Strategies for CISOs to Mitigate the Risks of Business Email Compromise Attacks
Published on: 2026-02-13
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: CISO’s guide How to prevent business email compromise
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
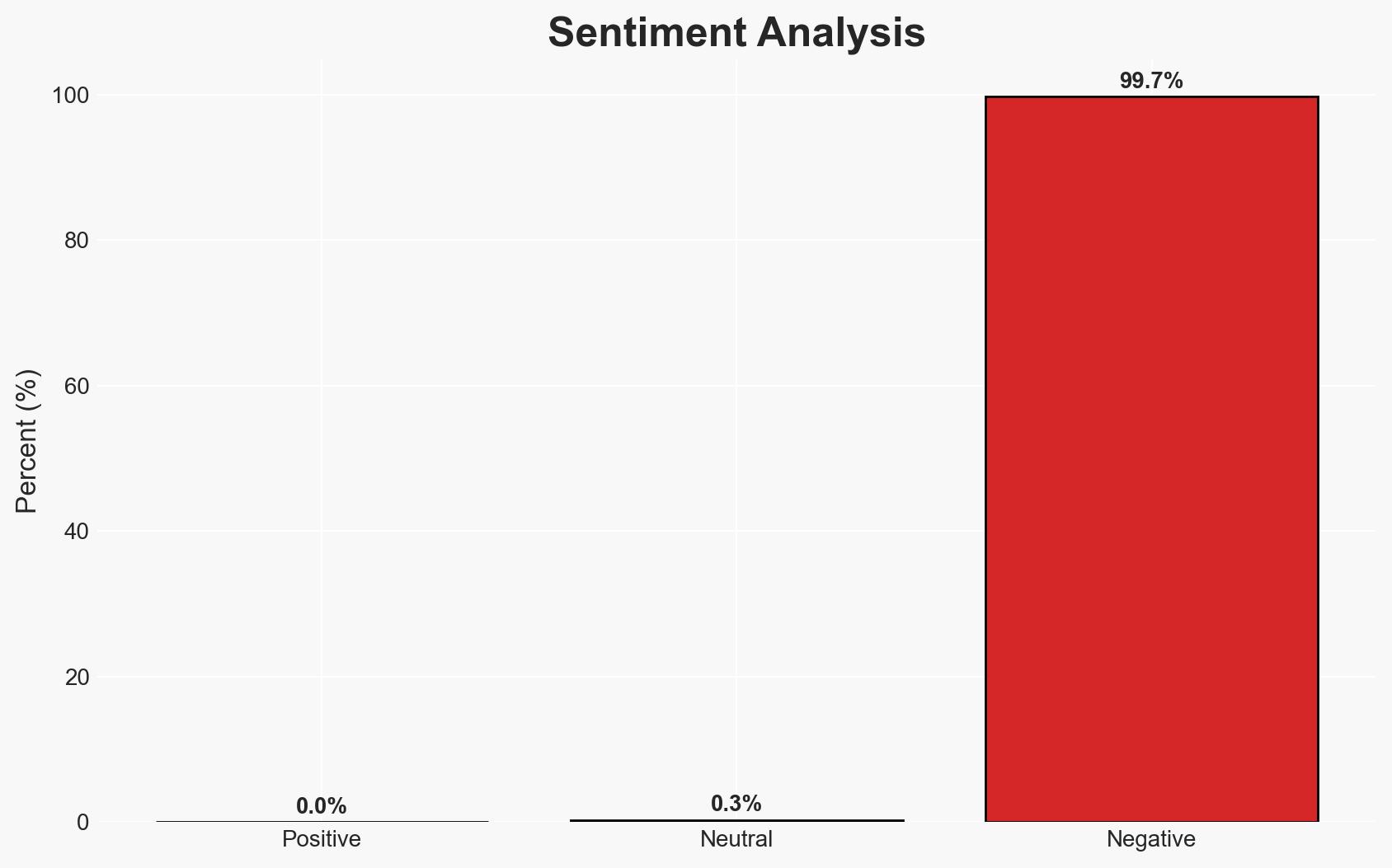
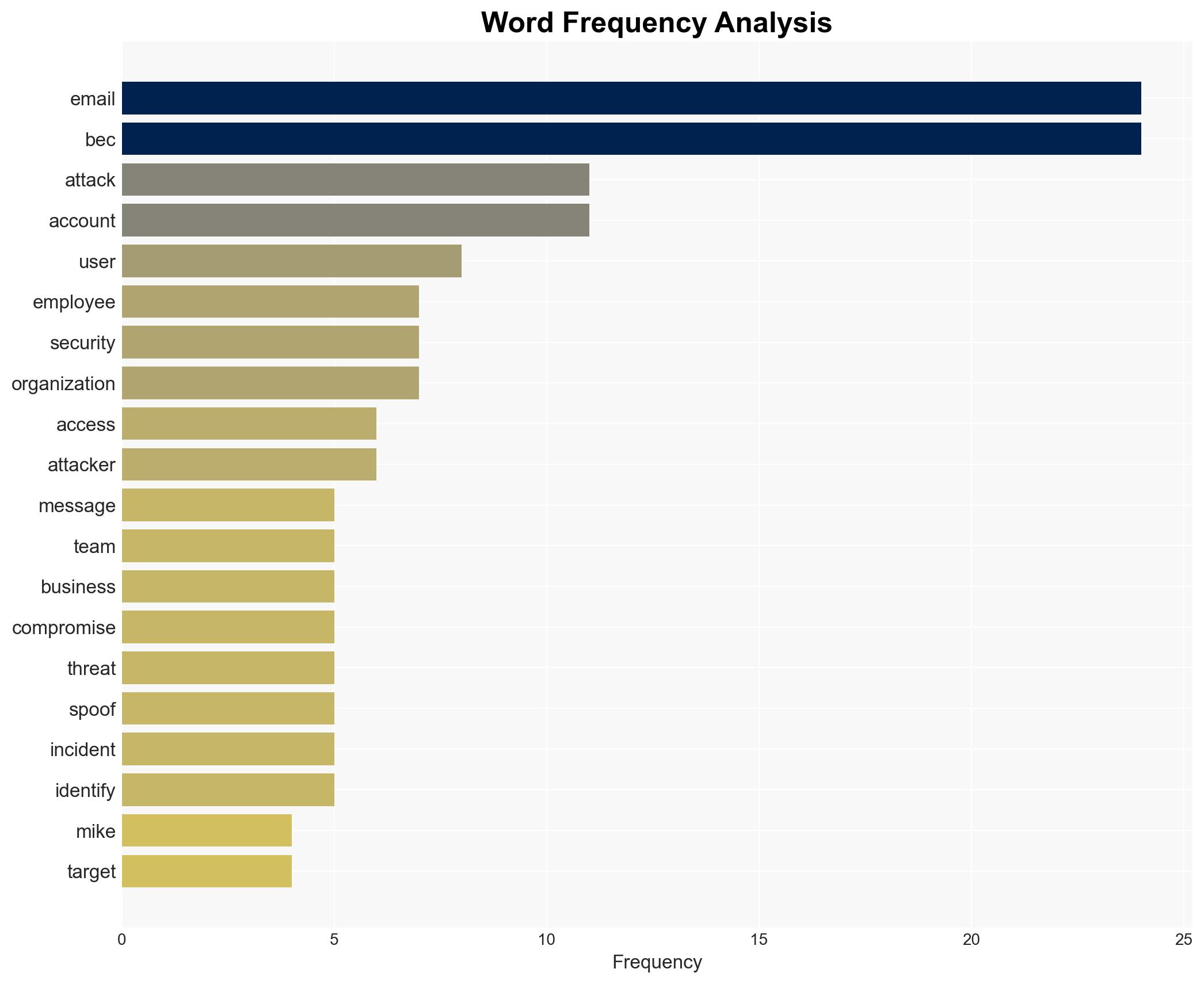
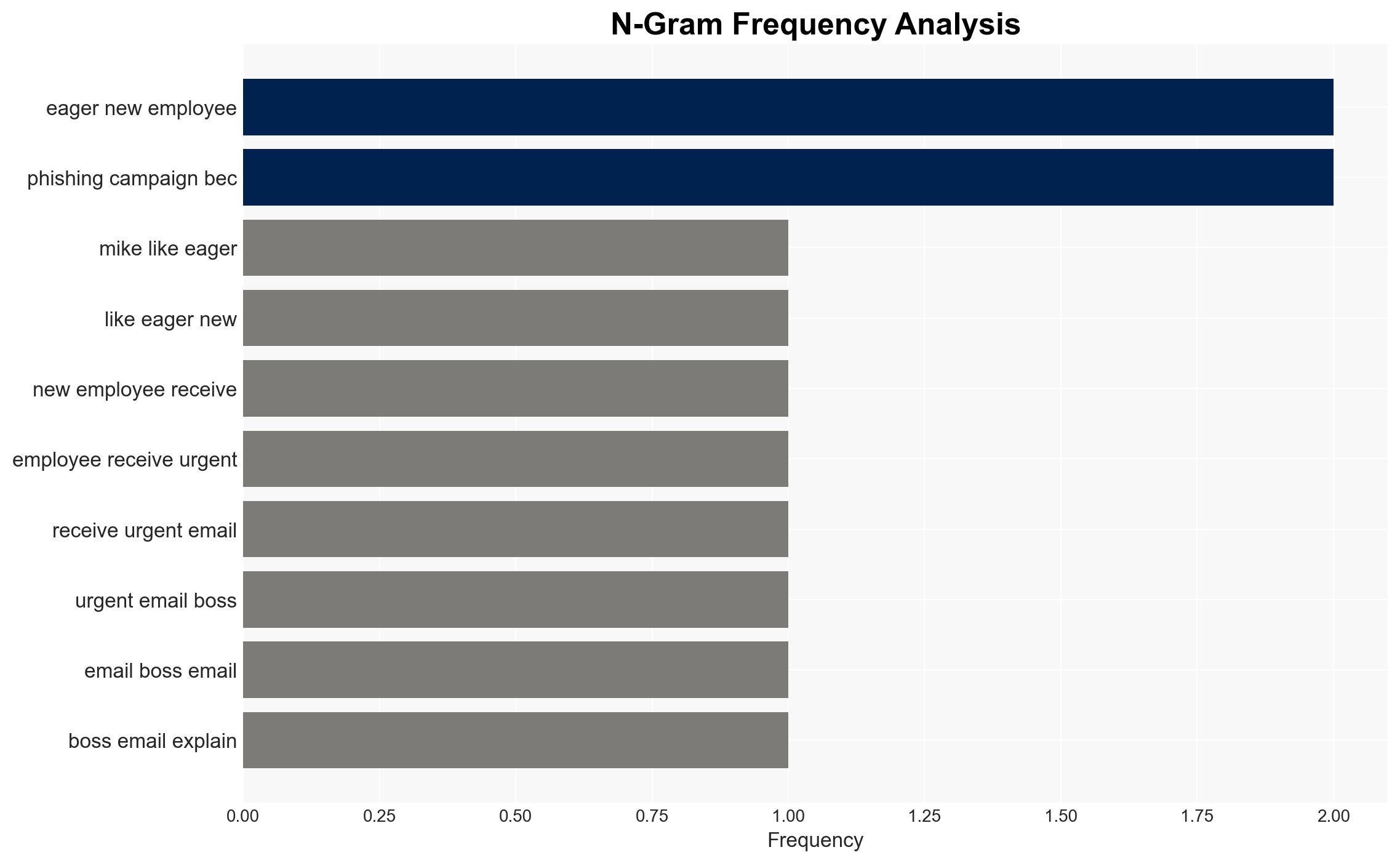
Business Email Compromise (BEC) represents a significant cyber threat due to its targeted nature and exploitation of workplace norms. The most likely hypothesis is that BEC will continue to grow in prevalence and sophistication, affecting organizations globally, with moderate confidence. This threat impacts financial stability and operational integrity across sectors.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: BEC attacks will increase in frequency and sophistication as cybercriminals refine their techniques. This is supported by the current trend of increasing incidents and financial losses. Key uncertainties include the effectiveness of new security measures and potential regulatory changes.
