Strategies for Enhancing Ransomware Resilience in AI Data Pipelines for Today’s Enterprises
Published on: 2026-01-05
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: How To Build Ransomware-Resilient AI Data Pipelines A Practical Guide for Modern Enterprises
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
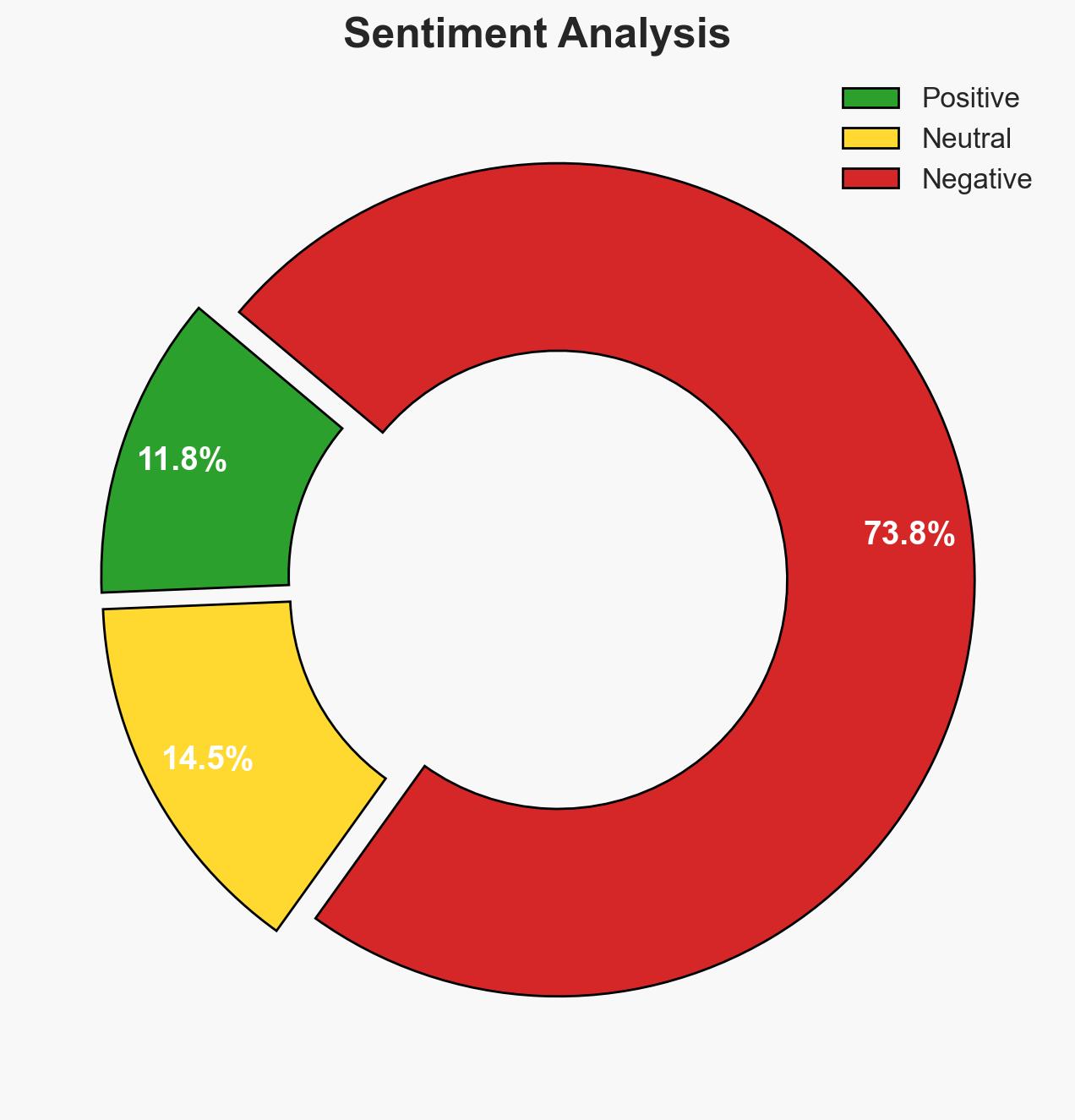
The integration of AI data pipelines in modern enterprises increases vulnerability to ransomware attacks, necessitating enhanced resilience strategies. The most likely hypothesis is that ransomware groups will increasingly target AI environments due to their high value and complexity. This affects enterprises globally, with moderate confidence in this assessment.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Ransomware groups will prioritize AI data pipelines due to their high value and the complexity of AI systems, which offer multiple points of entry and potential for widespread disruption. Supporting evidence includes the attractiveness of AI environments and the evolving sophistication of cyber threats. Key uncertainties involve the rate of adoption of protective measures by enterprises.
- Hypothesis B: Ransomware groups will not significantly shift focus to AI data pipelines, as traditional targets still offer easier access and similar financial gains. Contradicting evidence includes the continued prevalence of ransomware attacks on non-AI systems. However, the increasing integration of AI in business processes suggests a gradual shift.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the increasing integration of AI systems and their inherent vulnerabilities. Indicators that could shift this judgment include a significant increase in successful attacks on AI systems or a rapid improvement in AI security measures.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Enterprises will continue to integrate AI into critical operations; ransomware groups will adapt to target high-value systems; AI environments will remain complex and challenging to secure.
