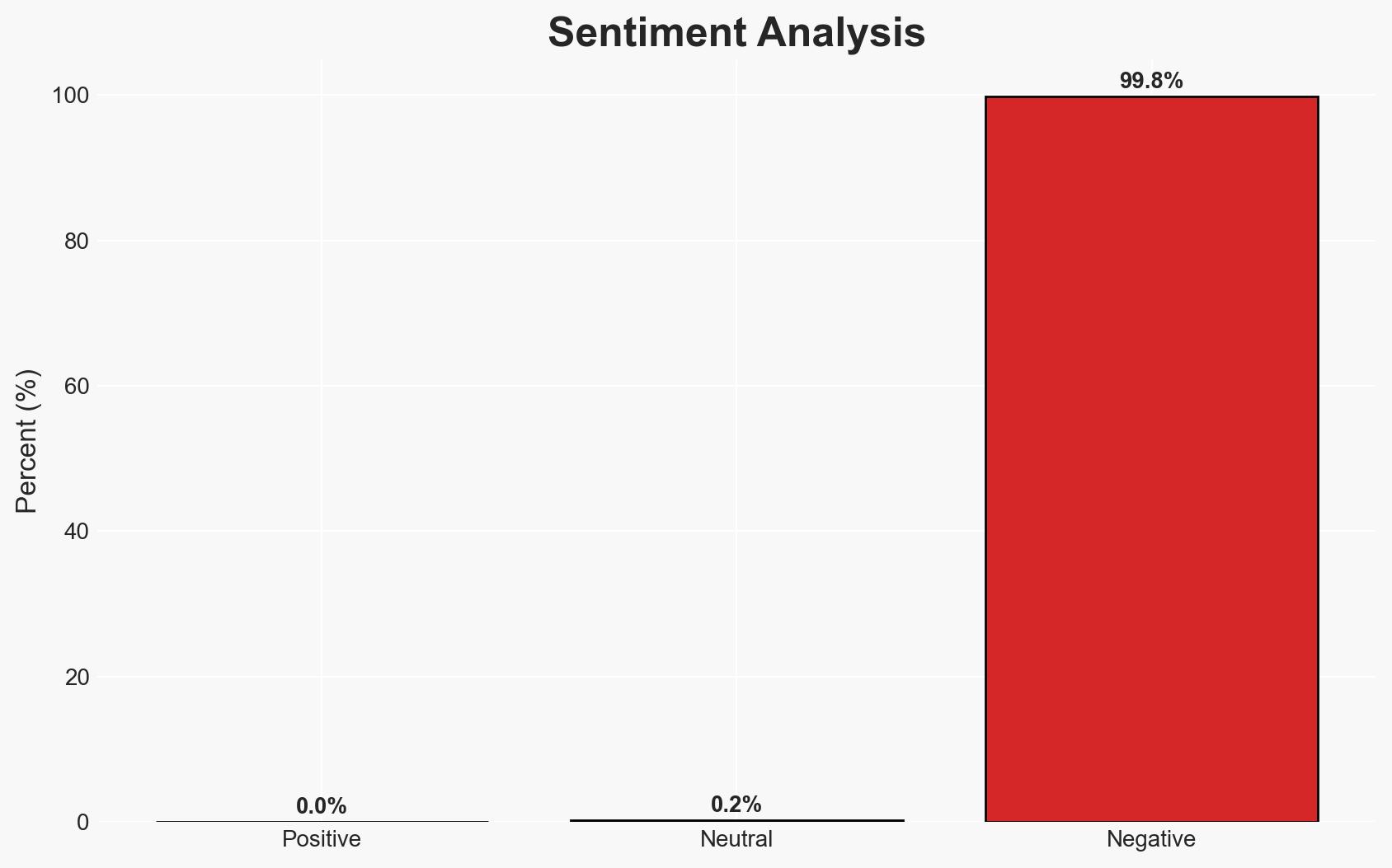
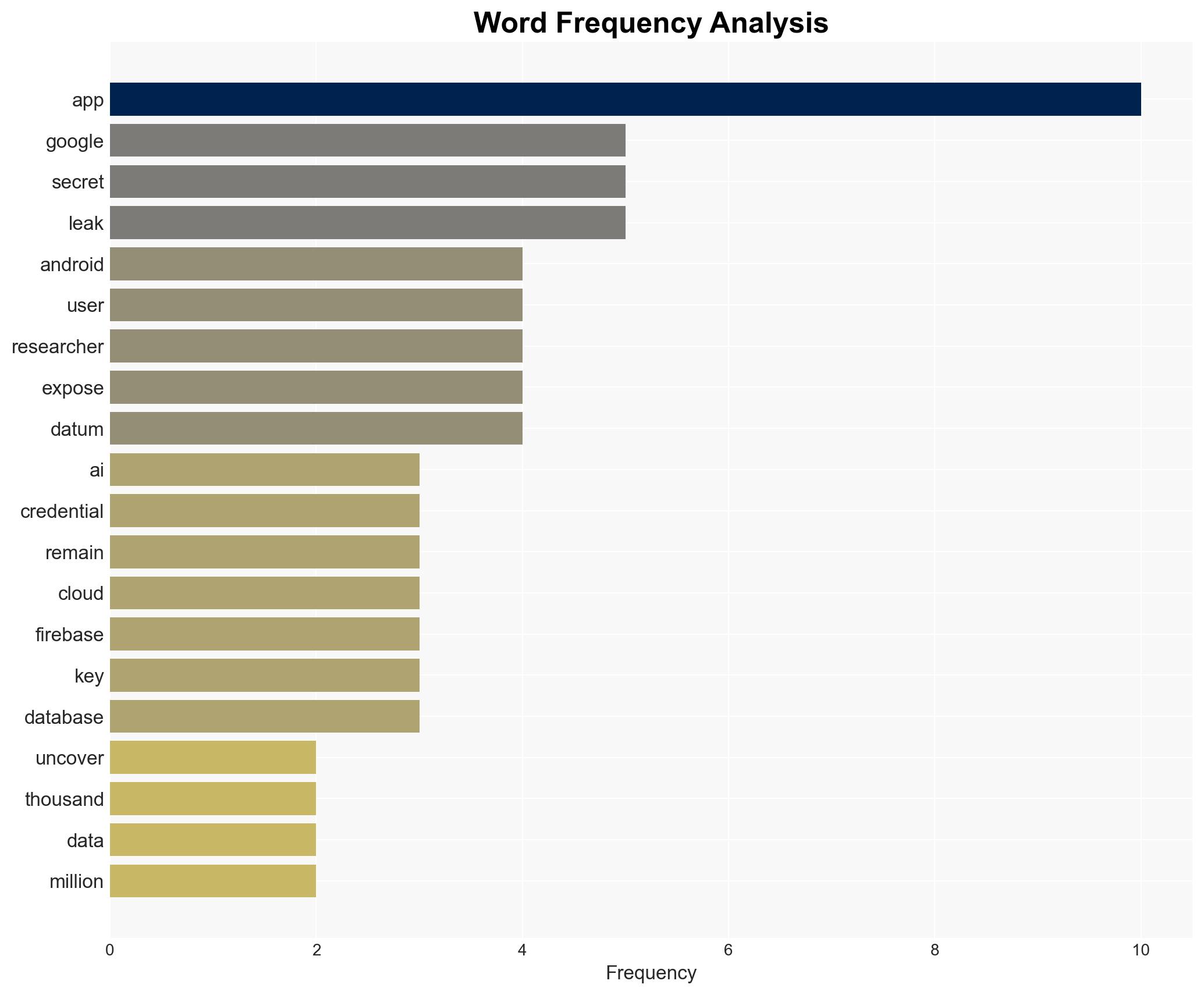
Recent findings reveal systemic vulnerabilities in AI-powered Android apps, with significant data exposure risks linked to hardcoded secrets. This affects millions of users and poses a threat to data integrity and privacy, particularly through Google Cloud services. The most likely hypothesis is that these vulnerabilities result from widespread poor coding practices rather than coordinated malicious intent. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The vulnerabilities in AI apps are primarily due to widespread poor coding practices and lack of security awareness among developers. Supporting evidence includes the high percentage of apps with hardcoded secrets and the systemic nature of the issue. However, the lack of specific developer intent or coordination remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The vulnerabilities are part of a coordinated effort to exploit AI apps for malicious purposes. This hypothesis is less supported due to the lack of direct evidence of coordinated attacks, although the presence of prior attacks on unsecured databases could suggest opportunistic exploitation.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the systemic nature of the vulnerabilities and the absence of clear indicators of coordination. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of organized exploitation or changes in the pattern of vulnerabilities.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Developers lack adequate security training, Google Cloud services are a primary target due to their widespread use, and the vulnerabilities are not intentionally introduced.
- Information Gaps: Specific details on the developers’ security practices and any potential links to coordinated exploitation efforts are missing.
