Security forces arrest four suspects linked to Islamabad mosque bombing as thousands mourn 32 victims.
Published on: 2026-02-07
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Thousands mourn 32 victims of Islamabad Shia mosque bombing in Pakistan
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
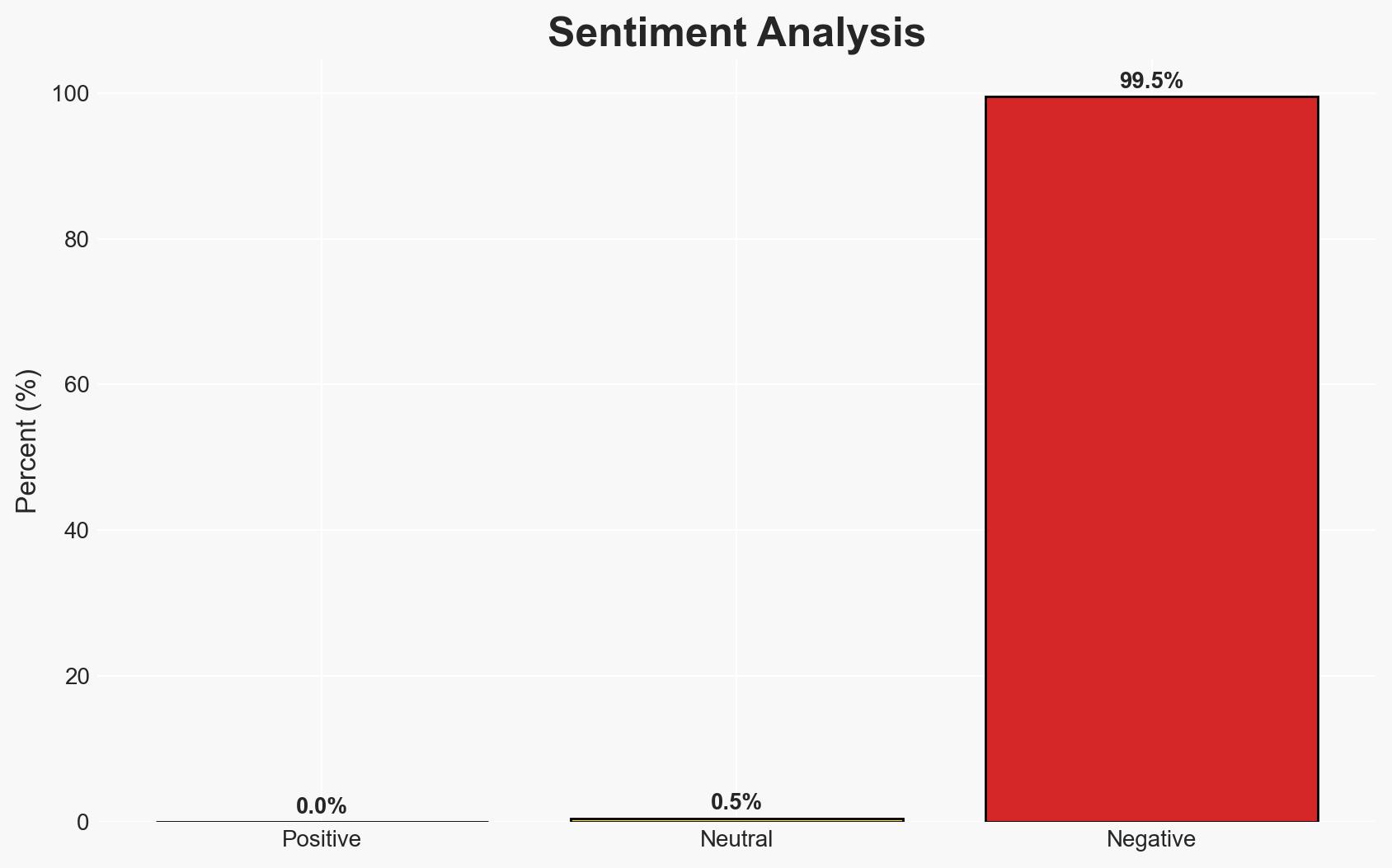
The Islamabad mosque bombing, claimed by ISIL, highlights increasing cross-border terrorism threats in Pakistan, with potential links to Afghanistan. The arrest of facilitators suggests a coordinated effort, raising concerns about regional security dynamics. Overall confidence in the assessment is moderate, given the complexity of regional alliances and limited open-source information.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The attack was orchestrated by ISIL with direct operational support from facilitators within Pakistan and strategic guidance from Afghanistan. This is supported by the arrests of facilitators and claims of Afghan-based planning. Key uncertainties include the extent of Afghan Taliban involvement.
- Hypothesis B: The attack was primarily a local initiative by ISIL sympathizers in Pakistan, with minimal external influence. Contradicting evidence includes the military’s claim of Afghan Daesh mastermind involvement and the historical pattern of cross-border terrorism.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the arrests and intelligence indicating Afghan involvement. Indicators such as further arrests or intelligence leaks could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: ISIL has operational capabilities in Pakistan; Afghan Taliban provides indirect support to extremist groups; local security forces can effectively disrupt terrorist networks.
- Information Gaps: Detailed evidence of Afghan Taliban’s role; the full network of facilitators; ISIL’s strategic objectives in Pakistan.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in military reporting; risk of overestimating Afghan Taliban’s involvement; ISIL’s propaganda may exaggerate its capabilities.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could exacerbate regional tensions, particularly between Pakistan and Afghanistan, and may lead to increased military operations in border areas. The attack underscores the persistent threat of terrorism in urban centers, potentially destabilizing local governance and security.
