SlowMist alerts to supply chain poisoning risks from malicious plugins targeting OpenClaw AI hub
Published on: 2026-02-09
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: OpenClaw AI hub faces wave of poisoned plugins SlowMist warns
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
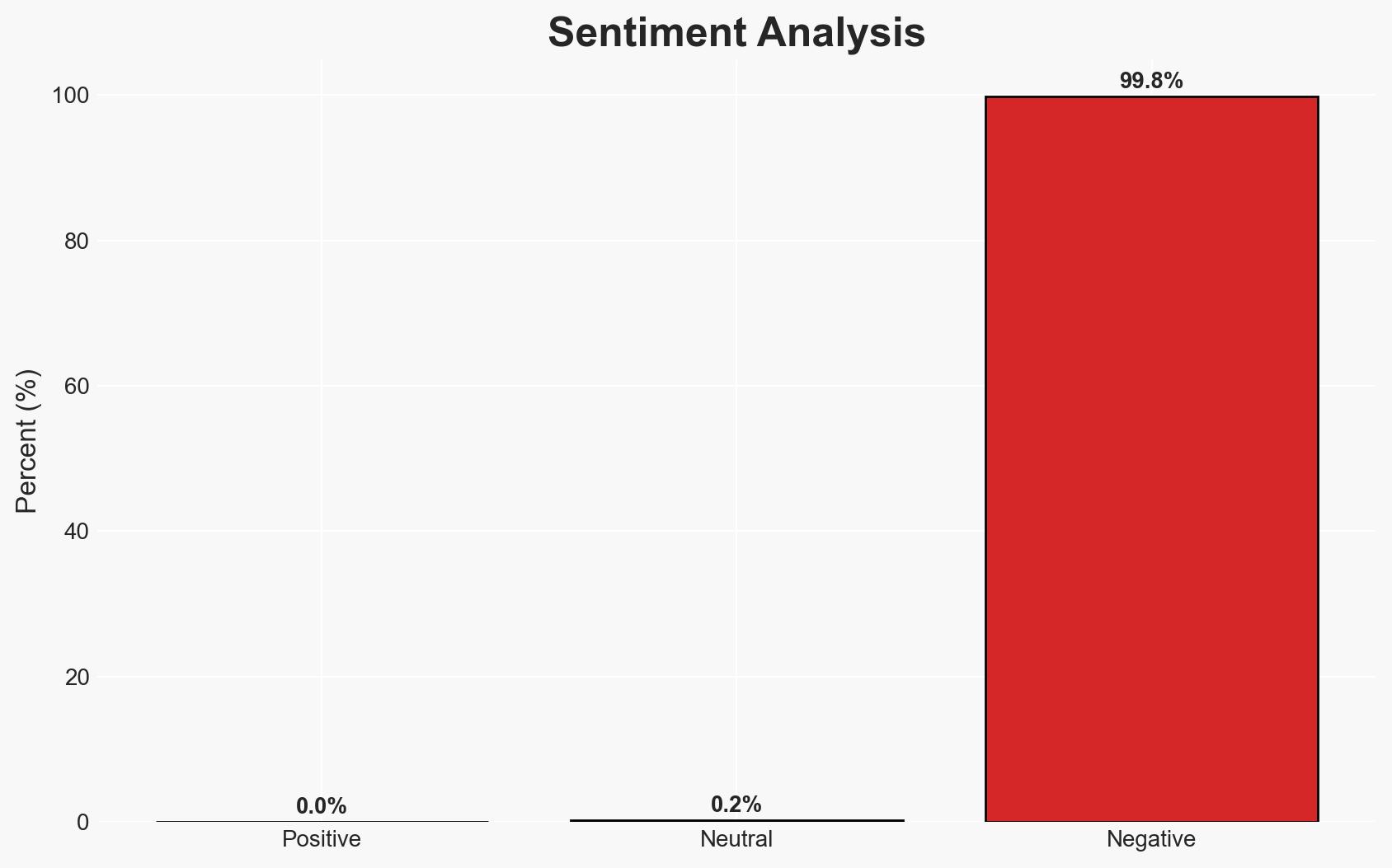
The OpenClaw AI project’s plugin hub, ClawHub, is experiencing a significant supply chain poisoning attack, with over 470 malicious plugins identified. This attack is likely orchestrated by an organized group exploiting weak review mechanisms. The threat primarily affects users of OpenClaw, potentially leading to data theft and extortion. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to limited information on the attackers’ full capabilities and intentions.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The attack is a coordinated effort by a sophisticated cybercriminal group aiming to exploit vulnerabilities in OpenClaw’s plugin ecosystem for financial gain. This is supported by the use of consistent domains/IPs and advanced techniques like Trojan horse tactics. However, the exact identity and broader objectives of the group remain uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The attack could be the work of multiple independent actors using similar methods and infrastructure, possibly due to shared tools or frameworks. This hypothesis is less supported due to the observed coordination and uniformity in attack patterns.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported, given the evidence of coordinated infrastructure and tactics. Indicators that could shift this judgment include new intelligence on the attackers’ identity or changes in attack patterns.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The attackers have a financial motive; OpenClaw’s security mechanisms are insufficient; the identified IPs/domains are controlled by a single entity.
- Information Gaps: Lack of detailed information on the attackers’ identity and broader strategic goals; insufficient data on the full scope of affected users.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in attributing attacks to a single group without conclusive evidence; risk of deception by attackers using false flags to mislead attribution efforts.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased scrutiny of open-source AI projects and their security practices. It may also prompt broader discussions on supply chain security in software development.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regulatory pressure on AI and software supply chains.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened awareness and potential for similar attacks on other platforms.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased focus on securing software supply chains and improving review mechanisms.
- Economic / Social: Potential loss of trust in open-source platforms, impacting their adoption and development.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of ClawHub and similar platforms; implement stricter review mechanisms for plugins; increase user awareness of potential threats.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms for threat intelligence sharing; invest in security infrastructure improvements; conduct regular security audits.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid mitigation of vulnerabilities and restoration of user trust, triggered by effective security measures.
- Worst: Widespread exploitation leading to significant data breaches and financial losses, triggered by failure to address security gaps.
- Most-Likely: Gradual improvement in security posture with ongoing challenges, triggered by incremental enhancements and continued vigilance.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, supply chain attack, open-source software, AI security, plugin vulnerabilities, data theft, cybercrime
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us