Surge in Hypervisor Ransomware Attacks Reaches 700 Percent, Driven by Akira Group
Published on: 2025-12-09
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Researchers spot 700 percent increase in hypervisor ransomware attacks
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
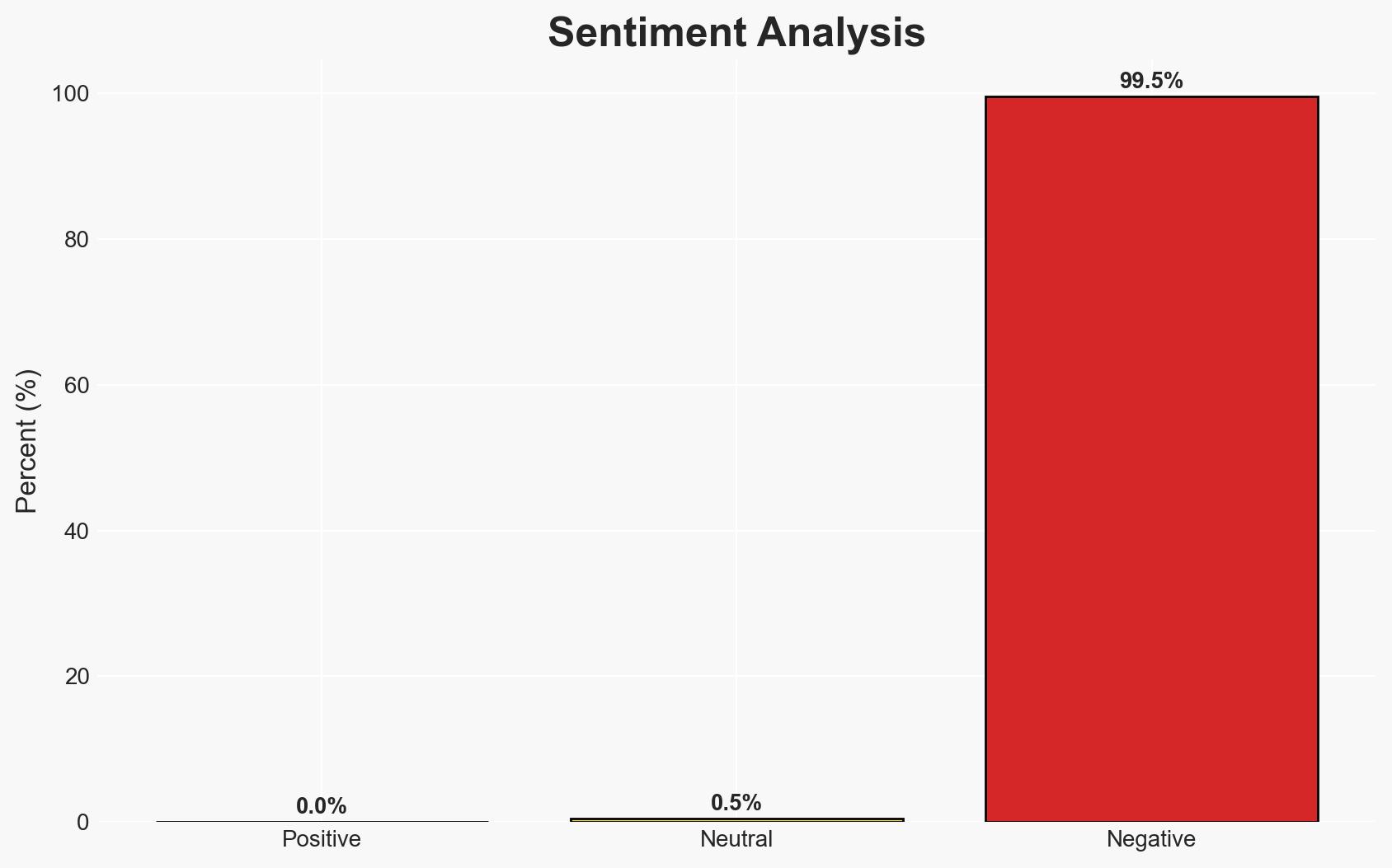
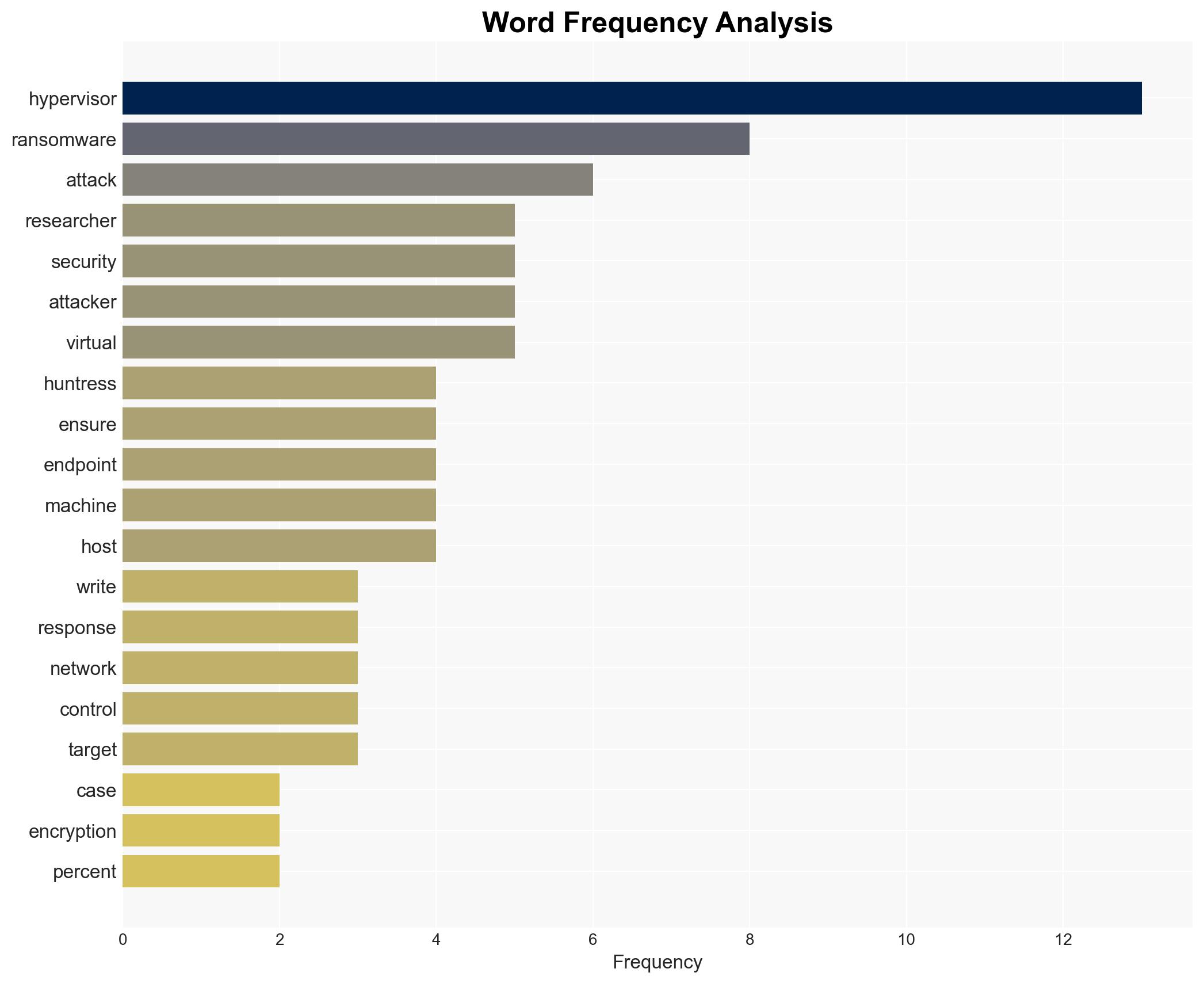
There is a significant increase in ransomware attacks targeting hypervisors, primarily driven by the Akira ransomware group. This trend poses a substantial threat to virtualized environments, potentially affecting numerous organizations reliant on virtual machines. The overall confidence level in this assessment is moderate, given the reliance on a single source and the emerging nature of the threat.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The increase in hypervisor ransomware attacks is primarily due to the Akira ransomware group exploiting vulnerabilities in hypervisor security. Supporting evidence includes the reported surge in attacks and the specific mention of Akira’s involvement. Key uncertainties include the extent of Akira’s capabilities and whether other groups are similarly active.
- Hypothesis B: The observed increase is part of a broader trend of targeting infrastructure components that lack robust security controls, not limited to the Akira group. This is supported by the mention of similar tactics used in VPN appliance attacks. Contradicting evidence includes the specific attribution to Akira, suggesting a focused campaign rather than a widespread trend.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to specific attribution to the Akira group and detailed tactics observed. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of other groups adopting similar tactics or a broader trend in targeting infrastructure components.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Hypervisors are less defended than other components, Akira group has the capability to exploit these vulnerabilities, and the reported data accurately reflects a broader trend.
