South Korea urges China to mediate a halt to North Korea’s nuclear activities during presidential visit
Published on: 2026-01-07
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Seoul calls for freeze of Norths nuclear programme Chinese mediation
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
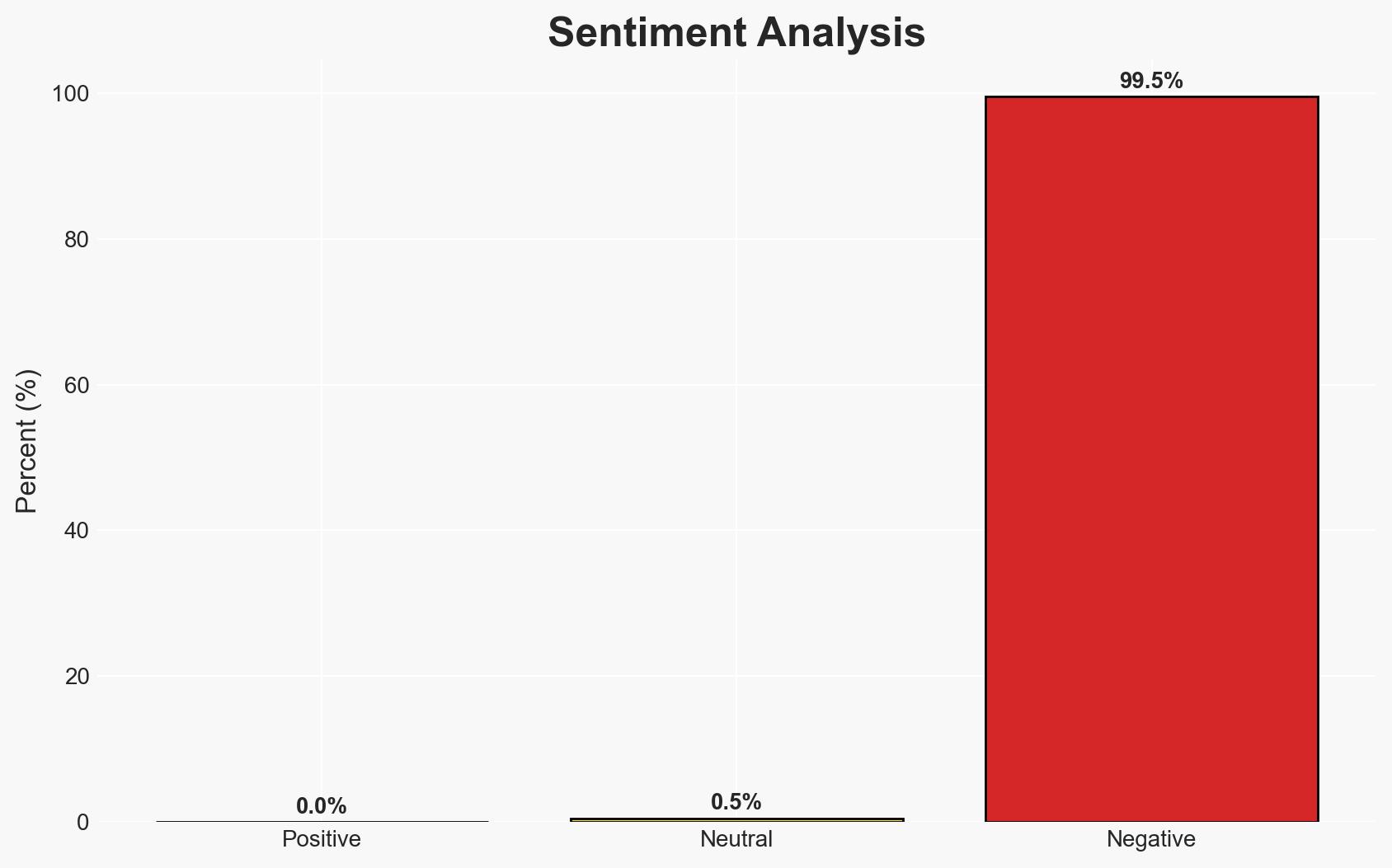
South Korea is seeking Chinese mediation to freeze North Korea’s nuclear program, proposing a halt in nuclear activities in exchange for compensation. This initiative reflects Seoul’s strategic pivot towards diplomatic engagement amidst regional tensions. The most likely hypothesis is that China will play a mediating role, albeit cautiously, given its geopolitical interests. Overall confidence in this judgment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: China will actively mediate between South Korea and North Korea, leveraging its influence to facilitate a freeze in North Korea’s nuclear activities. This is supported by South Korea’s request and China’s historical role in regional diplomacy. However, China’s strategic interests in maintaining North Korea as a buffer state introduce uncertainties.