- Hypothesis B: BEC attacks will plateau or decrease due to improved organizational defenses and awareness. This hypothesis is less supported due to the persistent financial incentives for attackers and the adaptability of their methods.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the ongoing increase in reported incidents and financial losses. Indicators such as the development of advanced detection technologies or significant regulatory interventions could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: BEC attacks rely on exploiting human psychology and workplace hierarchies; financial incentives drive attackers; current security measures are insufficient.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the effectiveness of specific security measures against BEC; comprehensive statistics on unreported BEC incidents.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential underreporting of incidents due to reputational concerns; cognitive bias towards overestimating the effectiveness of current security protocols.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The evolution of BEC attacks could lead to increased financial losses and operational disruptions, affecting trust in digital communications and corporate governance.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased international regulatory collaboration to combat BEC.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced focus on cybersecurity measures within national security frameworks.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased demand for advanced cybersecurity solutions and training.
- Economic / Social: Potential destabilization of affected businesses and loss of consumer trust in digital transactions.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Implement employee training programs on BEC awareness; enhance email filtering and authentication protocols.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms; invest in advanced threat detection technologies.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Significant reduction in BEC incidents due to improved defenses. Worst: Continued rise in incidents with substantial financial impacts. Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in defenses with ongoing BEC challenges.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, business email compromise, financial fraud, cybercrime, organizational security, digital communication, social engineering
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us