- Political / Geopolitical: Strained Pakistan-Afghanistan relations; potential for international diplomatic pressure on Afghanistan.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened security measures in urban centers; increased counter-terrorism operations in border regions.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for ISIL to exploit digital platforms for recruitment and propaganda; increased cyber monitoring by Pakistani authorities.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impact due to instability; heightened sectarian tensions and social unrest.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance intelligence-sharing with regional partners; increase security presence in vulnerable areas; monitor ISIL communications for actionable intelligence.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen border security; develop community resilience programs; engage in diplomatic efforts to address cross-border terrorism.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Successful disruption of ISIL networks; Worst: Escalation of cross-border attacks; Most-Likely: Continued sporadic attacks with gradual security improvements. Triggers include changes in Afghan policy or significant ISIL activity.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- ISIL (Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant)
- Pakistani Military
- Afghan Taliban
- Prime Minister Shehbaz Sharif
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
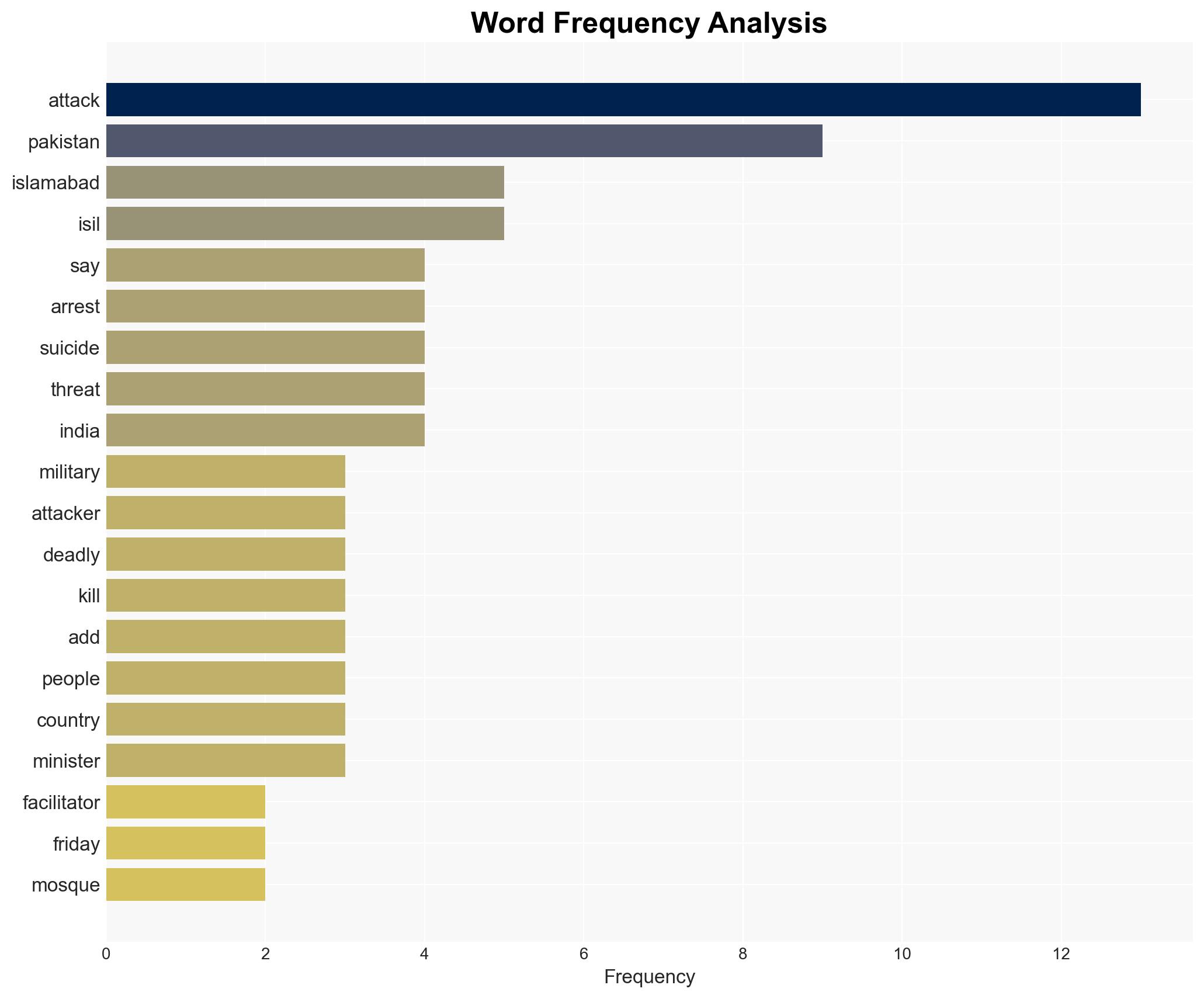
Counter-Terrorism, regional security, ISIL, cross-border attacks, Pakistan-Afghanistan relations, sectarian violence, intelligence operations
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- ACH 2.0: Reconstruct likely threat actor intentions via hypothesis testing and structured refutation.
- Indicators Development: Track radicalization signals and propaganda patterns to anticipate operational planning.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Analyze spread/adaptation of ideological narratives for recruitment/incitement signals.
Explore more:
Counter-Terrorism Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us