Surge in Android Threats in 2025: Mobile Devices Become Primary Targets for Cyber Attacks
Published on: 2025-12-16
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Android threats in 2025 When your phone becomes the main attack surface
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
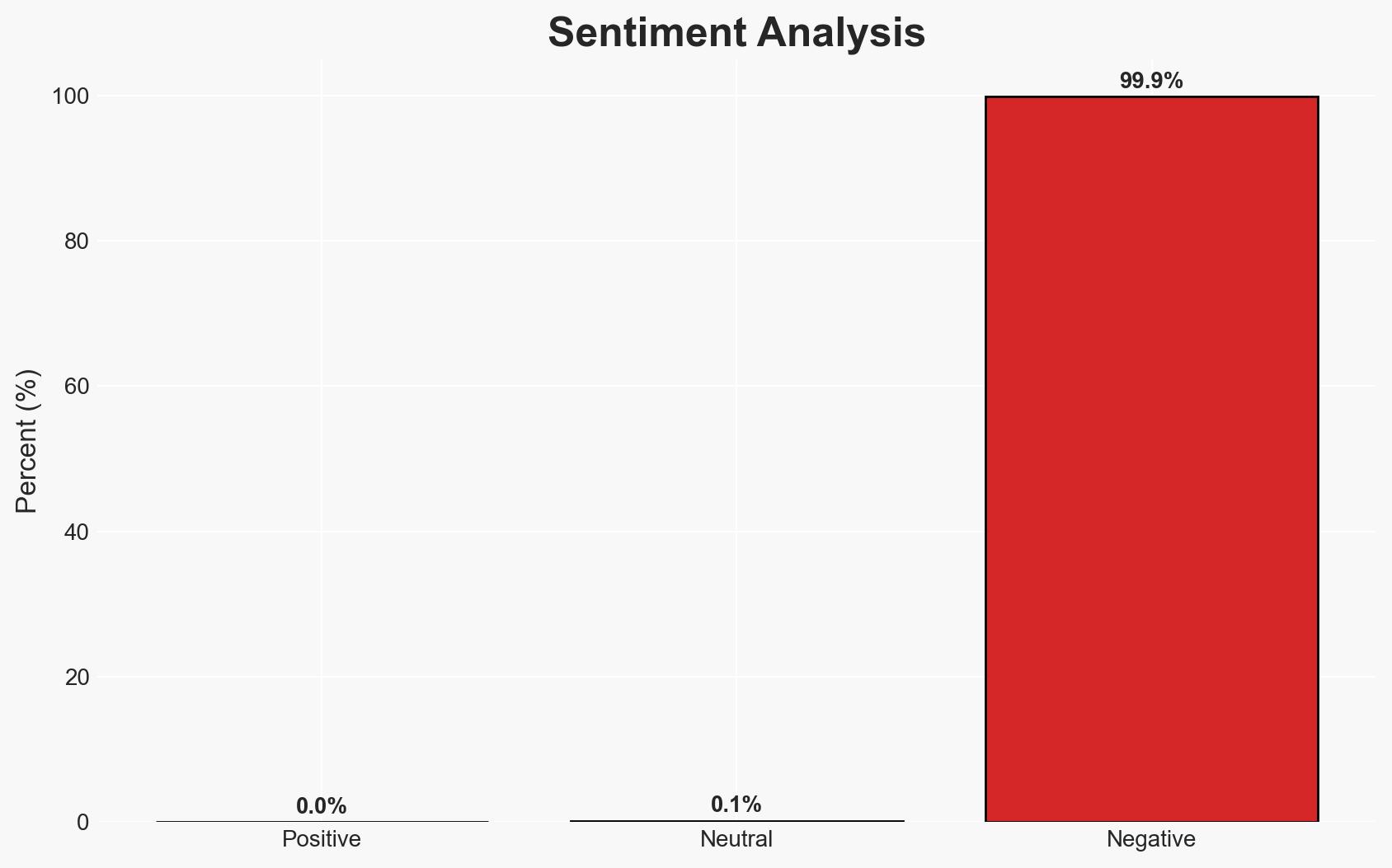
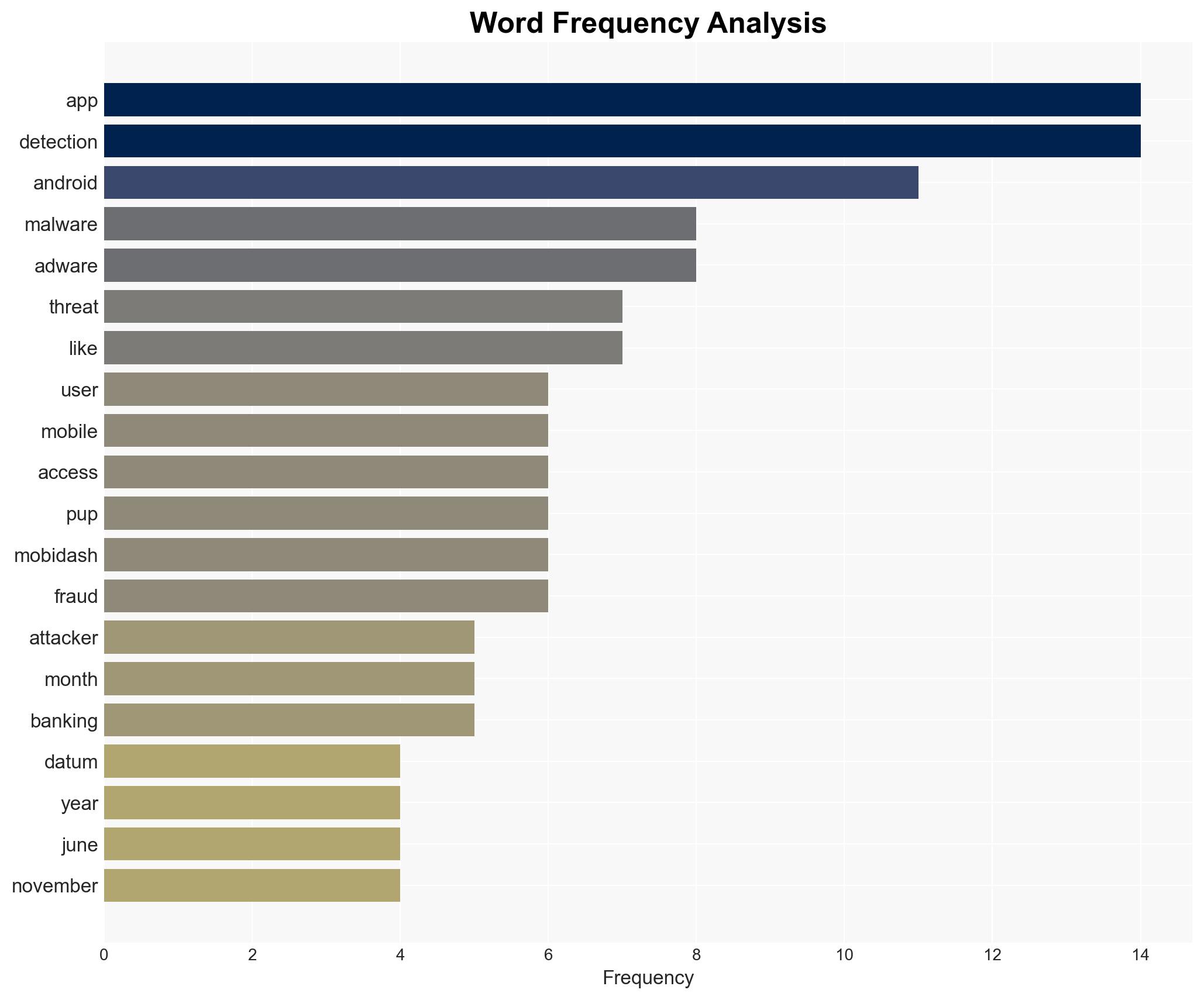
In 2025, Android devices became a primary target for cybercriminals, with significant increases in malware, potentially unwanted programs (PUPs), and adware. The shift towards sophisticated, coordinated attack frameworks marks a pivotal change in the threat landscape. This development poses a substantial risk to individual users and organizations reliant on Android platforms. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to data limitations and potential reporting biases.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The increase in Android threats is primarily driven by the maturation of cybercriminal business models focusing on mobile platforms. Evidence includes the sharp rise in malware and PUP detections, and the integration of advanced capabilities like one-time passcode theft. Key uncertainties include the extent of law enforcement and security industry countermeasures.
- Hypothesis B: The observed increase in threats is largely due to improved detection capabilities and reporting practices rather than an actual rise in malicious activity. Supporting evidence includes the consistent presence of threats like MobiDash and the potential for detection biases. Contradicting evidence is the significant uptick in specific threat categories, suggesting genuine growth in threat activity.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the alignment of threat increases with known trends in cybercriminal strategies and the deployment of new attack techniques. Indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in detection methodologies or significant law enforcement actions.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Cybercriminals will continue to prioritize mobile platforms; detection data accurately reflects threat levels; threat actors are increasingly sophisticated.
