The AI Triple Threat mitigating the dangers of AI adoption with identity security – TechRadar
Published on: 2025-08-19
Intelligence Report: The AI Triple Threat mitigating the dangers of AI adoption with identity security – TechRadar
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
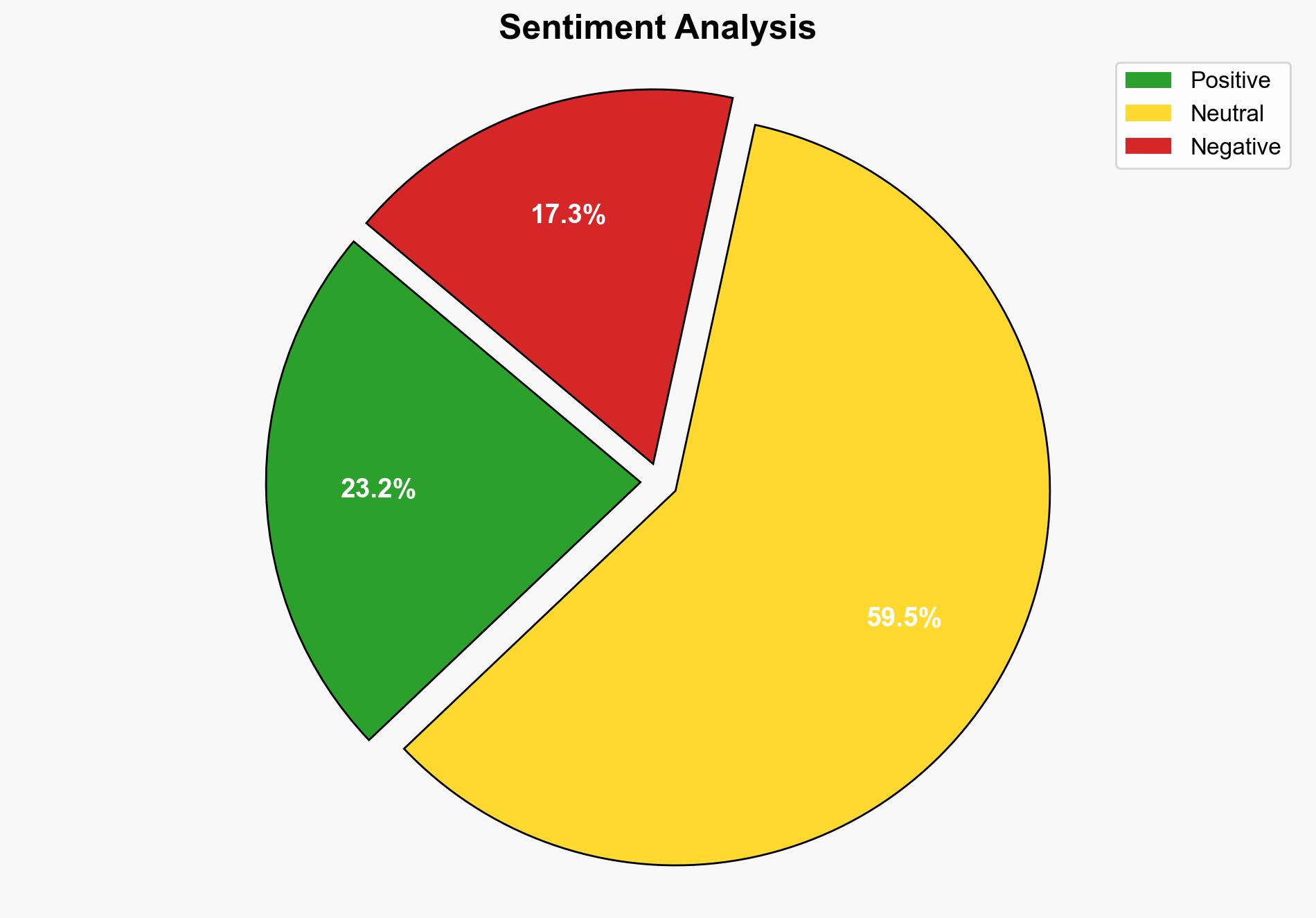
The most supported hypothesis is that AI adoption, while beneficial, significantly increases cybersecurity risks, particularly through identity security vulnerabilities. Organizations must prioritize robust identity security frameworks to mitigate these risks effectively. Confidence Level: High. Recommended action includes enhancing identity verification processes and increasing AI oversight to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: AI adoption increases cybersecurity risks primarily through identity security vulnerabilities, necessitating stronger identity verification and oversight measures.
Hypothesis 2: The benefits of AI adoption, such as improved productivity and operational efficiency, outweigh the cybersecurity risks, which can be managed with existing security protocols.
Using ACH 2.0, Hypothesis 1 is better supported due to the evidence of increased phishing attacks and the use of AI for sophisticated scams, as well as the rapid growth in machine identities that outnumber human users. Hypothesis 2 lacks sufficient evidence, as current security protocols are often circumvented by advanced AI-driven threats.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions:
– AI tools will continue to evolve, increasing both their utility and their potential for misuse.
– Organizations can effectively implement stronger identity verification processes without significant operational disruption.
Red Flags:
– Over-reliance on AI without adequate human oversight may lead to blind spots in security.
– Lack of comprehensive data on the effectiveness of current security measures against AI-driven threats.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The integration of AI into business operations poses significant strategic risks, including potential data breaches and regulatory non-compliance. The rapid increase in machine identities and unauthorized AI applications could lead to cascading security failures. Economically, the cost of breaches could outweigh productivity gains. Geopolitically, vulnerabilities in AI systems could be exploited by state actors for espionage or sabotage.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Enhance identity verification processes and implement multi-factor authentication to mitigate identity-related risks.
- Increase AI oversight and ensure AI tools are trained with high-quality data to prevent bias and drift.
- Develop clear policies on AI usage and educate staff on potential security threats.
- Scenario Projections:
- Best Case: Organizations successfully integrate AI with robust security measures, leading to enhanced productivity and security.
- Worst Case: AI-driven security breaches result in significant data loss and financial damage, undermining trust in AI technologies.
- Most Likely: Incremental improvements in security measures lead to a manageable level of risk, with occasional breaches.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– CyberArk (Research and insights on AI security threats)
– UK organizations (Target of AI-driven phishing attacks)
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, cybersecurity, counter-terrorism, regional focus