Taiwan warns of biases data breach in Deepseek other Chinese AI – Globalsecurity.org
Published on: 2025-11-17
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report:
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
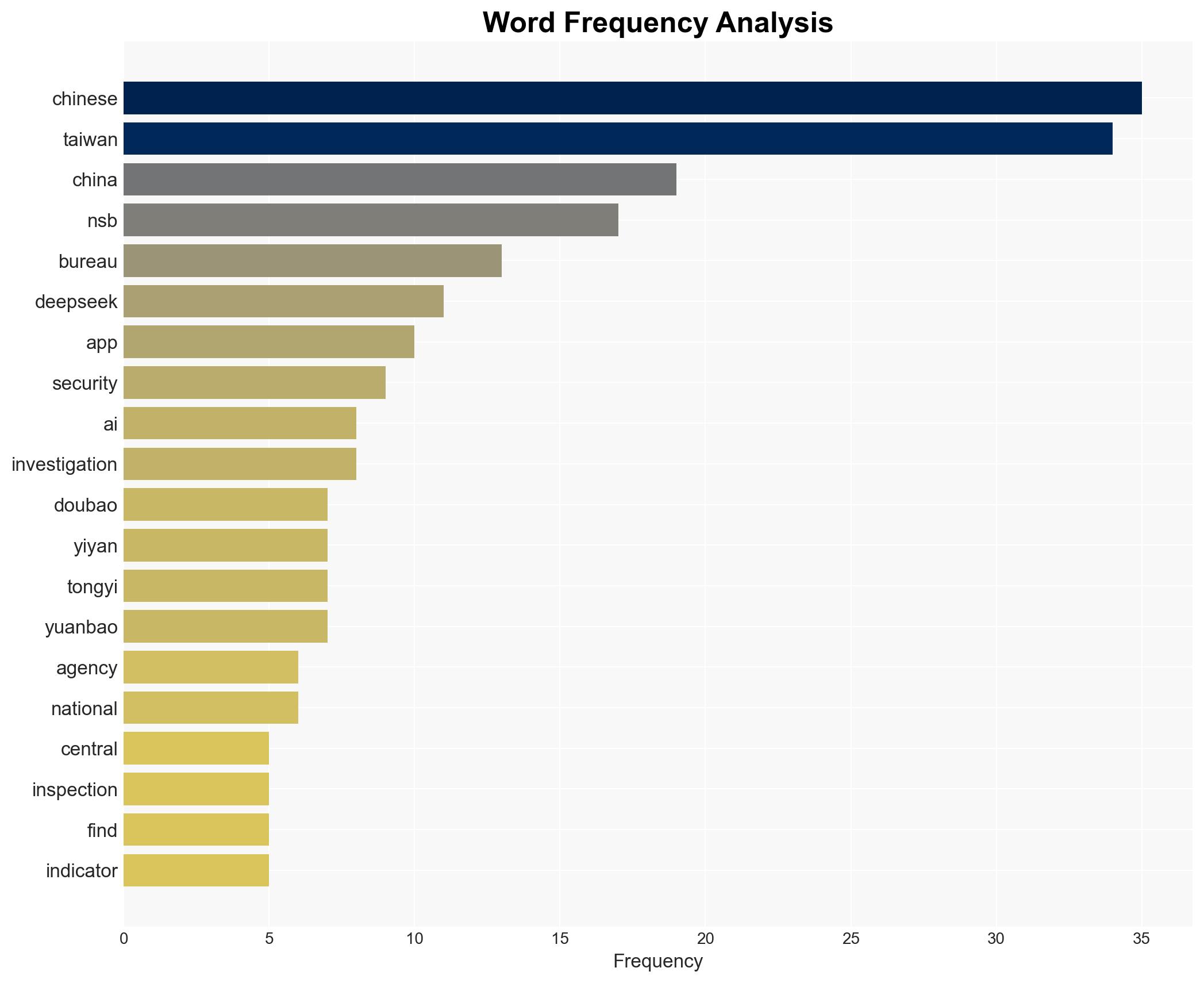
The strategic judgment is that Chinese AI applications, including Deepseek, pose a significant cybersecurity and informational threat to Taiwan, with a moderate to high confidence level. The most supported hypothesis is that these applications are being used to collect sensitive data and disseminate pro-China narratives, potentially under the influence or control of the Chinese government. Recommended actions include enhancing cybersecurity measures, increasing public awareness, and considering broader bans on Chinese AI applications.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: Chinese AI applications are being used to deliberately collect sensitive data and spread disinformation in Taiwan, as part of a coordinated effort by the Chinese government to influence public opinion and gather intelligence.
Hypothesis 2: The data breaches and biases in Chinese AI applications are primarily due to commercial interests and technical shortcomings, rather than a deliberate state-sponsored strategy.
The first hypothesis is more likely given the evidence of political censorship and the alignment of AI-generated content with official Chinese narratives. The second hypothesis cannot be entirely ruled out but lacks supporting evidence of purely commercial motivations.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions include the belief that Chinese AI applications are under the influence of the Chinese government and that Taiwan’s cybersecurity measures are currently insufficient to counter these threats. Red flags include the systematic bias in AI-generated content and the excessive data permissions requested by these applications. Deception indicators are present in the avoidance of politically sensitive topics by the AI models.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The implications of these findings include potential escalation in cross-strait tensions, increased cybersecurity threats to Taiwanese individuals and institutions, and the erosion of public trust in digital platforms. Strategically, this could lead to heightened political and economic friction between Taiwan and China, as well as increased scrutiny of Chinese technology globally.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Enhance cybersecurity protocols and conduct regular audits of foreign applications used within Taiwan.
- Increase public awareness campaigns about the risks associated with Chinese AI applications.
- Consider expanding bans on Chinese AI applications beyond government devices to include critical infrastructure sectors.
- Best-case scenario: Taiwan successfully mitigates the cybersecurity threat, maintaining its digital sovereignty.
- Worst-case scenario: A significant data breach or disinformation campaign destabilizes Taiwan’s political landscape.
- Most-likely scenario: Continued low-level cyber and informational threats from Chinese AI applications, requiring ongoing vigilance and adaptation.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Joseph Yeh (Taiwanese official mentioned in the source)
National Security Bureau (NSB)
Ministry of Justice Investigation Bureau (MJIB)
Criminal Investigation Bureau (CIB)
7. Thematic Tags
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Structured challenge to expose and correct biases.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us
·