ShinyHunters exploit MFA vulnerabilities in sophisticated social engineering attacks across multiple sectors
Published on: 2026-02-02
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: ShinyHunters flip the script on MFA in new data theft attacks
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
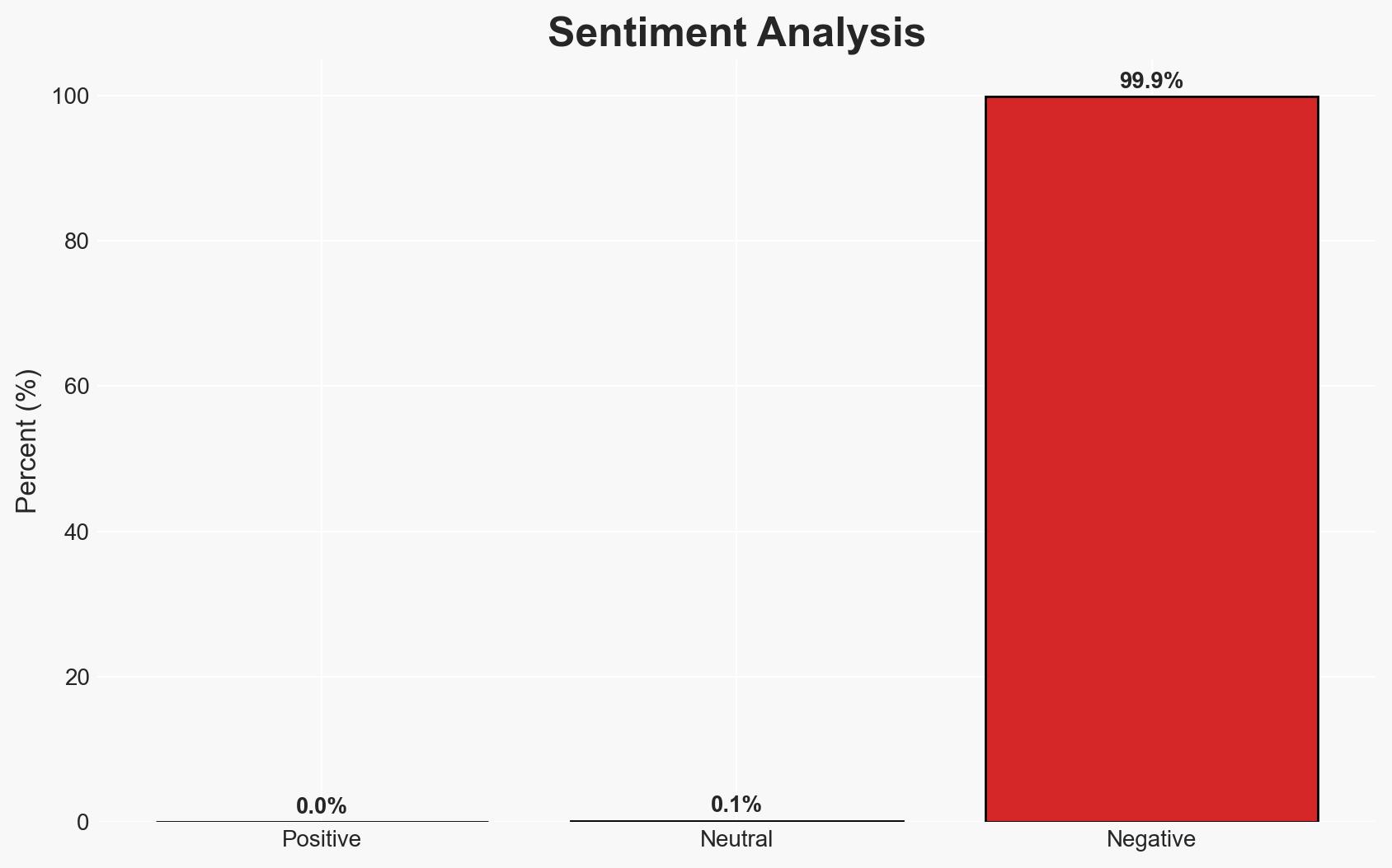
The ShinyHunters group is exploiting multi-factor authentication (MFA) as a vector for social engineering attacks, targeting various sectors including tech, fintech, and healthcare. This tactic involves impersonating IT staff to harvest credentials and bypass MFA, affecting organizations like Panera Bread and SoundCloud. The most likely hypothesis is that these attacks are part of a coordinated effort by multiple threat actors using similar methodologies. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: ShinyHunters is a singular, coordinated group using advanced social engineering techniques to exploit MFA vulnerabilities. Supporting evidence includes consistent methodologies across incidents and targeting patterns. Key uncertainties include the full extent of their network and potential undiscovered victims.
