Six Detained in Violent Kidnapping of French Magistrate, Highlighting Security Concerns Amid DeFi Developments
Published on: 2026-02-09
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
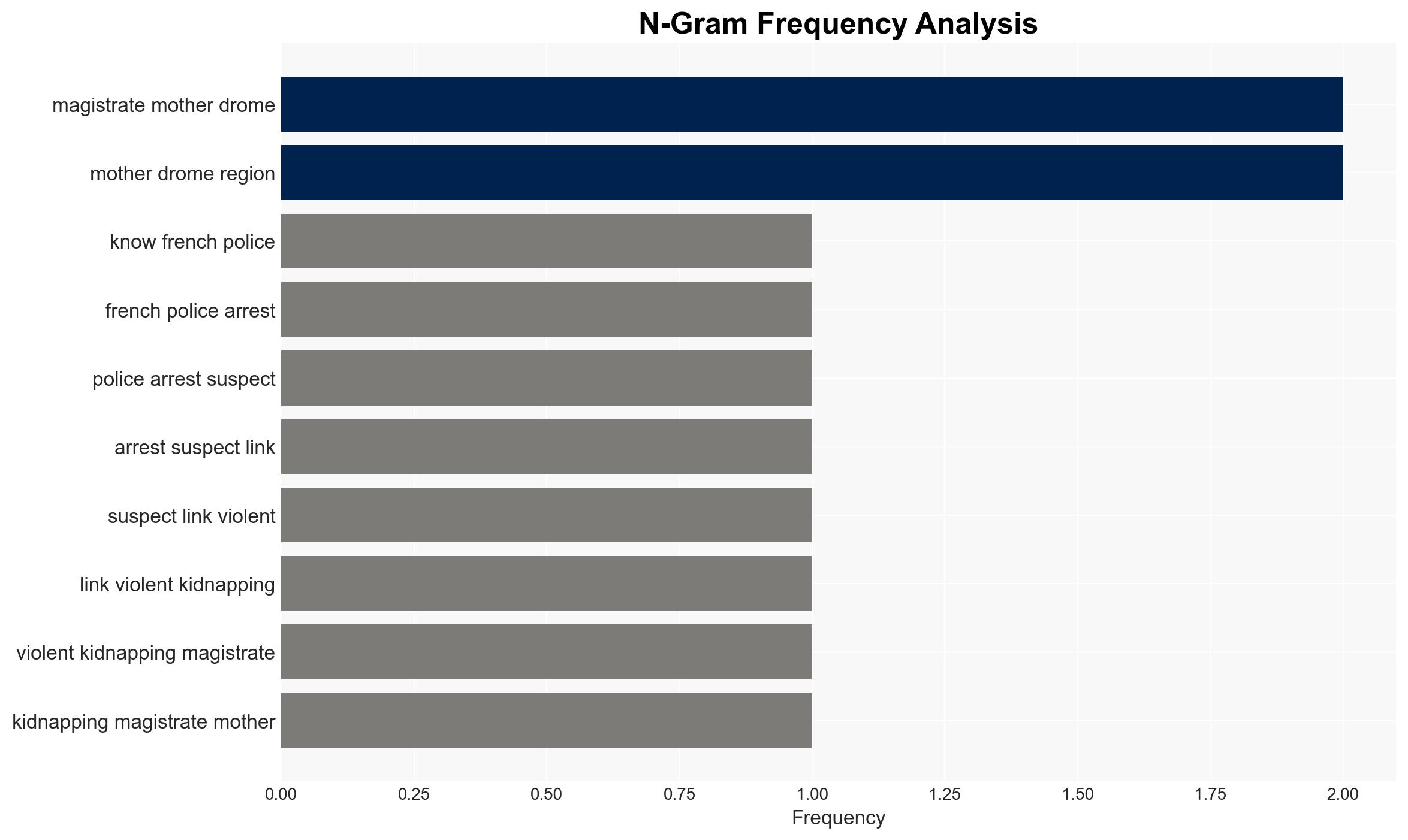
Intelligence Report: French Police Arrest 6 Suspects in Versailles Magistrate Kidnapping Case While LiquidChain Reshapes DeFi
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
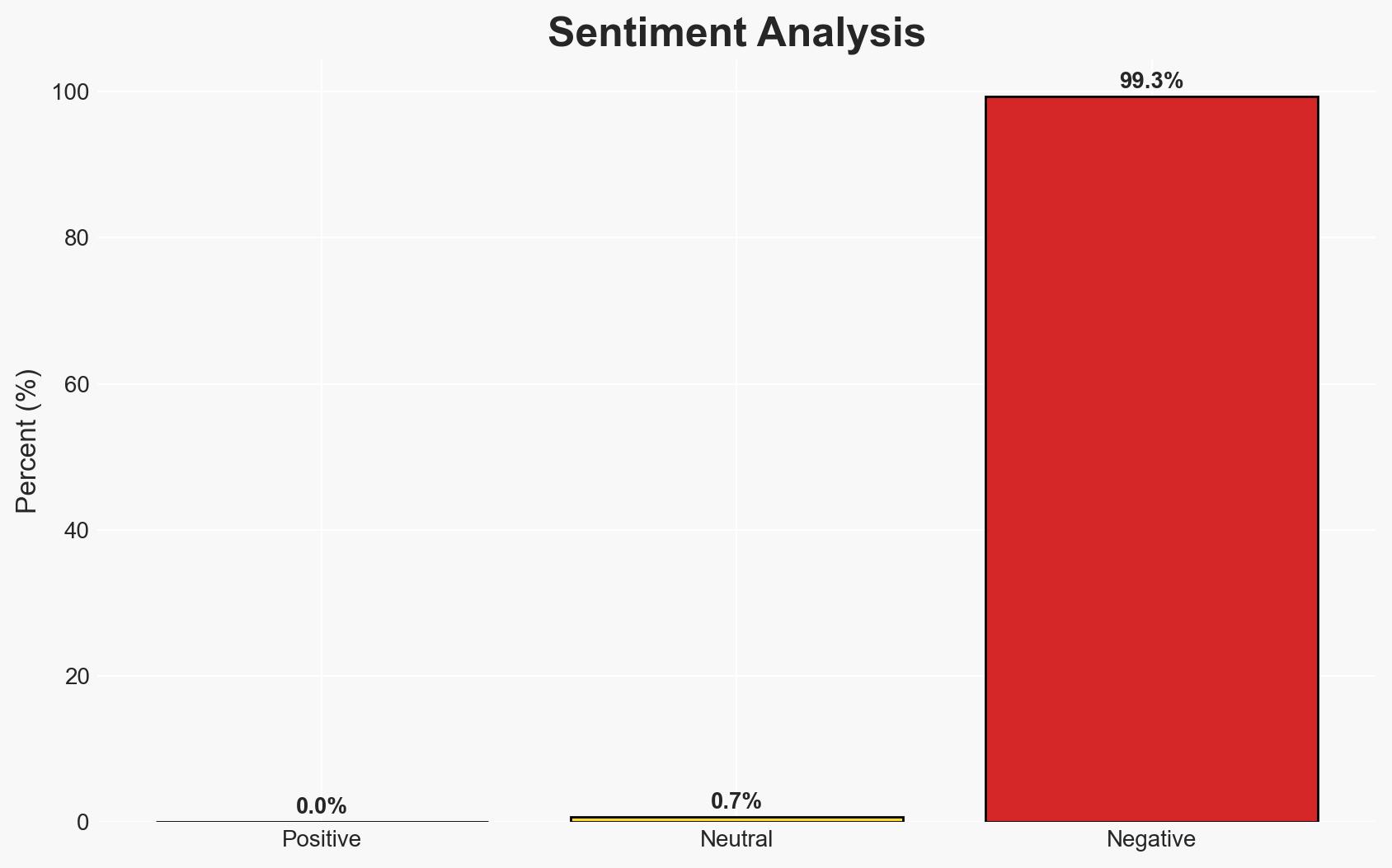
The arrest of six suspects in the kidnapping of a magistrate in France highlights vulnerabilities in institutional security, potentially influencing shifts towards decentralized financial systems. This incident underscores the fragility of centralized structures, which may drive further interest in decentralized finance (DeFi) solutions like LiquidChain. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The kidnapping was primarily financially motivated, targeting a magistrate to exploit perceived weaknesses in institutional security for ransom. This is supported by the organized nature of the crime and the demand for ransom. However, uncertainties remain about potential political motives.
- Hypothesis B: The attack was politically motivated, aiming to destabilize public trust in judicial institutions. While the targeting of a magistrate suggests potential political motives, the lack of explicit political demands weakens this hypothesis.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the financial demands and lack of overt political messaging. Indicators such as further attacks on public officials or political statements by the suspects could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The suspects acted primarily for financial gain; institutional security weaknesses are perceived as exploitable; decentralized financial systems are seen as more secure alternatives.
- Information Gaps: Detailed motives of the suspects, any potential political affiliations, and the full extent of their organizational network.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in interpreting financial motives over political ones; risk of deception in suspect statements or misdirection by involved parties.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This incident may lead to increased scrutiny of institutional security and accelerate interest in decentralized systems. Over time, this could influence broader financial and security dynamics.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential erosion of public trust in government institutions; increased political discourse on security reforms.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment for public officials; possible increase in similar incidents.