- Bias & Deception Risks: There is a risk of confirmation bias in attributing vulnerabilities solely to poor practices without considering potential malicious intent. Source bias may exist if researchers have a vested interest in highlighting security flaws.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The exposure of vulnerabilities in AI apps could lead to increased scrutiny of app security practices and regulatory pressures on developers and platforms. Over time, this may drive improvements in coding standards but also create opportunities for malicious actors to exploit existing weaknesses.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regulatory actions and international cooperation on cybersecurity standards.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of data breaches and exploitation by cybercriminals or state actors.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased focus on securing cloud services and app ecosystems, with potential for misinformation campaigns exploiting vulnerabilities.
- Economic / Social: Possible loss of consumer trust in AI apps and economic impacts on companies reliant on these technologies.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a comprehensive audit of AI apps on the Google Play Store, prioritize securing exposed credentials, and engage with developers to improve security practices.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms to enhance app security, invest in developer training programs, and advocate for stronger regulatory frameworks.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid adoption of improved security practices reduces vulnerabilities significantly.
- Worst: Continued exploitation of vulnerabilities leads to major data breaches and loss of consumer trust.
- Most-Likely: Gradual improvements in security practices with intermittent exploitation incidents.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, data privacy, AI applications, cloud services, app vulnerabilities, Google Play Store, developer practices
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us