Survey Reveals 30% of Young Voters Support Justifying Violence, Sparking Concerns Over American Values and Ed…
Published on: 2025-11-27
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: YAF Survey 3 in 10 Young Voters Say Violence Can Be Justified Doubts Grow on US Ideals and College Degree Value
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
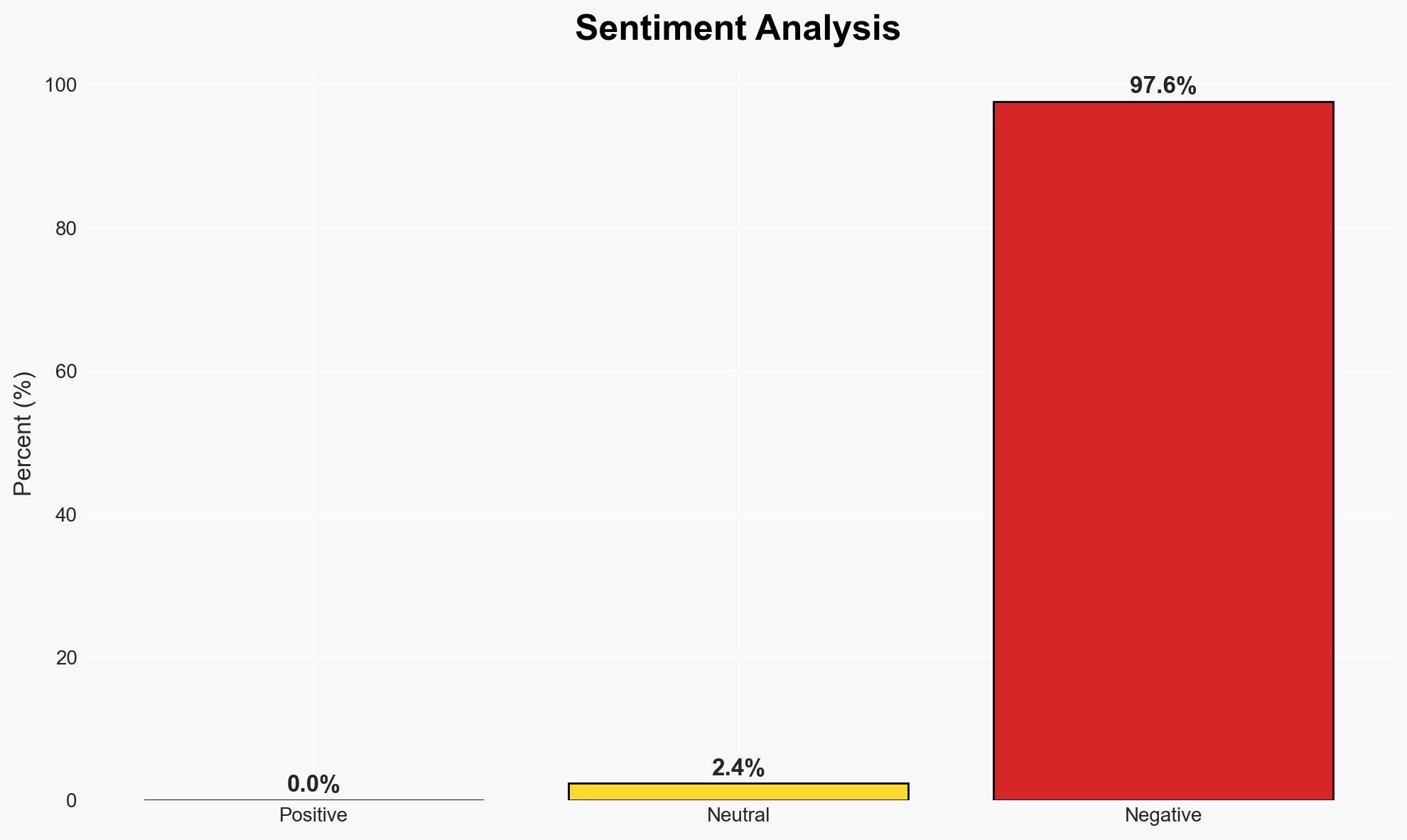
The recent YAF survey reveals significant generational skepticism among young voters regarding American foundational principles, the value of higher education, and the justification of political violence. This sentiment could influence political engagement and societal cohesion. The most likely hypothesis is that these attitudes reflect broader disillusionment with current socio-political structures. Overall confidence in this judgment is moderate, given the potential for bias in survey responses and the lack of longitudinal data.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The survey results indicate a genuine shift in values among young voters, driven by perceived failures of American ideals and economic opportunities. Supporting evidence includes the high percentage of young voters expressing skepticism about free speech and economic mobility. However, the lack of historical data to compare these attitudes over time is a key uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: The survey results are an artifact of methodological bias or temporary socio-political conditions, rather than a long-term trend. This hypothesis is supported by potential biases in survey design and the influence of current political events. Contradicting evidence includes the consistent expression of these views across different demographic groups.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the breadth of skepticism across multiple domains (political, economic, educational) and demographic groups. Indicators that could shift this judgment include longitudinal studies showing changes over time or significant shifts in political or economic conditions.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Young voters’ attitudes are reflective of broader societal trends; survey respondents accurately represent the demographic; current socio-political conditions have a significant impact on youth perspectives.
- Information Gaps: Longitudinal data on young voters’ attitudes; detailed demographic breakdowns of respondents; contextual factors influencing survey responses.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential cognitive bias in interpreting survey results; source bias from the survey’s commissioning organization; possible manipulation in survey question framing.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The development of skepticism among young voters could lead to decreased political engagement, increased polarization, and challenges to social cohesion. These attitudes may evolve into more organized political movements or influence policy debates.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased political polarization and decreased trust in democratic institutions.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased justification of political violence could lead to heightened security risks and challenges for law enforcement.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased online radicalization and spread of extremist ideologies.
- Economic / Social: Skepticism about economic mobility and education value may impact workforce development and economic stability.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor online discourse for signs of radicalization; engage with youth organizations to understand underlying concerns.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures to address polarization; foster partnerships with educational institutions to address skepticism about higher education.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Increased dialogue leads to policy reforms that address youth concerns, reducing polarization.
- Worst Case: Escalation of political violence and further erosion of trust in institutions.
- Most-Likely: Continued skepticism with periodic spikes in political activism and unrest.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Young America’s Foundation (YAF)
- Echelon Insights (Polling Organization)
- Charlie Kirk (Conservative Figure)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet for other individuals.
7. Thematic Tags
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us