Texas Files Lawsuit Against TP-Link for Misleading Security Claims Amid Chinese Hacking Concerns
Published on: 2026-02-19
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Texas sues TP-Link over Chinese hacking risks user deception
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
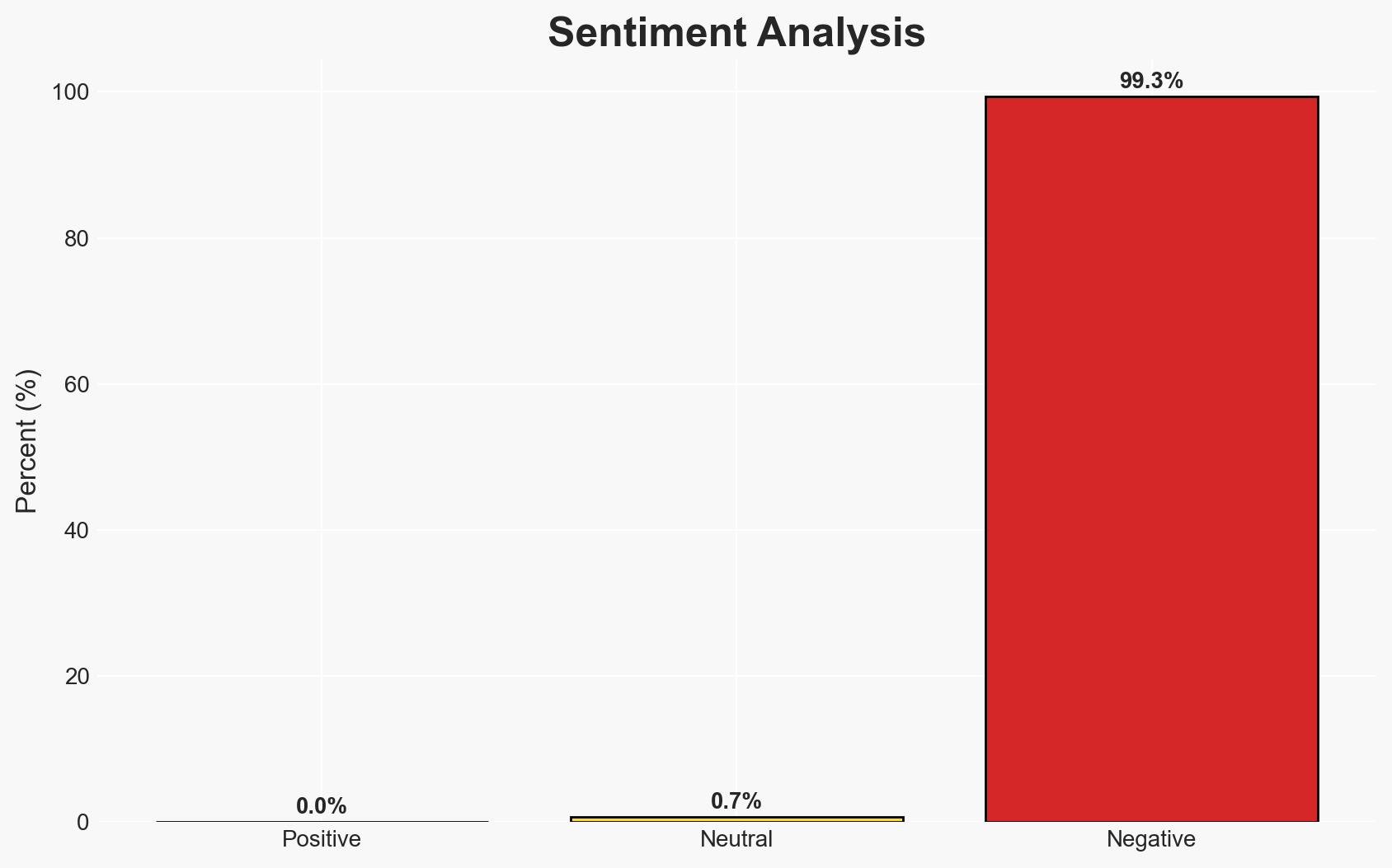
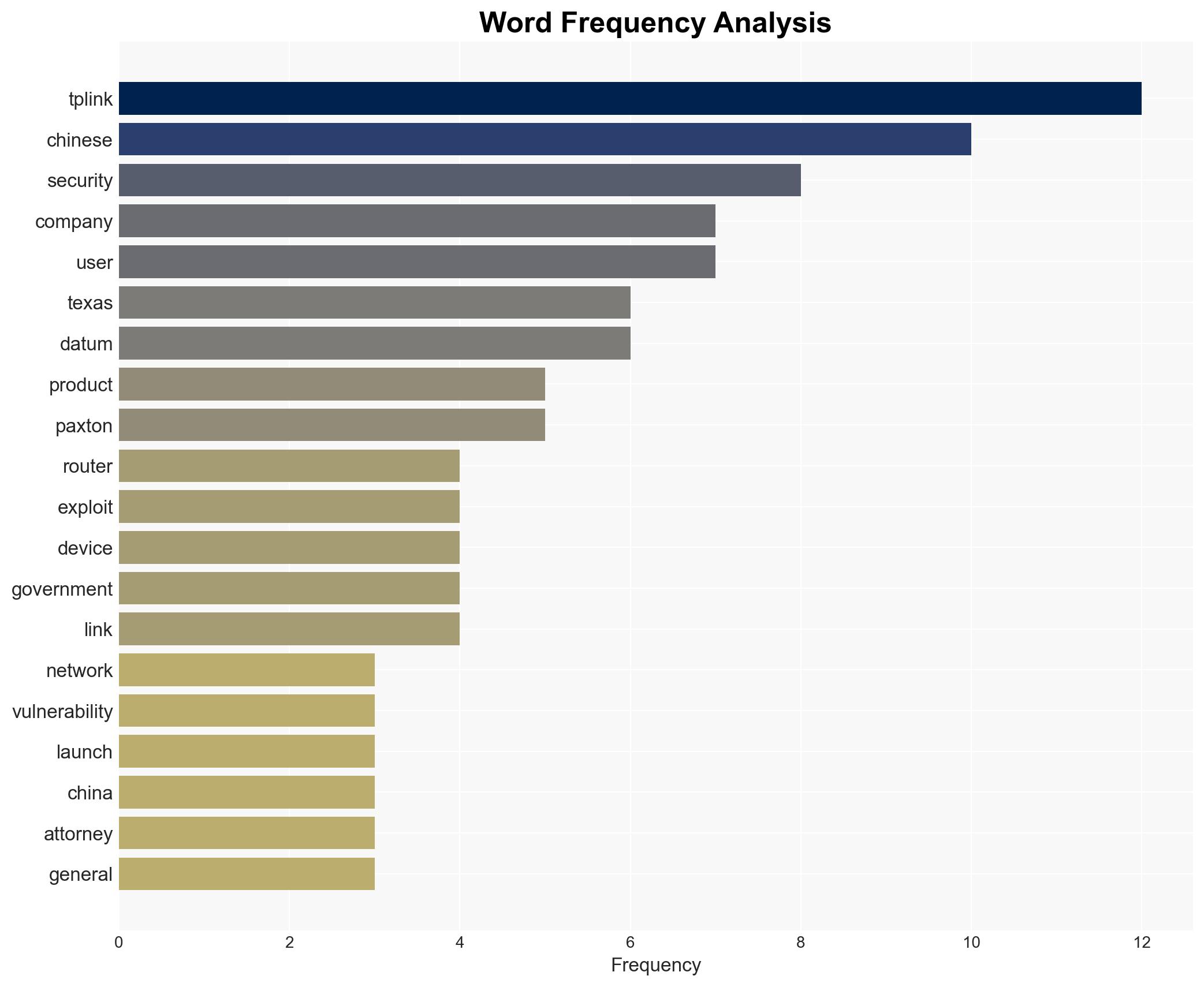
The Texas lawsuit against TP-Link highlights significant cybersecurity and national security concerns due to alleged deceptive practices and vulnerabilities exploited by Chinese state-backed hackers. The most likely hypothesis is that TP-Link’s supply chain ties to China pose a genuine security risk, exacerbated by potential Chinese government influence. This situation affects U.S. national security and consumer privacy, with moderate confidence in this assessment.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: TP-Link’s routers, due to their Chinese supply chain, are vulnerable to exploitation by Chinese state-backed hackers, posing a national security threat. Supporting evidence includes the lawsuit’s claims, historical security failures, and federal investigations. Key uncertainties involve the extent of TP-Link’s compliance with Chinese intelligence requests.
- Hypothesis B: The allegations against TP-Link are exaggerated or politically motivated, with vulnerabilities being typical of industry standards rather than deliberate negligence. Contradicting evidence includes the lack of direct proof of TP-Link’s compliance with Chinese intelligence and potential political bias in the lawsuit.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the convergence of multiple sources indicating security vulnerabilities and the geopolitical context of U.S.-China tensions. Indicators such as further disclosures of TP-Link’s cooperation with Chinese authorities could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: TP-Link’s supply chain is significantly influenced by Chinese regulations; vulnerabilities in TP-Link routers are actively exploited by Chinese hackers; U.S. legal actions are based on credible intelligence.
- Information Gaps: Detailed evidence of TP-Link’s compliance with Chinese intelligence requests; comprehensive technical analysis of the alleged vulnerabilities.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential political bias in the lawsuit; risk of overestimating Chinese influence without concrete evidence; TP-Link’s public statements may be influenced by reputational concerns.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased scrutiny of Chinese technology firms in the U.S., affecting bilateral relations and domestic cybersecurity policies. The lawsuit may set a precedent for further legal actions against other companies with Chinese ties.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential escalation in U.S.-China tensions; increased regulatory actions against Chinese firms.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened awareness and mitigation of supply chain vulnerabilities; potential increase in cyber defense measures.