- Hypothesis B: China will maintain a passive stance, offering limited mediation to avoid straining its relations with North Korea. This is supported by China’s cautious diplomatic approach and its emphasis on patience. Contradictory evidence includes South Korea’s active engagement with China and the potential for regional instability affecting China’s interests.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to South Korea’s direct request and China’s past involvement in Korean Peninsula issues. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in China’s diplomatic rhetoric or actions, and North Korea’s response to diplomatic overtures.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: South Korea’s proposal is genuine and not a strategic ploy; China is willing to risk its relationship with North Korea for regional stability; North Korea is open to negotiation under Chinese mediation.
- Information Gaps: North Korea’s internal decision-making processes and its response to the proposal; China’s internal deliberations on its role as a mediator.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias from South Korean sources aiming to portray diplomatic progress; possible North Korean deception in negotiations to buy time for further nuclear development.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to a temporary de-escalation of tensions on the Korean Peninsula, but risks remain if negotiations stall or fail. The interplay between diplomatic efforts and military posturing will be crucial.
- Political / Geopolitical: Successful mediation could enhance China’s regional influence and alter the power dynamics in Northeast Asia.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: A freeze in nuclear activities may reduce immediate military threats but does not eliminate long-term security concerns.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased cyber espionage activities as parties seek intelligence on negotiation positions.
- Economic / Social: Economic incentives or sanctions relief could impact regional economies, particularly if linked to broader trade agreements.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor diplomatic communications between China, South Korea, and North Korea; assess North Korea’s military activities for compliance with proposed freeze.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for potential diplomatic setbacks; strengthen alliances with regional partners to support diplomatic efforts.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Successful freeze and gradual denuclearization; Worst: Breakdown in talks leading to increased tensions; Most-Likely: Partial freeze with ongoing diplomatic engagement. Triggers include changes in North Korean military posture and China’s diplomatic initiatives.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
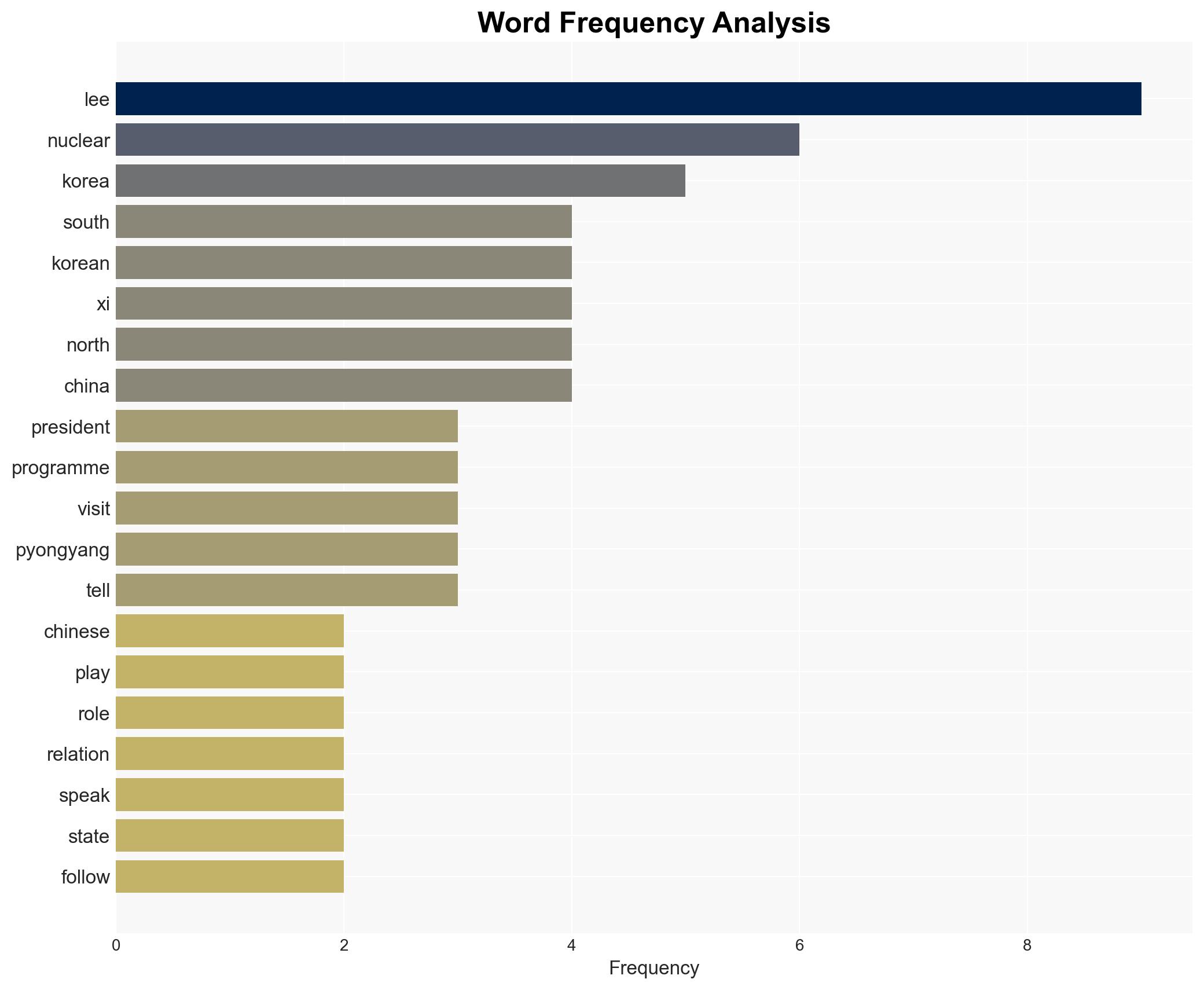
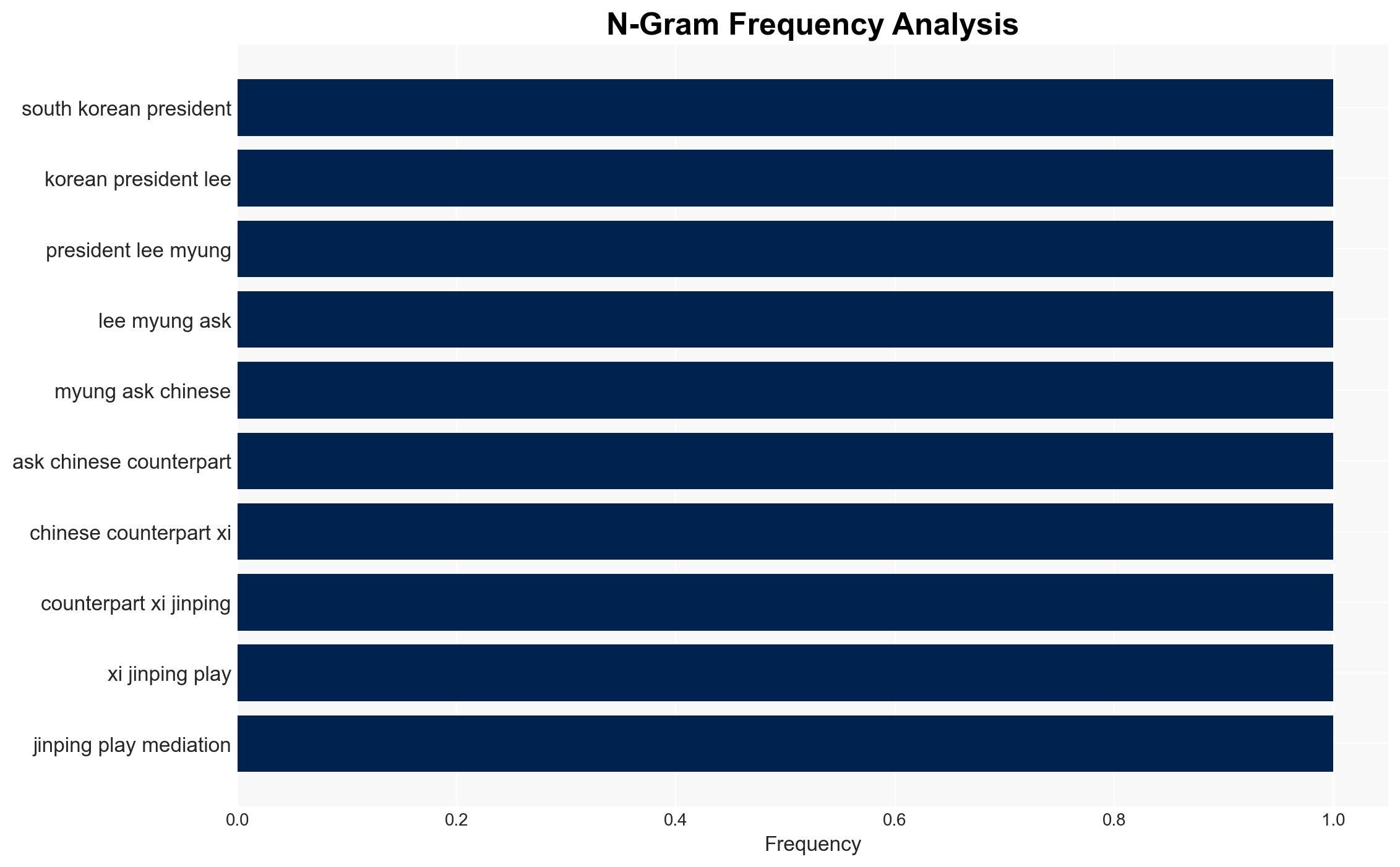
- Lee Jae Myung, South Korean President
- Xi Jinping, Chinese President
- Kim Jong Un, North Korean Leader
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
regional conflicts, diplomacy, nuclear non-proliferation, regional stability, China-South Korea relations, North Korea, mediation, geopolitical strategy
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us