Tesla Infotainment System Compromised with 37 Zero-Day Exploits at Pwn2Own Automotive 2026
Published on: 2026-01-21
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Tesla hacked 37 zero-days demoed at Pwn2Own Automotive 2026
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
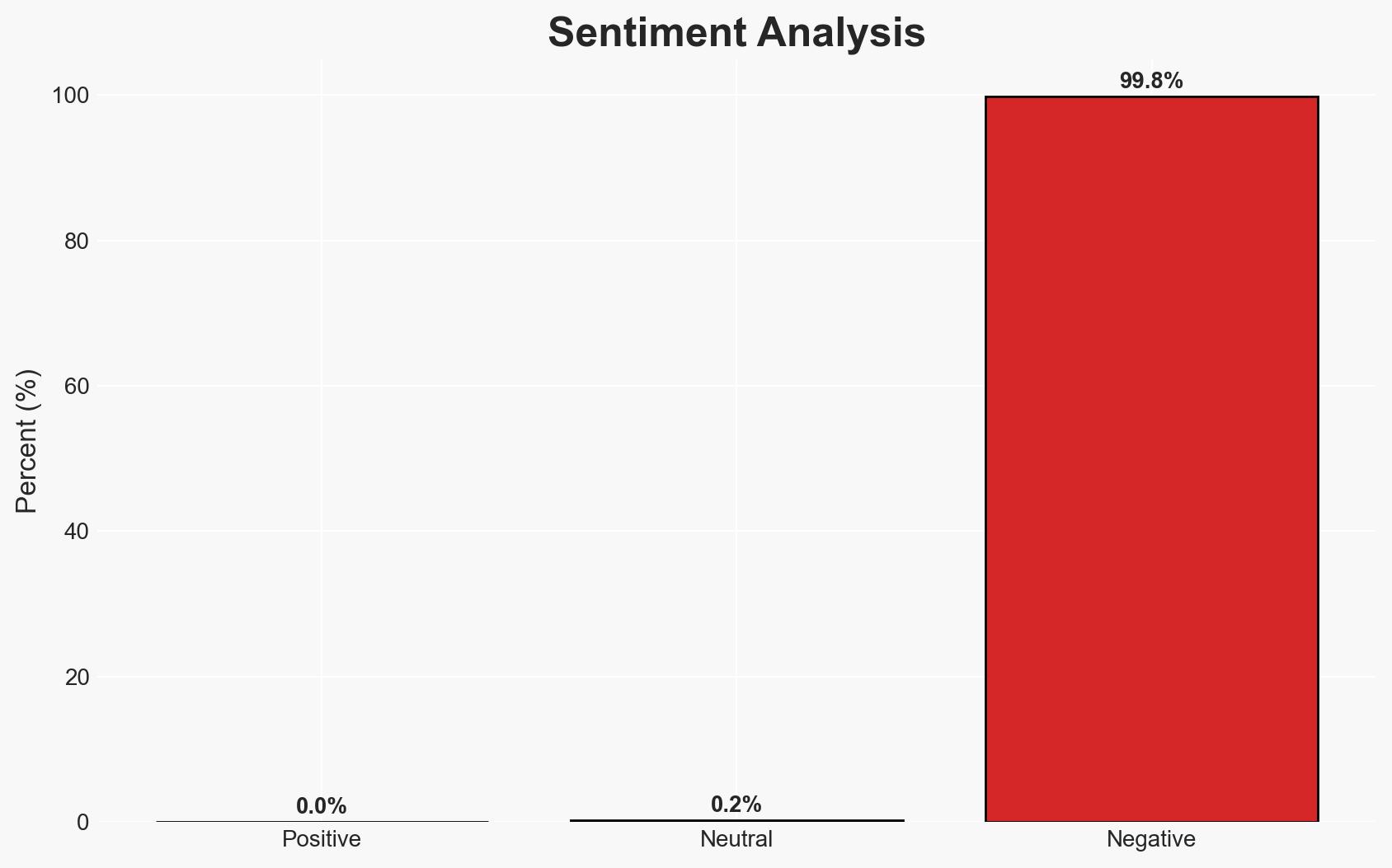
The Pwn2Own Automotive 2026 competition demonstrated significant vulnerabilities in automotive infotainment systems and EV chargers, with 37 zero-day exploits revealed. This highlights ongoing cybersecurity challenges in the automotive sector, particularly affecting manufacturers like Tesla. The event underscores the need for robust security measures in automotive technology. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The vulnerabilities exposed at Pwn2Own are indicative of systemic cybersecurity weaknesses in the automotive industry. Supporting evidence includes the successful exploitation of numerous zero-days across multiple systems. However, the extent to which these vulnerabilities are representative of the entire industry remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The vulnerabilities are primarily due to specific oversights by individual manufacturers and do not reflect broader industry trends. This hypothesis is supported by the fact that the competition targets specific systems and may not account for recent security improvements elsewhere. Contradicting evidence includes the repeated success of similar exploits in previous years.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the consistent pattern of vulnerabilities revealed over successive competitions, suggesting systemic issues. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of widespread security improvements or a reduction in successful exploits in future competitions.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The vulnerabilities demonstrated are exploitable in real-world scenarios; manufacturers will prioritize patching these vulnerabilities within the 90-day window; the competition’s findings are representative of broader industry trends.
- Information Gaps: Detailed technical specifics of the vulnerabilities; the full scope of affected systems beyond those demonstrated; manufacturers’ timelines and strategies for deploying patches.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in the selection of systems targeted by the competition; the possibility of manufacturers underreporting vulnerabilities to protect brand reputation.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The exposure of these vulnerabilities could lead to increased regulatory scrutiny and pressure on automotive manufacturers to enhance cybersecurity measures. If unaddressed, these vulnerabilities could be exploited by malicious actors, posing risks to consumer safety and data privacy.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regulation and international cooperation on automotive cybersecurity standards.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of cyber-attacks targeting automotive systems, potentially impacting public safety.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased focus on automotive cybersecurity could drive innovation and investment in security technologies.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impact on manufacturers due to the cost of patching vulnerabilities and potential loss of consumer trust.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor manufacturers’ responses and patch deployment; engage with industry stakeholders to discuss cybersecurity best practices.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms to enhance automotive security; advocate for industry-wide cybersecurity standards.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Rapid patch deployment and improved security measures reduce future vulnerabilities. Worst: Manufacturers fail to address vulnerabilities, leading to high-profile cyber incidents. Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in security with ongoing challenges in keeping pace with emerging threats.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Synacktiv Team
- Fuzzware.io
- PetoWorks
- Team DDOS
- Tesla
- TrendMicro’s Zero Day Initiative
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, automotive cybersecurity, zero-day vulnerabilities, Pwn2Own competition, Tesla, electric vehicles, infotainment systems, cyber defense
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us