- Hypothesis B: Multiple independent threat actors are using similar tactics, possibly sharing tools or methodologies, but operating independently. This is supported by reports of seemingly independent groups like UNC6661 and UNC6671 using similar approaches. Contradicting evidence is the lack of clear differentiation in tactics and targets.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the uniformity in attack methods and the strategic targeting of high-value sectors. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of distinct operational patterns or separate command structures.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: MFA remains a primary security measure; threat actors have access to sophisticated phishing tools; targeted organizations have similar vulnerabilities.
- Information Gaps: Detailed attribution of attacks to specific actors; comprehensive list of affected entities; full scope of data exfiltrated.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential over-reliance on reports from cybersecurity firms with vested interests; deception by threat actors to obscure true identity or motives.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased vulnerabilities in sectors heavily reliant on digital infrastructure, potentially prompting a reevaluation of MFA protocols.
- Political / Geopolitical: Escalation in cyber tensions between state and non-state actors, possibly affecting international relations.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment requiring enhanced cyber defense measures across critical sectors.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for widespread adoption of similar tactics by other threat actors, increasing overall cyber risk.
- Economic / Social: Financial losses and reputational damage to affected companies, with possible impacts on consumer trust and market stability.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Strengthen MFA protocols, increase awareness and training on social engineering tactics, and enhance monitoring for phishing attempts.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for intelligence sharing, invest in advanced threat detection capabilities, and conduct regular security audits.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Improved defenses reduce attack success rates; Worst: Widespread adoption of these tactics leads to systemic vulnerabilities; Most-Likely: Continued targeted attacks with gradual improvement in defensive measures.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
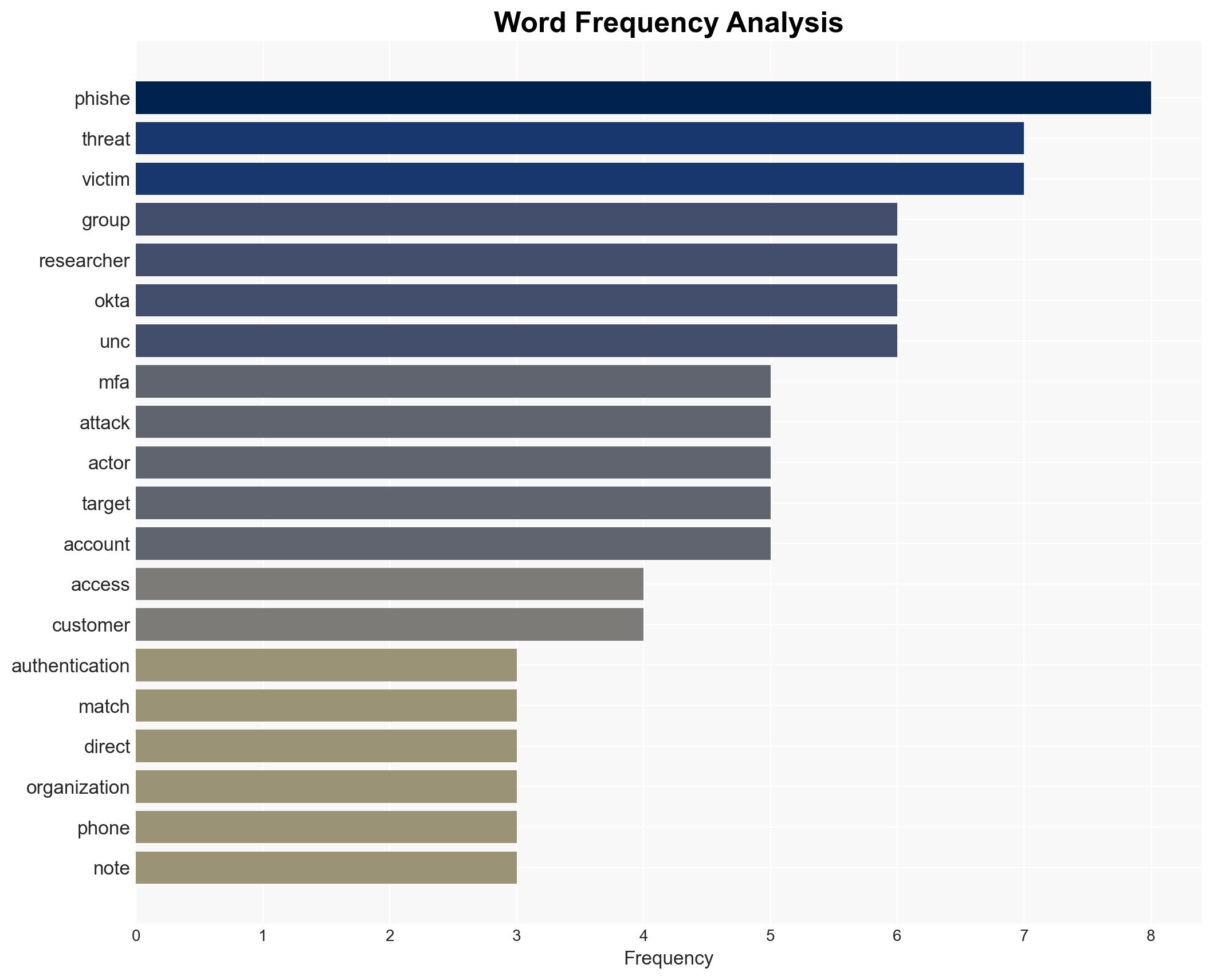
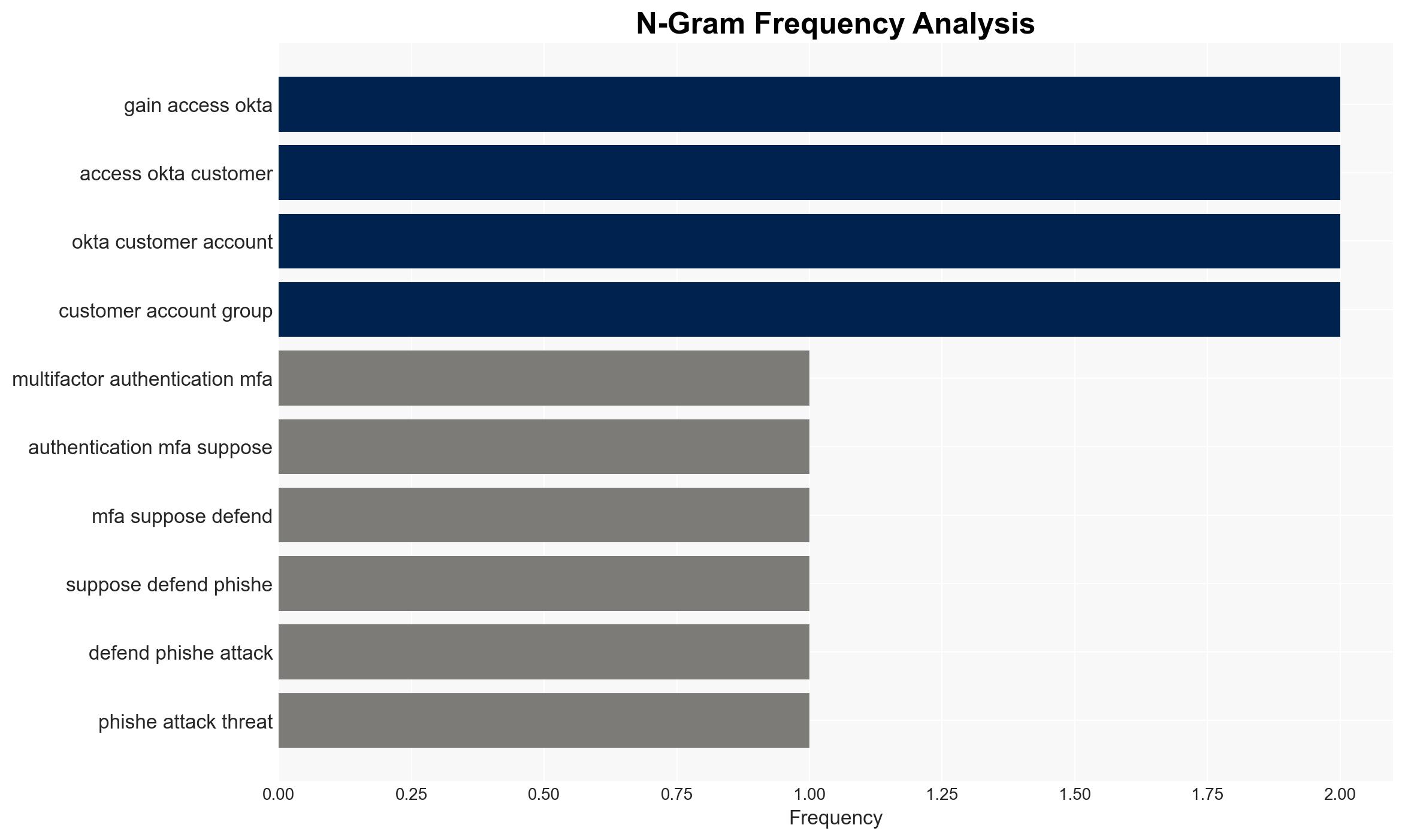
- ShinyHunters, UNC6661, UNC6671, Panera Bread, SoundCloud, Match Group, Crunchbase, Okta, Mandiant
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, social engineering, multi-factor authentication, phishing, threat actors, data theft, information security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us