- Cyber / Information Space: Greater emphasis on securing digital financial systems; potential rise in cyber threats targeting decentralized platforms.
- Economic / Social: Shift in investment towards DeFi; potential social unrest if institutional trust continues to erode.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance security protocols for public officials; monitor suspect communications for further insights.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with DeFi platforms to understand security implications; invest in institutional security enhancements.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Improved institutional security deters future attacks; DeFi adoption stabilizes.
- Worst: Continued attacks erode public trust; rapid, unregulated DeFi growth leads to financial instability.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in security; steady growth in DeFi adoption as a parallel financial system.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
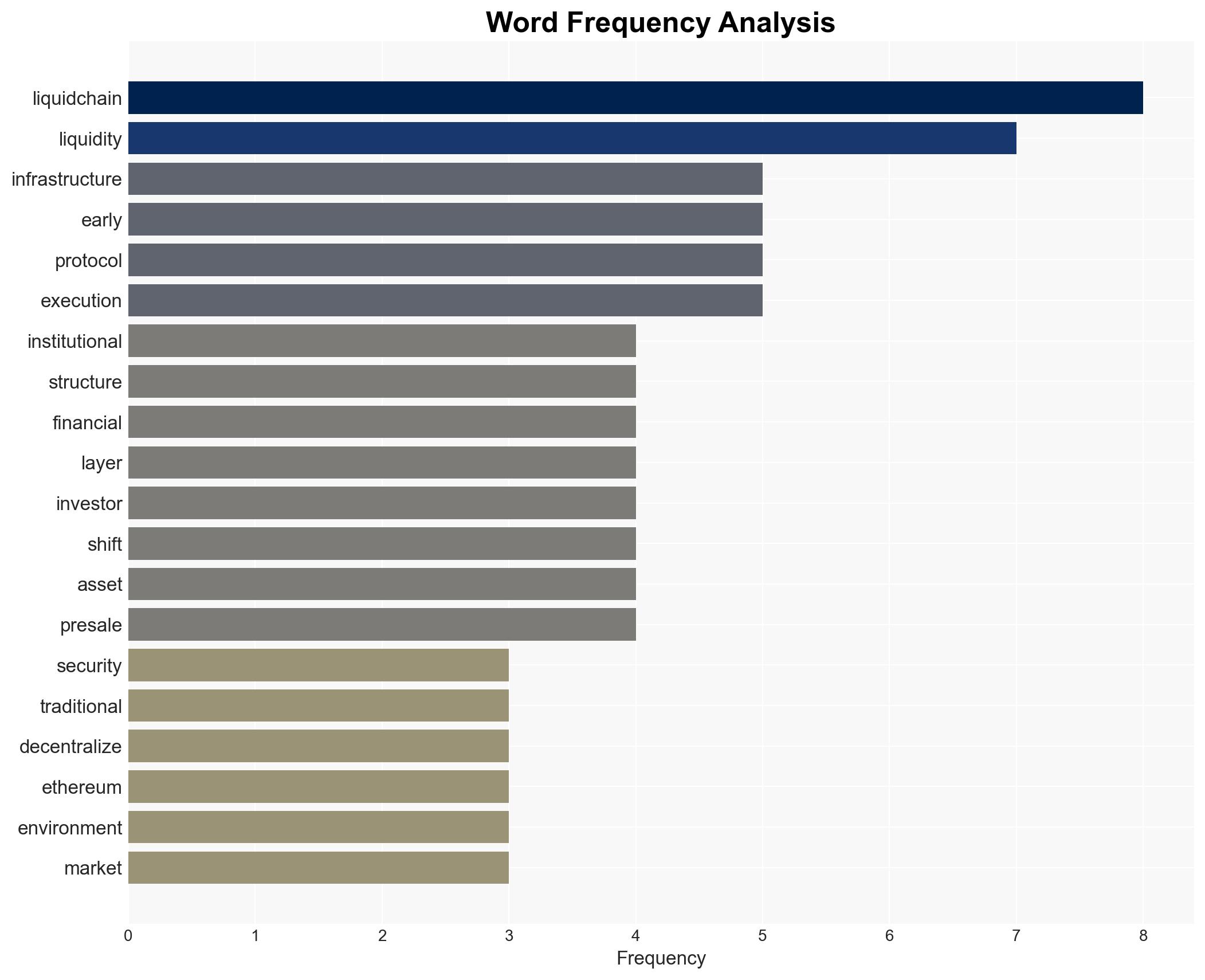
national security threats, institutional security, decentralized finance, kidnapping, public trust, financial systems, cyber security, judicial safety
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us