Severe n8n Vulnerability CVE-2026-25049 Allows Command Execution Through Malicious Workflow Manipulation
Published on: 2026-02-05
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Critical n8n Flaw CVE-2026-25049 Enables System Command Execution via Malicious Workflows
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
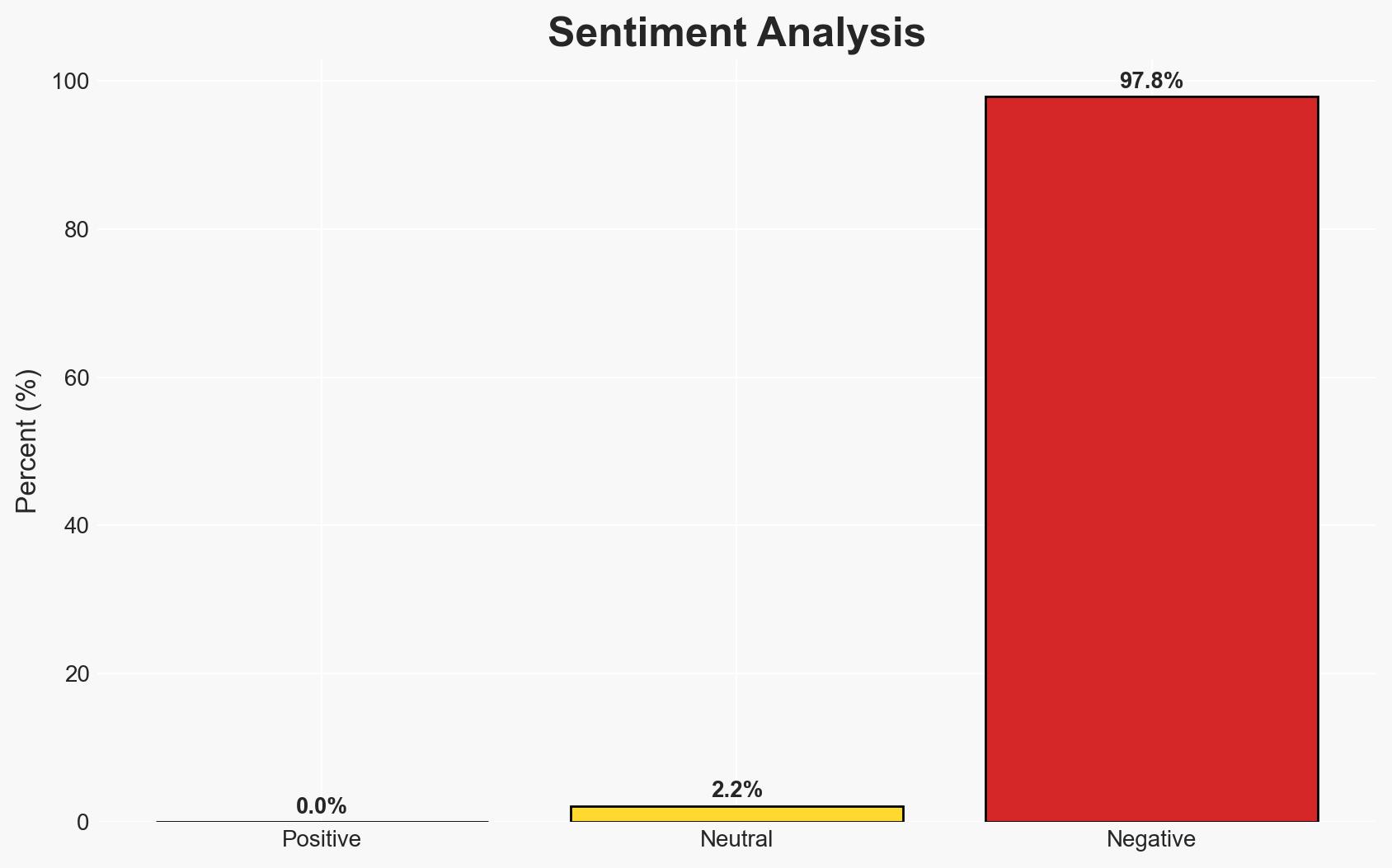
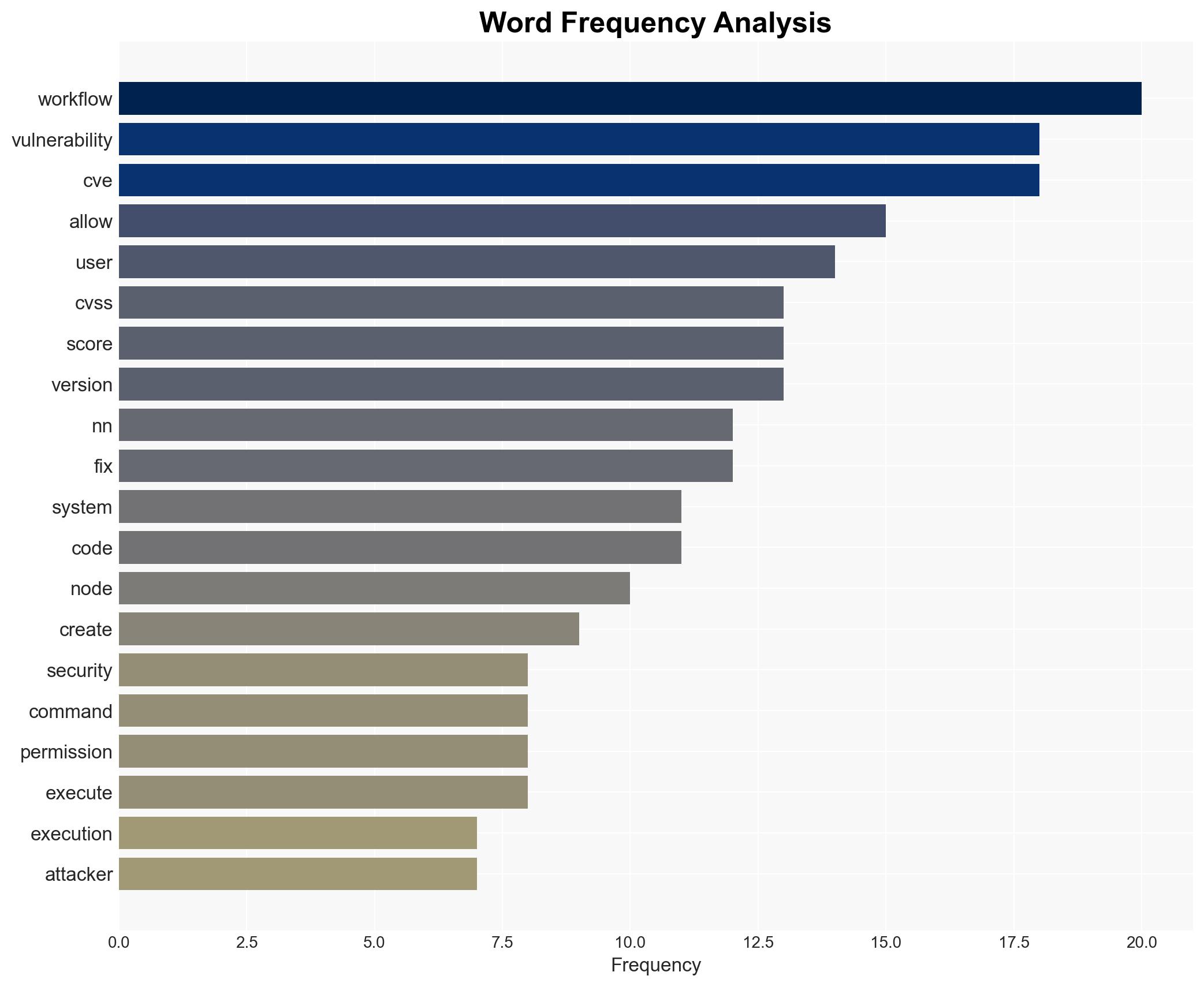
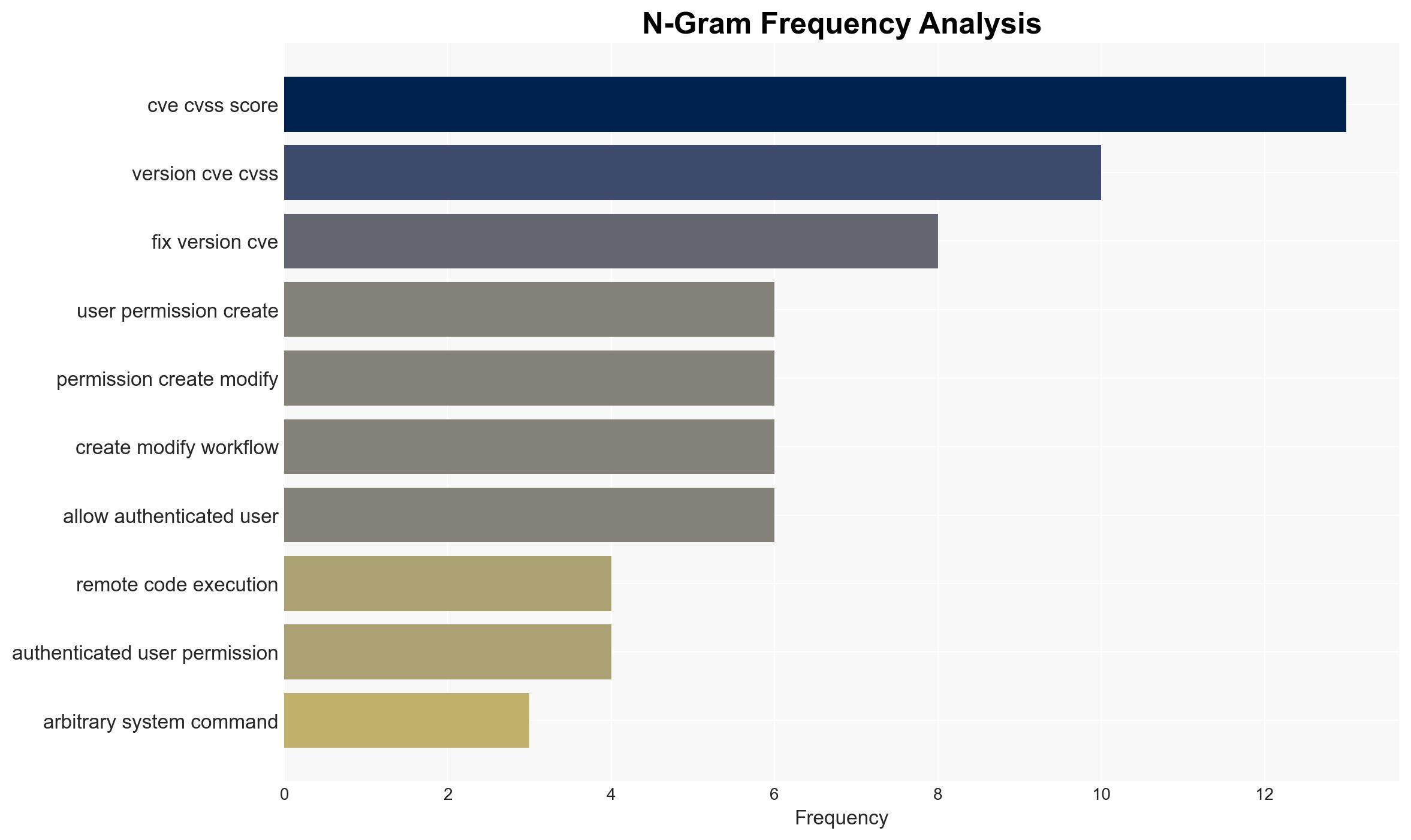
The n8n workflow automation platform is vulnerable to a critical security flaw (CVE-2026-25049) that allows arbitrary system command execution. This vulnerability primarily affects systems running versions prior to 1.123.17 and 2.5.2. The flaw could be exploited by authenticated users to compromise servers, steal credentials, and exfiltrate data. Given the potential for widespread impact, the overall confidence level in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The vulnerability is primarily a result of inadequate patching and oversight following the initial CVE-2025-68613 fix. Supporting evidence includes the bypass nature of CVE-2026-25049 and the history of related vulnerabilities. Key uncertainties include whether further undisclosed vulnerabilities exist.
- Hypothesis B: The vulnerability is an intentional exploitation by malicious insiders or external actors with privileged access. Supporting evidence is limited, and this hypothesis is contradicted by the public disclosure and patching efforts. Key uncertainties involve the potential for insider threats or advanced persistent threats (APTs).