- Information Gaps: Detailed attribution of threat actors; comprehensive impact assessments on specific sectors; effectiveness of countermeasures.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in data collection favoring high-profile threats; deception by threat actors using false flag operations.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The evolution of Android threats could lead to increased vulnerabilities across sectors reliant on mobile technology, affecting both personal and organizational security. This trend may accelerate the adoption of enhanced security measures and regulatory responses.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased international cooperation on cybercrime; risk of state-sponsored exploitation of vulnerabilities.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced threat environment for mobile-dependent operations; potential for exploitation by terrorist groups.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased demand for cybersecurity solutions; potential for misinformation campaigns leveraging mobile platforms.
- Economic / Social: Economic impact on sectors reliant on mobile technology; potential erosion of trust in digital services.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of Android threat vectors; increase public awareness campaigns; strengthen incident response capabilities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with tech companies for threat intelligence sharing; invest in cybersecurity training and resources; advocate for stronger regulatory frameworks.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Effective countermeasures reduce threat levels; triggers include successful international cooperation.
- Worst: Threats continue to grow unchecked; triggers include lack of regulatory response and technological adaptation.
- Most-Likely: Gradual improvement in threat management; triggers include incremental advancements in detection and response technologies.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Shahak Shalev, Head of AI and Scam Research at Malwarebytes
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, mobile threats, malware, Android security, cybercrime, threat intelligence, digital safety
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us