Security Vulnerabilities in Popular AI Coding Tool Exposed by BBC Reporter
Published on: 2026-02-13
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: AI coding platform’s flaws allow BBC reporter to be hacked
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The AI coding platform Orchids presents significant cybersecurity vulnerabilities, demonstrated by a zero-click attack on a BBC reporter’s device. This flaw poses risks to its million users, including major companies. The most likely hypothesis is that the platform’s security architecture is fundamentally flawed, with moderate confidence in this assessment due to the lack of company response and the demonstrated exploit.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Orchids’ platform has inherent security vulnerabilities that allow unauthorized access to user projects and devices. This is supported by the demonstrated zero-click attack and lack of company response. However, the specific technical details of the exploit remain undisclosed, creating uncertainty about the scope of the vulnerability.
- Hypothesis B: The security breach was an isolated incident, possibly due to user error or a specific configuration issue. This hypothesis is less supported due to the nature of the zero-click attack, which typically does not rely on user interaction or error.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the evidence of a zero-click vulnerability and the absence of mitigating information from Orchids. Indicators that could shift this judgment include a detailed technical response from Orchids or evidence of similar vulnerabilities in other platforms.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Orchids has not implemented adequate security measures; the vulnerability affects all users equally; the exploit can be replicated by other malicious actors; the company is aware of the vulnerability but has not addressed it.
- Information Gaps: Specific technical details of the vulnerability; Orchids’ internal security protocols; response from Orchids or affected companies.
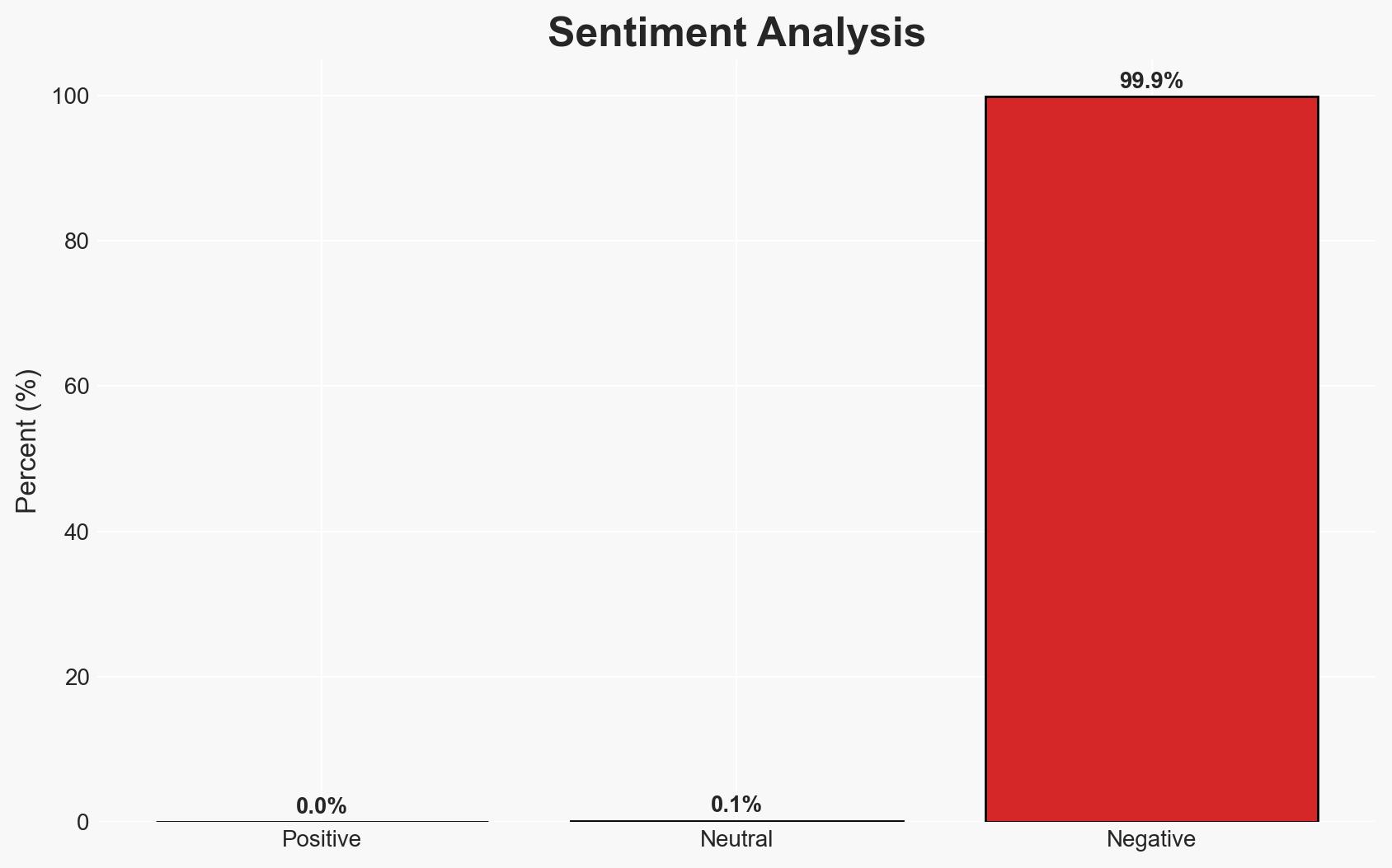
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in the reporting due to the lack of a response from Orchids; possible exaggeration of the threat by the cybersecurity researcher to highlight personal expertise.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The identified vulnerability in Orchids could lead to widespread exploitation if not addressed, impacting user trust and corporate security policies. The situation may evolve as more users become aware of the risks and demand accountability.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential regulatory scrutiny on AI platforms, especially those used by major corporations.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of cyber-attacks leveraging AI platforms, potentially targeting sensitive corporate or personal data.
- Cyber / Information Space: Heightened awareness of AI-related vulnerabilities could lead to increased cyber defense measures and innovation in security protocols.
- Economic / Social: Potential loss of consumer confidence in AI platforms, affecting market growth and innovation in the sector.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a comprehensive security audit of Orchids; engage with Orchids for a response; increase monitoring of AI platform vulnerabilities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms to enhance AI platform security; advocate for industry standards in AI security.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Orchids addresses the vulnerability, restoring user confidence and setting a precedent for AI security.
- Worst: Exploits proliferate, leading to significant data breaches and regulatory backlash.
- Most-Likely: Orchids issues a patch, but similar vulnerabilities emerge in other platforms, prompting ongoing security challenges.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Etizaz Mohsin – Cybersecurity researcher
- Orchids – AI coding platform
- BBC – Media organization
- Google, Uber, Amazon – Major companies reportedly using Orchids
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, AI vulnerabilities, zero-click attacks, corporate security, AI platforms, data protection, regulatory scrutiny
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us