Shifting Global Dynamics: The U.S. Navigates a Multipolar World Amidst Evolving Power Structures
Published on: 2025-12-19
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: The Next World Order How the Great Powers Are Dividing the Globe
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
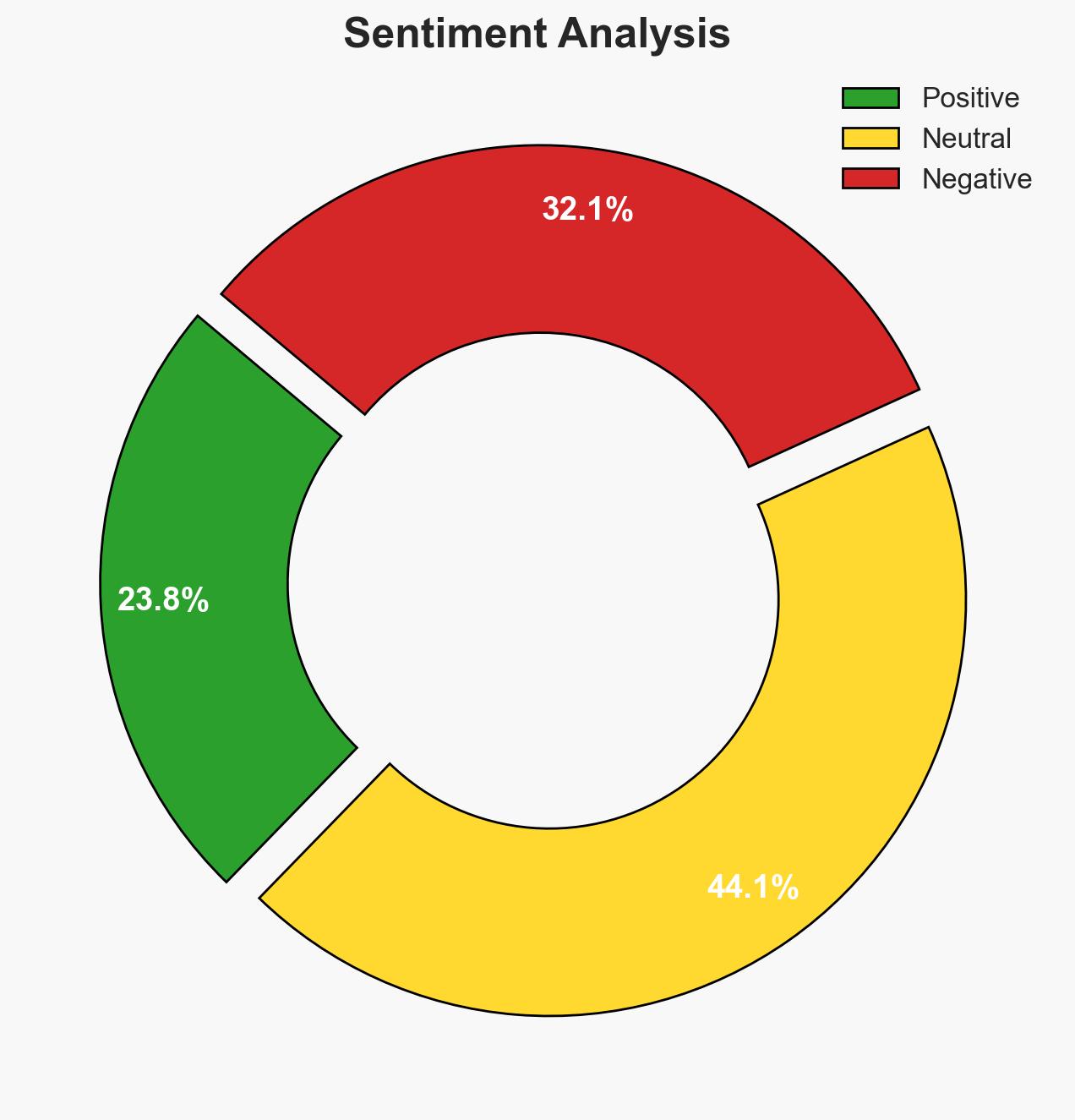
The global power structure is transitioning from a unipolar to a multipolar world, with the United States, Russia, and China vying for influence. The U.S. is adapting to this shift by attempting to maintain its dominance through strategic retrenchment. This situation presents significant geopolitical risks, including potential proxy conflicts and economic competition. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The U.S. will successfully adapt to a multipolar world by redefining its sphere of influence and maintaining its status as the primary global power. This is supported by historical precedence of U.S. interventions and current strategic retrenchment efforts. However, uncertainties include the reaction of other powers and internal U.S. political dynamics.
- Hypothesis B: The U.S. will struggle to maintain its influence as other powers, particularly China and Russia, expand their spheres of influence. This is supported by the growing economic and military capabilities of these nations. Contradicting evidence includes the U.S.’s existing alliances and military capabilities.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the U.S.’s historical adaptability and strategic initiatives. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include significant geopolitical shifts or changes in U.S. domestic policy.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The U.S. will continue to prioritize its global influence; Russia and China will seek to expand their influence; multipolarity will not immediately lead to direct conflict.