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the technical nature of the flaw and the historical context of similar issues. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of insider involvement or sophisticated exploitation patterns.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The vulnerability is unintentional; n8n will continue to patch vulnerabilities; authenticated users have legitimate access.
- Information Gaps: Details on the extent of exploitation in the wild; comprehensive analysis of potential insider threats.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in source reporting due to vested interests in cybersecurity solutions; risk of underestimating insider threat potential.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This vulnerability could lead to significant security breaches if exploited, affecting both individual organizations and broader industry trust in automation platforms. The evolution of this threat will depend on patch adoption rates and the emergence of additional vulnerabilities.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regulatory scrutiny on software security standards.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Elevated risk of cyber-attacks targeting critical infrastructure using compromised automation platforms.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased activity in cyber forums discussing exploitation techniques; potential for information warfare tactics.
- Economic / Social: Financial losses for affected businesses; erosion of trust in digital transformation initiatives.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Urgent patching of affected systems; enhanced monitoring for signs of exploitation; dissemination of threat intelligence to stakeholders.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Development of robust patch management processes; partnerships with cybersecurity firms for threat intelligence sharing; investment in user access controls.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid patch adoption mitigates risk, leading to minimal exploitation.
- Worst: Widespread exploitation results in significant data breaches and financial losses.
- Most-Likely: Moderate exploitation occurs, prompting increased security measures and regulatory attention.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Fatih Çelik, Endor Labs’ Cris Staicu, Pillar Security’s Eilon Cohen, SecureLayer7’s Sandeep Kamble
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, vulnerability management, automation platforms, insider threats, patch management, cyber-espionage
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us