Strategic Rivalry Between Saudi Arabia and UAE in Yemen: Consequences for India
Published on: 2026-01-02
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Saudi-UAE contest for the empty quarter Implications for India
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
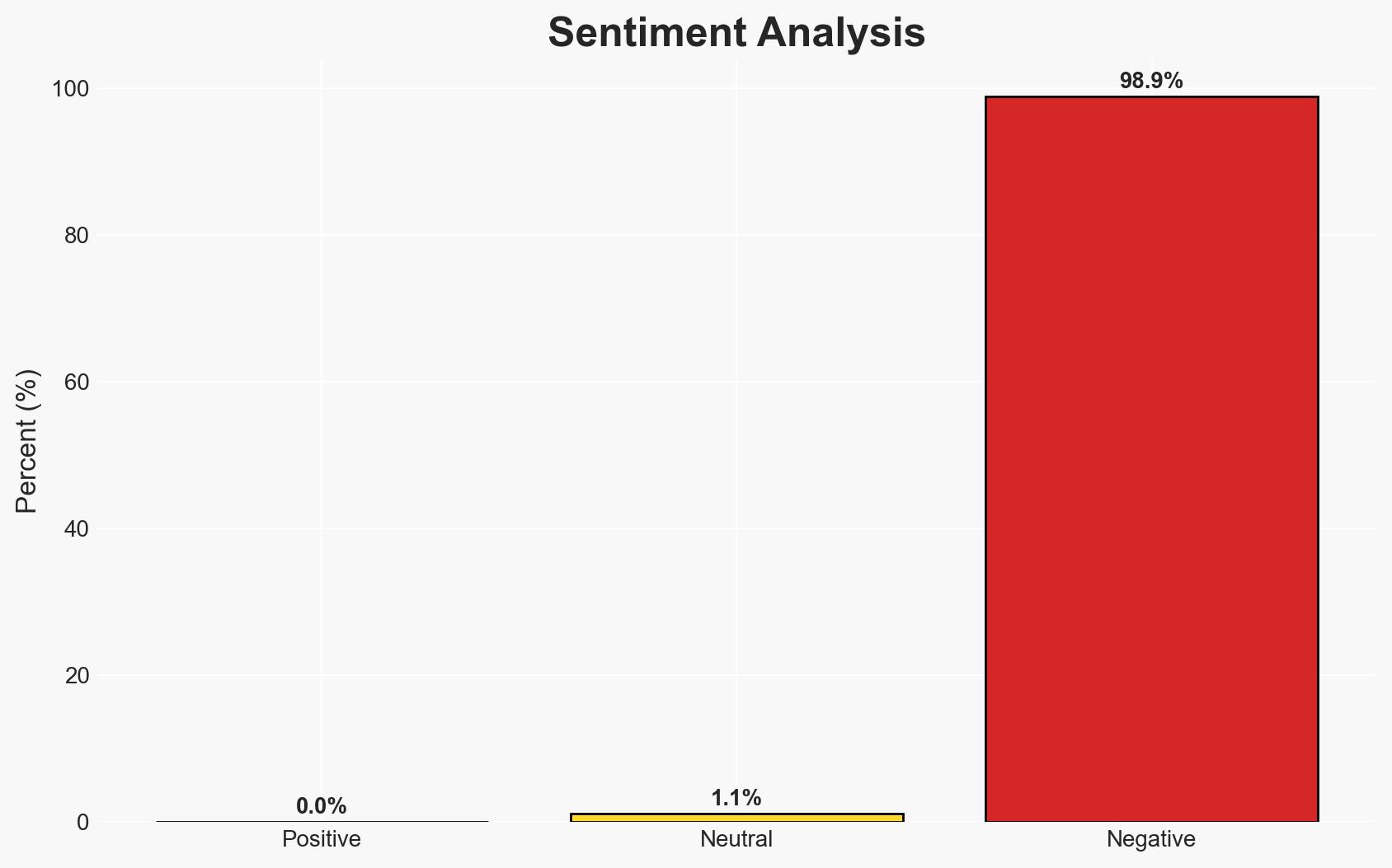
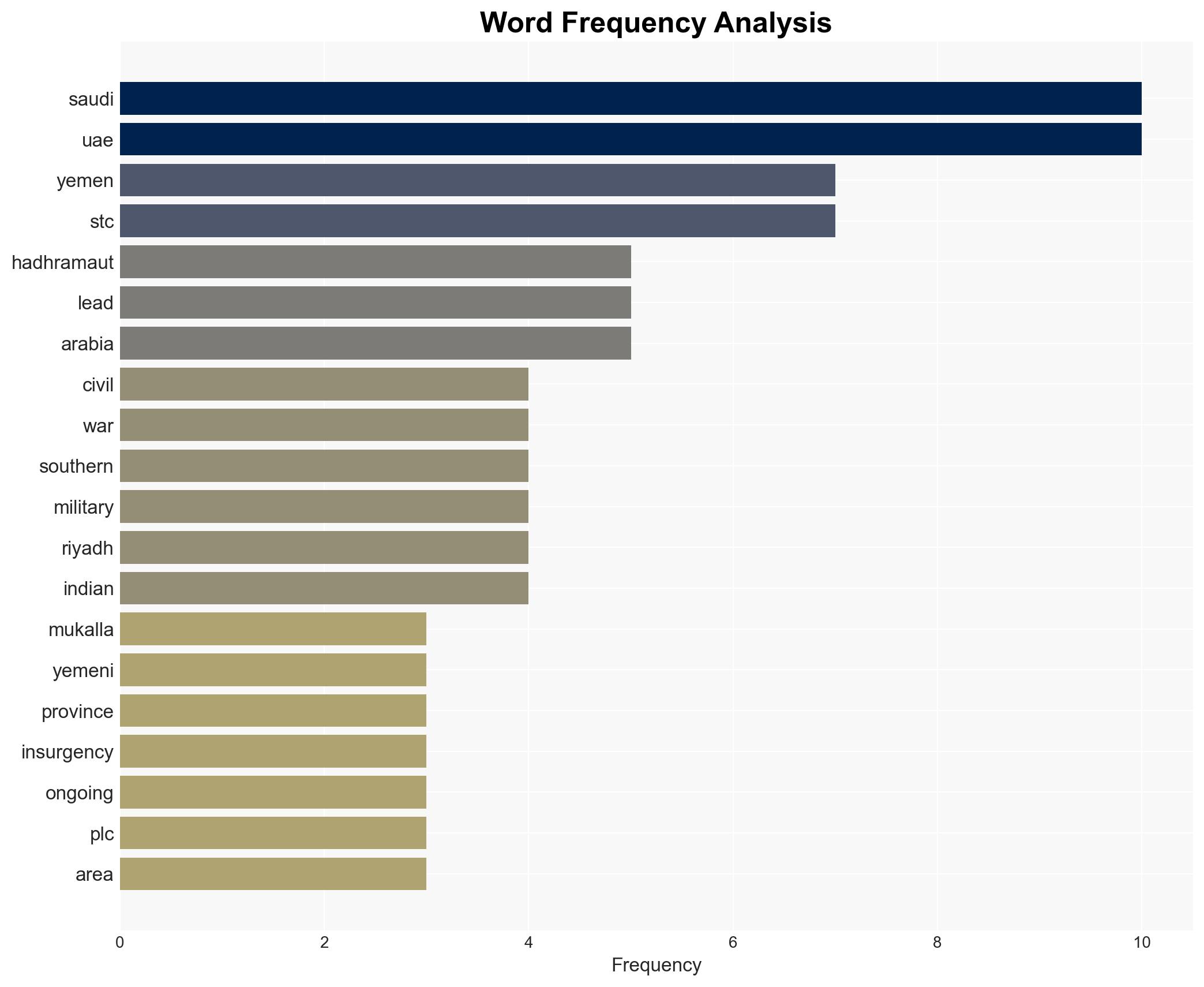
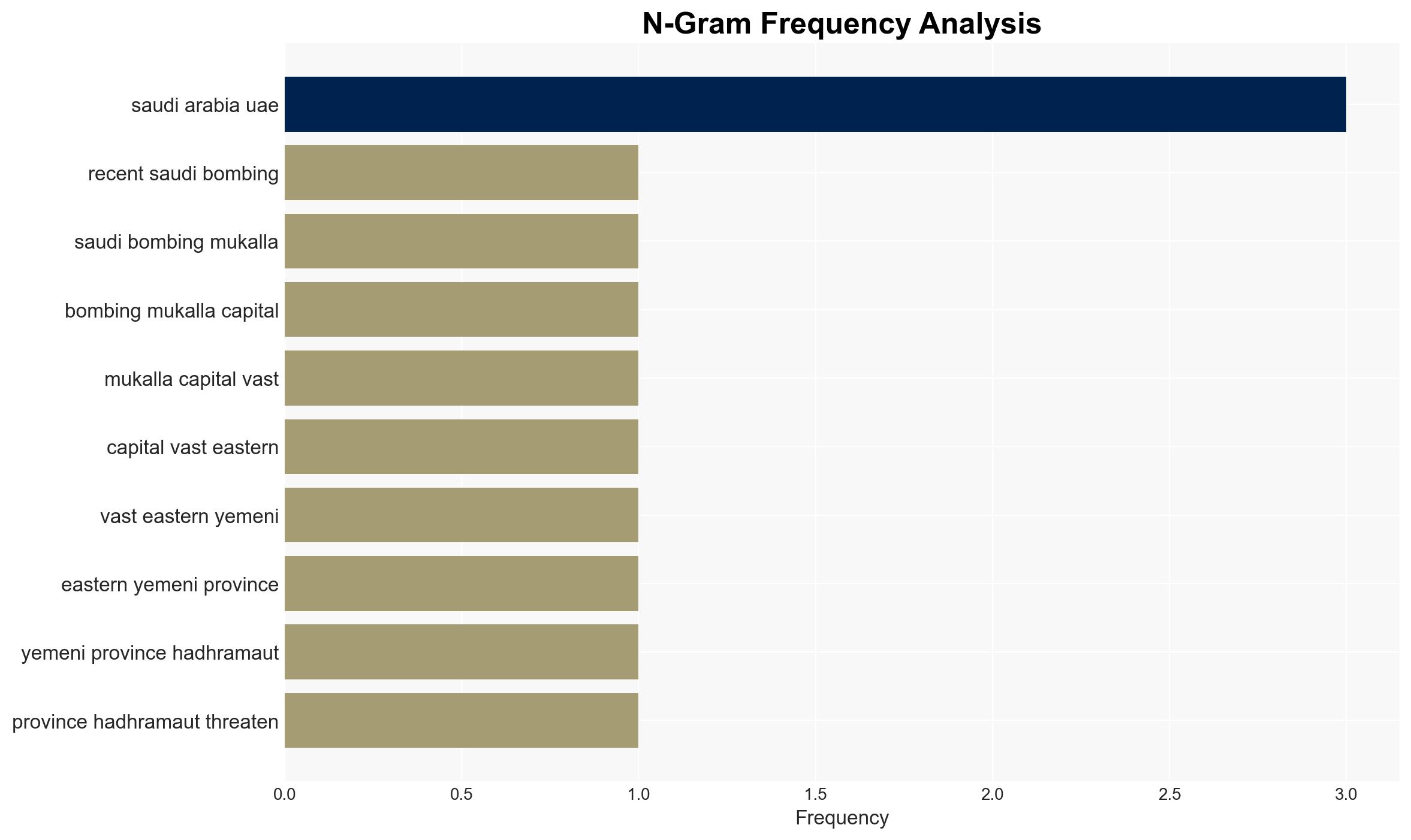
The Saudi-UAE tensions in Yemen, particularly the recent Saudi bombings in Mukalla, highlight a significant geopolitical rift that could destabilize the region further. The most likely hypothesis is that Saudi Arabia aims to assert control over strategic areas in Yemen to secure future energy export routes, with moderate confidence. This development affects regional stability and global shipping routes, with potential implications for India’s energy security and trade.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Saudi Arabia’s actions are primarily driven by a strategic need to secure energy export routes through Yemen, bypassing traditional choke points. This is supported by Saudi plans to export gas from new fields and the strategic importance of the Hadhramaut coast. However, the extent of Saudi commitment to this strategy remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The Saudi bombings are a reaction to UAE’s support for the STC, perceived as a threat to Saudi influence in Yemen. The UAE’s alleged military support to STC and the public clash between Saudi and UAE forces support this hypothesis. Contradictory UAE claims about the military hardware’s purpose introduce uncertainty.