- Cyber / Information Space: Greater focus on securing network infrastructure; possible rise in public-private cybersecurity collaborations.
- Economic / Social: Impact on consumer trust in technology products; potential economic repercussions for companies with Chinese supply chains.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase monitoring of TP-Link products for vulnerabilities; engage with federal agencies to align on cybersecurity strategies.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for supply chain security; foster partnerships with non-Chinese technology providers.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: TP-Link enhances security measures, reducing vulnerabilities.
- Worst: Escalation of U.S.-China tech conflicts, leading to widespread bans.
- Most-Likely: Continued legal and regulatory scrutiny of Chinese tech firms, with incremental security improvements.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- TP-Link Systems
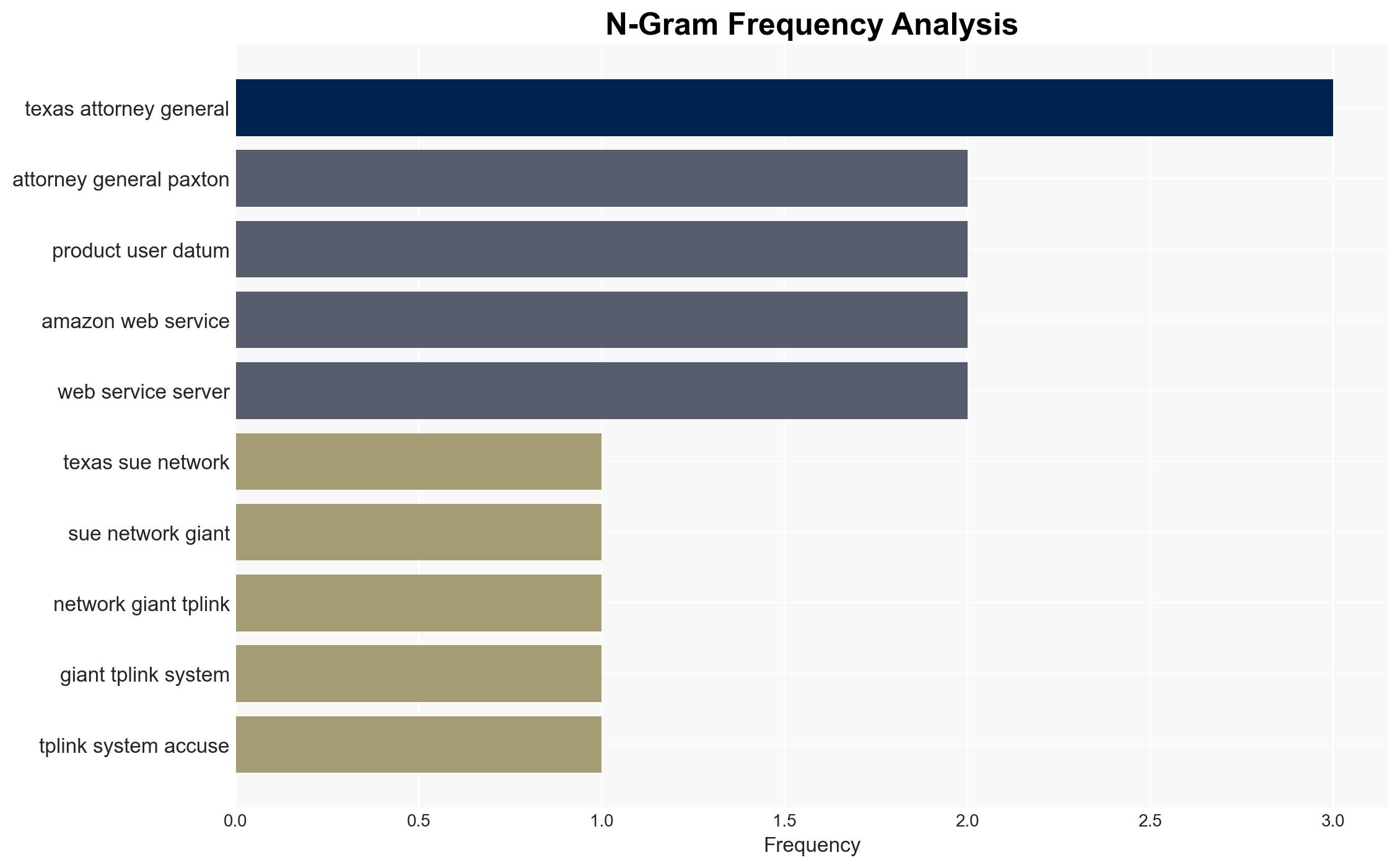
- Texas Attorney General Ken Paxton
- Chinese state-backed hackers
- U.S. Departments of Justice, Commerce, and Defense
- CISA (Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency)
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, national security, U.S.-China relations, supply chain vulnerabilities, legal actions, consumer privacy, technology regulation
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us