Siemens Interniche IP-Stack
Published on: 2025-12-18
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Siemens Interniche IP-Stack
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
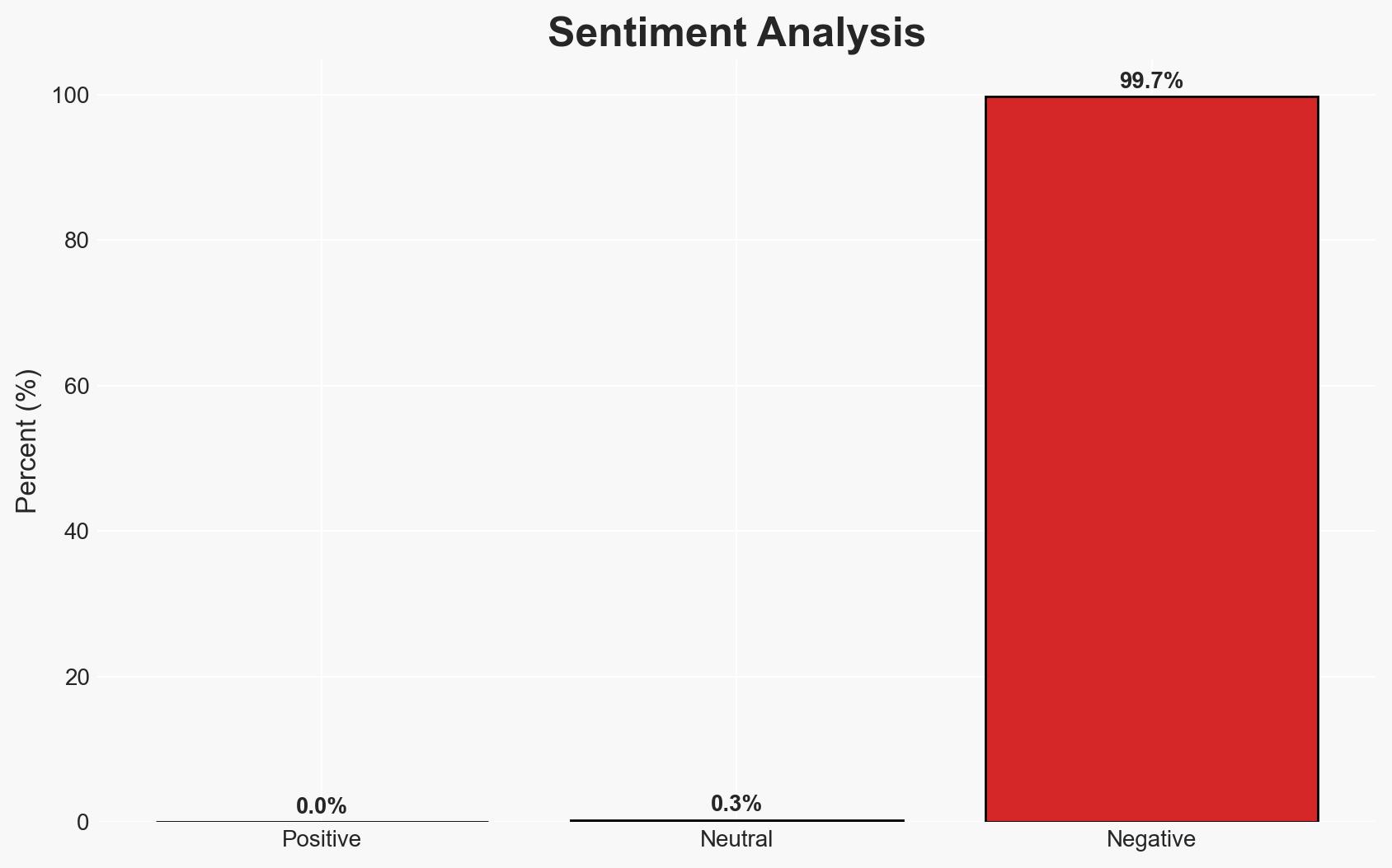
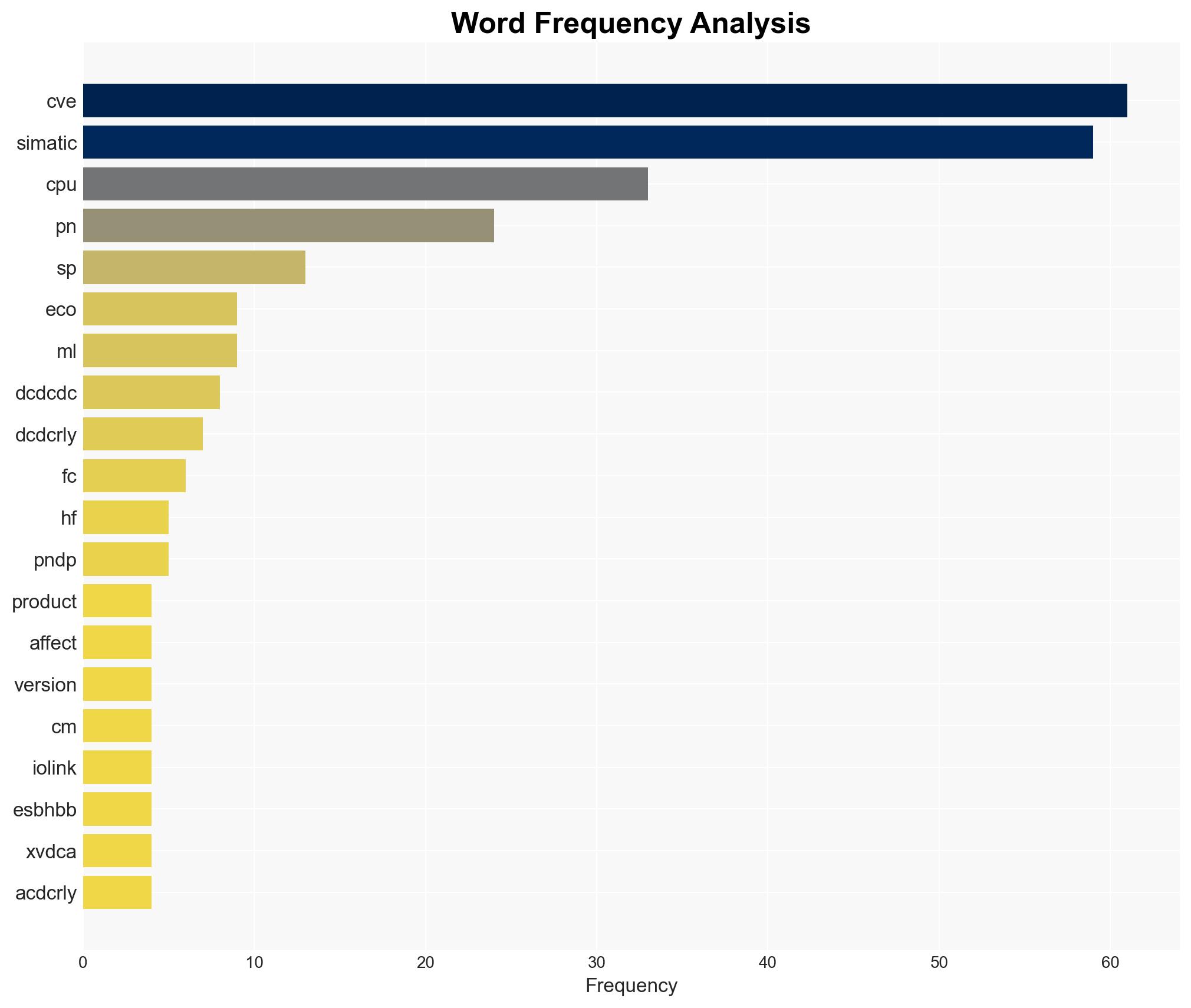
The Siemens Interniche IP-Stack vulnerability affects multiple industrial products, potentially allowing unauthenticated remote attackers to cause denial of service. Siemens has issued updates and countermeasures, but the risk remains for products without available fixes. The most likely hypothesis is that this vulnerability will be exploited opportunistically rather than systematically. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The vulnerability will be exploited primarily by opportunistic attackers targeting unpatched systems. This is supported by the complexity of the attack method, which requires precise timing and spoofed IP packets, limiting the pool of potential attackers. However, the widespread nature of the affected products increases the attack surface.
- Hypothesis B: The vulnerability will be exploited by state-sponsored actors or organized cybercriminal groups as part of a coordinated campaign. This hypothesis is less supported due to the lack of evidence of targeted campaigns and the current focus on opportunistic attacks in similar scenarios.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the technical requirements of the attack and the absence of indicators of coordinated exploitation. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include reports of targeted attacks or evidence of state-sponsored involvement.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The vulnerability requires precise timing for successful exploitation; Siemens will continue to release timely patches; affected organizations will follow Siemens’ recommendations.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the current exploitation of the vulnerability; effectiveness of Siemens’ countermeasures in real-world scenarios.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential underreporting of successful exploitations; Siemens’ communications may downplay the severity to protect brand reputation.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The vulnerability could lead to increased cyber risks for industrial sectors, affecting operational continuity and safety. Over time, this could prompt regulatory scrutiny and impact Siemens’ market position.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions if state actors are implicated in exploiting the vulnerability.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of disruption in critical infrastructure sectors reliant on Siemens products.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased focus on securing industrial control systems and potential for information operations exploiting perceived vulnerabilities.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impacts from operational disruptions and increased costs for patching and securing systems.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor for exploitation attempts, ensure timely application of Siemens patches, and implement recommended countermeasures.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures, enhance partnerships with cybersecurity firms, and invest in capability development for industrial cybersecurity.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid patch adoption minimizes exploitation, leading to negligible impact.
- Worst: Coordinated attacks exploit the vulnerability, causing significant operational disruptions.
- Most-Likely: Sporadic exploitation occurs, with moderate operational impacts mitigated by patching and countermeasures.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Siemens AG
- Unauthenticated remote attackers (not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet)
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, industrial control systems, vulnerability management, Siemens, denial of service, patch management, critical infrastructure
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us