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the strategic significance of energy export routes and Saudi Arabia’s historical interest in securing such pathways. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in Saudi or UAE military deployments or diplomatic engagements in Yemen.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Saudi Arabia prioritizes securing energy routes; UAE continues to support STC; STC remains a significant force in southern Yemen; regional powers avoid direct military confrontation.
- Information Gaps: Detailed intentions of Saudi and UAE leadership regarding Yemen; the full scope of military capabilities and deployments in the region; the extent of STC’s control and influence.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential source bias from regional media; strategic misinformation by involved parties to obscure true intentions; cognitive bias towards assuming rational state behavior.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The Saudi-UAE contest in Yemen could exacerbate regional instability and impact global shipping routes, with broader implications for energy markets and geopolitical alignments.
- Political / Geopolitical: Escalation could lead to broader regional conflicts, affecting alliances and power balances in the Middle East.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased instability may provide opportunities for extremist groups to expand operations in Yemen and beyond.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased cyber operations targeting critical infrastructure or information campaigns to influence regional narratives.
- Economic / Social: Disruptions in shipping routes could affect global trade, particularly energy supplies, impacting economies reliant on stable oil and gas imports.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of military movements and diplomatic communications; engage with regional partners to de-escalate tensions; prepare contingency plans for potential disruptions in shipping routes.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen regional partnerships to support stability; invest in alternative energy sources to mitigate dependency risks; develop capabilities to counter potential cyber threats.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Diplomatic resolution leads to stabilization, with energy routes secured peacefully.
- Worst: Escalation into broader conflict disrupts global energy supplies and regional stability.
- Most-Likely: Protracted tensions with intermittent clashes and continued geopolitical maneuvering.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Saudi Arabian leadership
- UAE leadership
- Southern Transitional Council (STC)
- Yemeni Presidential Leadership Council (PLC)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
regional conflicts, geopolitical tensions, energy security, regional stability, military conflict, shipping routes, Middle East politics, Yemen conflict
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us