- Information Gaps: Lack of comprehensive data on other groups’ activities, limited visibility into the full scope of hypervisor vulnerabilities, and absence of independent corroboration of Huntress’s findings.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias from reliance on a single source (Huntress), and the possibility of misinformation or exaggeration by threat actors to amplify perceived threat levels.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The increase in hypervisor ransomware attacks could lead to significant disruptions in virtualized environments, affecting both public and private sectors. Over time, this trend may encourage further exploitation of infrastructure components lacking robust security.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased international cooperation on cybersecurity measures, especially among countries heavily reliant on virtualized infrastructure.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment for organizations using virtual machines, necessitating enhanced security measures.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased focus on securing hypervisors and similar infrastructure components, possibly leading to new cybersecurity standards and practices.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impact due to disruptions in services reliant on virtualized environments, with possible social unrest if critical services are affected.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Organizations should review and enhance hypervisor security, implement multi-factor authentication, and ensure regular backups. Monitoring for signs of intrusion and updating security patches are critical.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for threat intelligence sharing, invest in hypervisor-specific security solutions, and conduct regular security audits of virtualized environments.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Improved security measures reduce attack success rates, leading to a decline in hypervisor-targeted ransomware.
- Worst: Continued increase in attacks causes widespread disruptions, prompting regulatory interventions.
- Most-Likely: Gradual improvement in defenses leads to a stabilization of attack rates, with ongoing vigilance required.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Anna Pham, Senior Hunt & Response Analyst, Huntress
- Ben Bernstein, Technical Account Manager, Huntress
- Dray Agha, Senior Manager for Hunt & Response, Huntress
- Akira Ransomware Group
7. Thematic Tags
Cybersecurity, ransomware, hypervisors, Akira group, virtual machines, infrastructure security, threat intelligence
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us