- Information Gaps: Specific data on the frequency and success rate of ransomware attacks on AI systems; effectiveness of current AI security measures.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting from cybersecurity firms with vested interests; deceptive practices by ransomware groups to obscure true targets.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The targeting of AI data pipelines by ransomware groups could lead to significant disruptions in enterprise operations and broader economic impacts. This development may evolve with increasing sophistication of attacks and defensive measures.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for international tensions if state-sponsored groups are implicated in attacks.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased demand for cybersecurity resources and potential for collaboration between law enforcement and private sector.
- Cyber / Information Space: Escalation in cyber warfare tactics and countermeasures; potential for misinformation campaigns leveraging AI vulnerabilities.
- Economic / Social: Disruptions in business operations could lead to economic instability and affect consumer trust in digital systems.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of AI systems for unusual activity; conduct security audits of AI data pipelines; increase awareness and training for employees on ransomware threats.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms; invest in AI-specific security technologies; establish incident response protocols tailored to AI environments.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Enterprises successfully implement robust security measures, reducing ransomware incidents.
- Worst: Significant ransomware attacks on AI systems cause widespread operational disruptions.
- Most-Likely: Gradual increase in ransomware targeting AI, with mixed success due to varying security postures.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
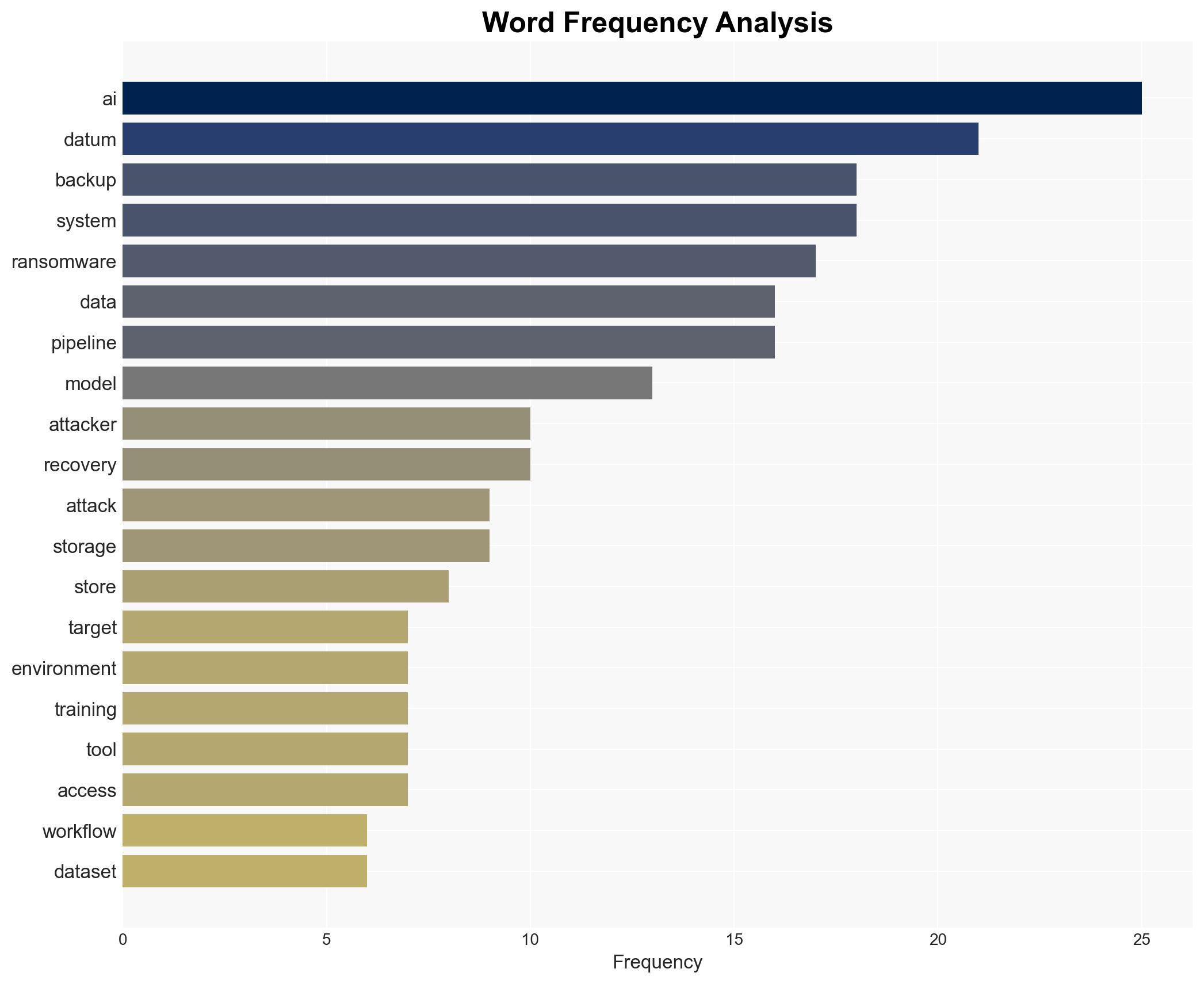
cybersecurity, ransomware, AI systems, enterprise risk, data protection, cyber threats, digital resilience
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model hostile behavior to identify vulnerabilities.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us