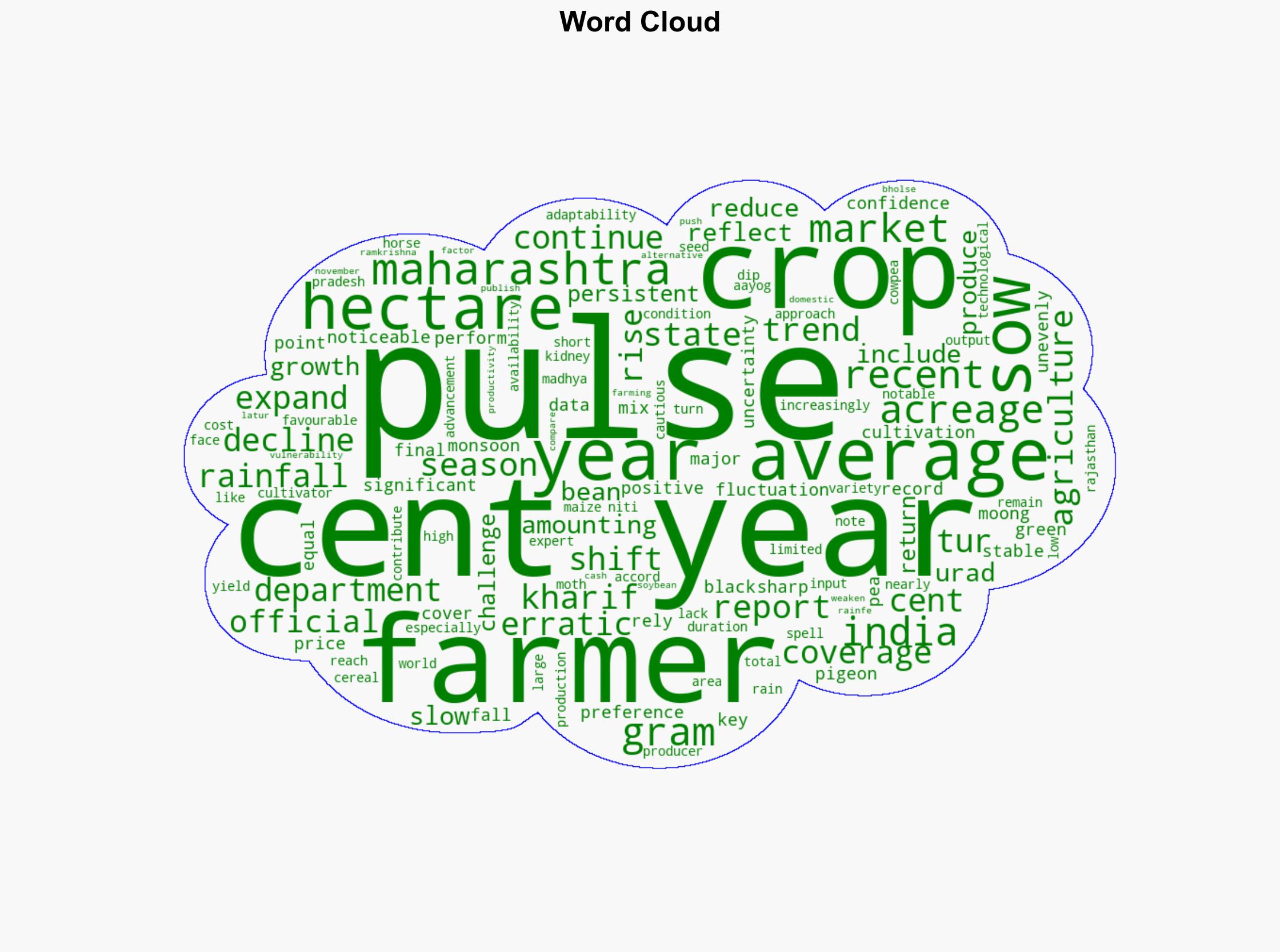
Shifting pulses Maharashtra farmers cut moong acreage maintain tur and expand urad – BusinessLine
Published on: 2025-11-13
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Shifting pulses Maharashtra farmers cut moong acreage maintain tur and expand urad – BusinessLine
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
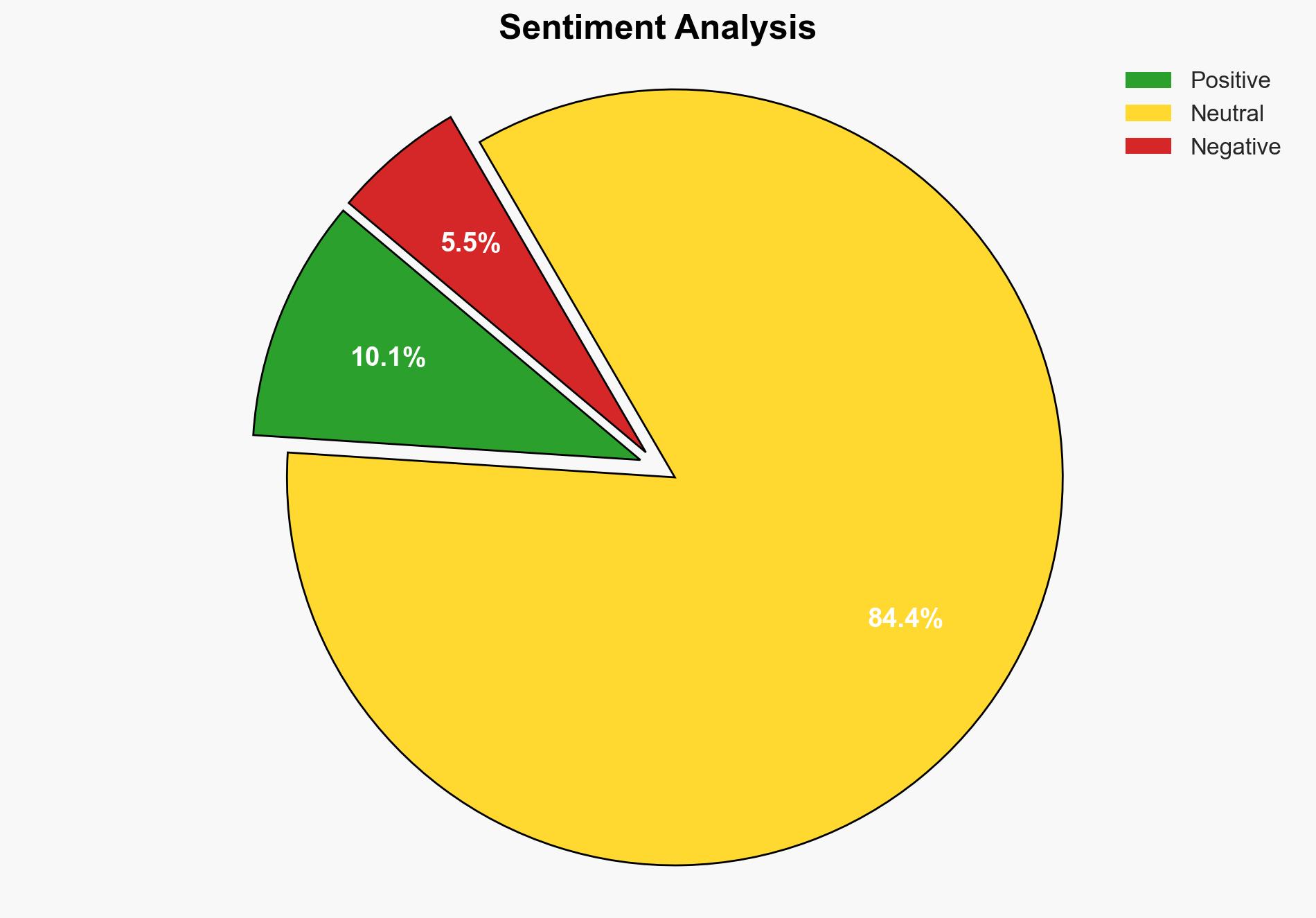
The strategic judgment is that Maharashtra farmers are adapting their crop strategies in response to erratic rainfall and market conditions by reducing moong acreage, maintaining tur, and expanding urad cultivation. The most supported hypothesis is that these changes are driven by economic incentives and environmental adaptability. Confidence level: Moderate. Recommended action includes supporting technological advancements in pulse agriculture and providing market stability measures.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: Farmers are shifting crop patterns primarily due to economic factors, such as market prices and input costs. This hypothesis is supported by the reported favorable market conditions for urad and price fluctuations for moong.
Hypothesis 2: The shift is primarily driven by environmental factors, specifically erratic rainfall patterns, which influence the suitability of certain crops like urad that adapt better to short rain spells. This is supported by the adaptability of urad to varying rainfall conditions.
Hypothesis 1 is more likely given the explicit mention of market conditions as a driving factor, although environmental factors also play a significant role.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: It is assumed that market prices and rainfall patterns will continue to influence farmer decisions. It is also assumed that the data from the Maharashtra Agriculture Department is accurate and comprehensive.
Red Flags: Potential bias in reporting from local officials or misinterpretation of data trends. Deception indicators include possible underreporting of crop failures or overestimation of successful crop yields.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The shift in crop patterns could lead to economic risks if market conditions change unfavorably or if environmental conditions worsen. There is a risk of reduced food security if pulse production does not meet domestic demand. Politically, dissatisfaction among farmers could lead to unrest if government support is perceived as inadequate. Economically, increased reliance on specific crops could lead to market volatility.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Promote research and development in high-yield, drought-resistant pulse varieties to mitigate environmental risks.
- Implement policies to stabilize market prices for pulses to reduce economic uncertainty for farmers.
- Best-case scenario: Successful adaptation leads to increased pulse production and economic stability for farmers.
- Worst-case scenario: Continued erratic weather and market instability lead to significant economic losses and potential farmer unrest.
- Most-likely scenario: Gradual adaptation with moderate success, requiring ongoing support and intervention.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Ramkrishna Bholse, a farmer from Latur, is mentioned as a source of insight into farmer perspectives.
7. Thematic Tags
Economic Adaptation, Agricultural Policy, Climate Resilience, Market Stability
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Methodology