- Information Gaps: Detailed strategies of Russia and China regarding their spheres of influence; internal political dynamics within the U.S. that could affect foreign policy.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in historical interpretations of U.S. interventions; risk of underestimating the strategic capabilities of Russia and China.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The transition to a multipolar world could lead to increased geopolitical tensions and competition, potentially destabilizing regions as powers assert their influence.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regional conflicts and shifts in alliances as powers vie for influence.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of proxy wars and asymmetric threats as powers engage in indirect confrontations.
- Cyber / Information Space: Likely increase in cyber operations and information warfare as tools for influence and destabilization.
- Economic / Social: Economic competition could lead to trade conflicts, impacting global markets and social stability.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance intelligence monitoring of geopolitical developments; engage in diplomatic dialogues to reduce tensions.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen alliances and partnerships; invest in cyber and information warfare capabilities.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Peaceful negotiation of spheres of influence, leading to stable multipolarity.
- Worst: Escalation into proxy conflicts or economic warfare.
- Most-Likely: Ongoing strategic competition with intermittent regional tensions.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
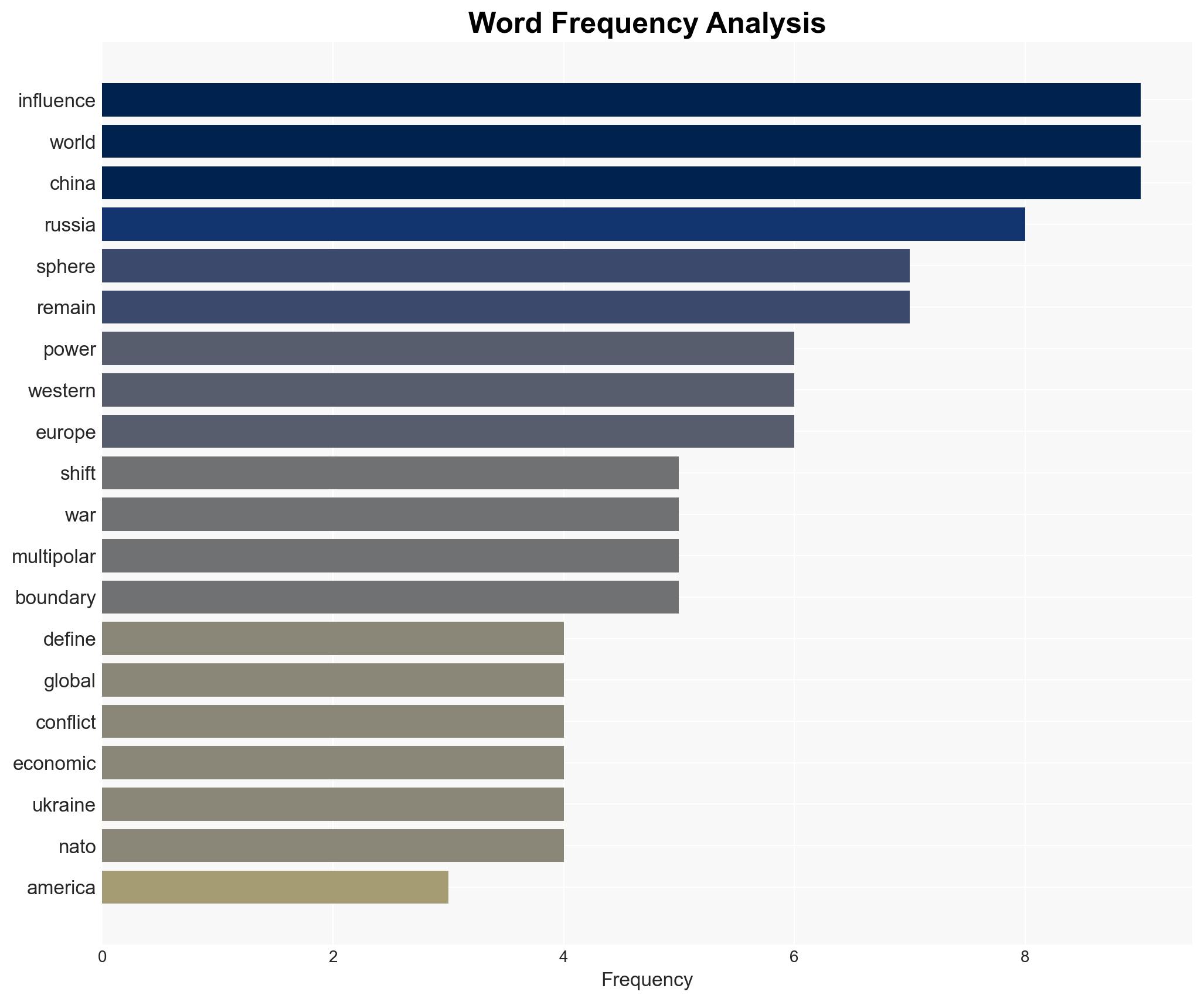
regional conflicts, geopolitics, multipolarity, U.S. foreign policy, Russia-China relations, proxy conflicts, economic competition, cyber warfare
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us