The Civil War in Sudan Big Money Foreign Powers Taking Rival Sides May Turn Even More Destructive Using Heavier Weapons – Globalresearch.ca
Published on: 2025-04-05
Intelligence Report: The Civil War in Sudan Big Money Foreign Powers Taking Rival Sides May Turn Even More Destructive Using Heavier Weapons – Globalresearch.ca
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
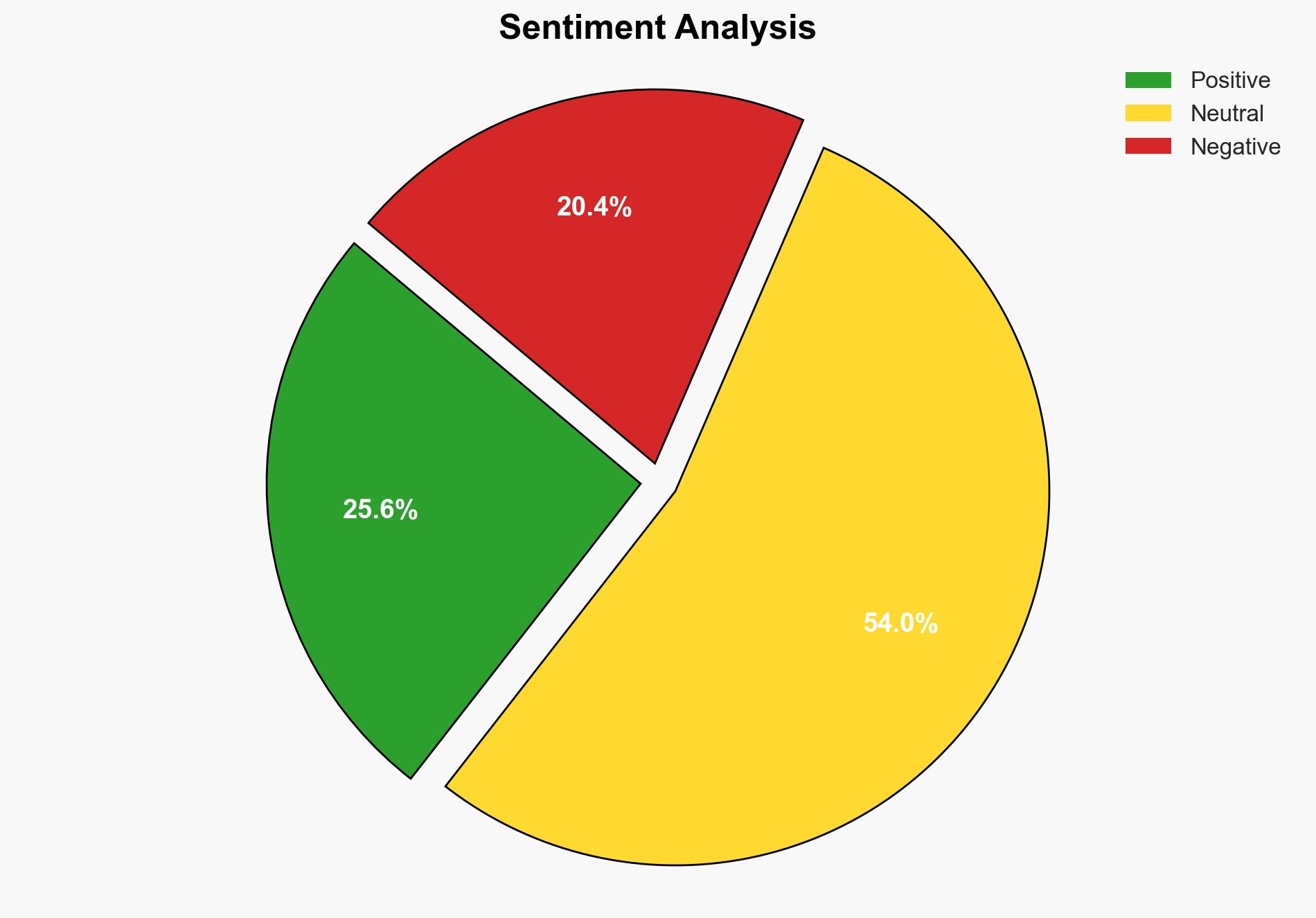
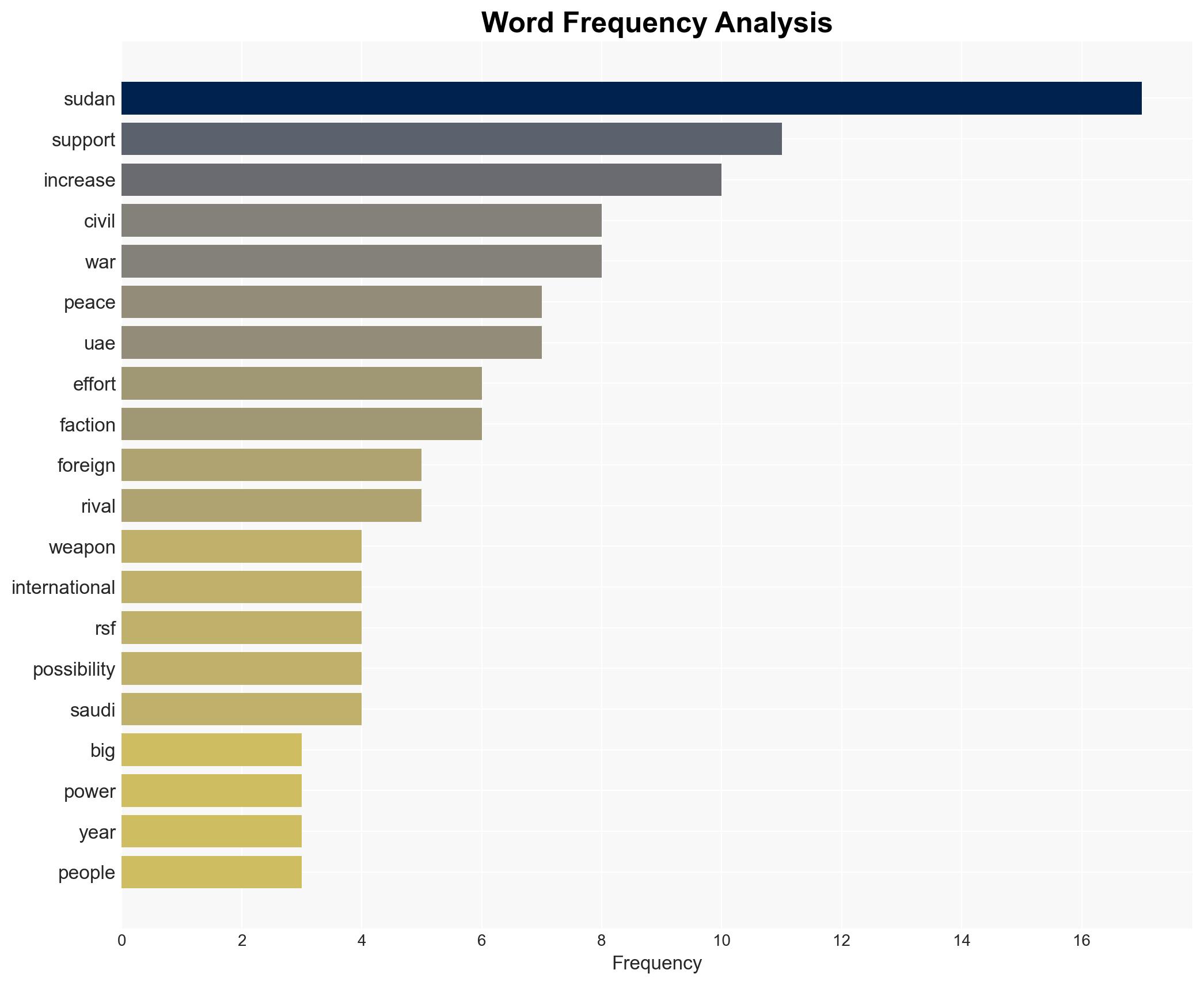
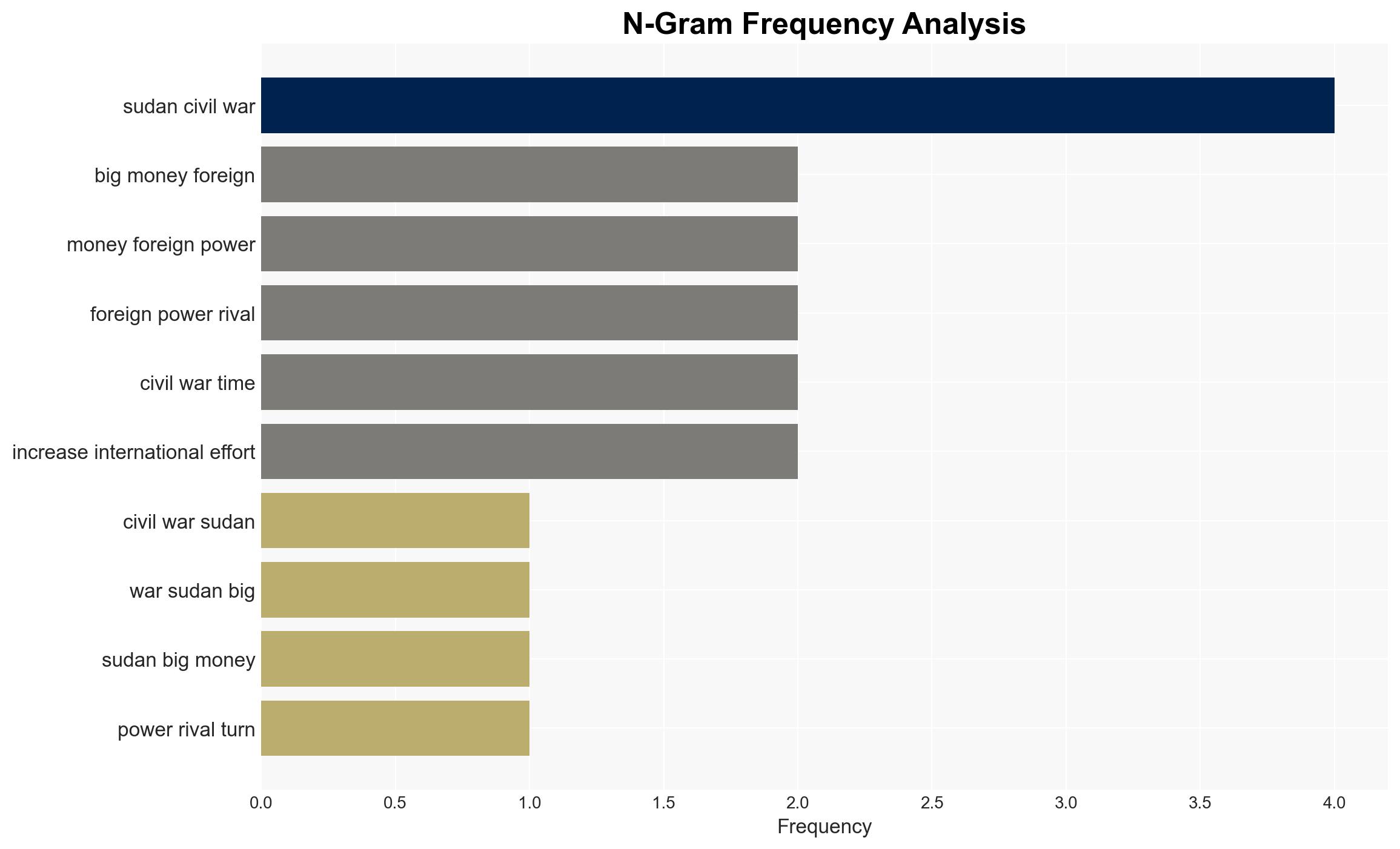
The ongoing civil war in Sudan is exacerbated by foreign powers taking rival sides, leading to increased weapon supplies and heightened destruction. The United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Saudi Arabia are key players, supporting different factions for strategic and economic gains. This involvement is likely to prolong the conflict and complicate peace efforts. Immediate international intervention is necessary to prevent further escalation and humanitarian crises.
2. Detailed Analysis
The following structured analytic techniques have been applied for this analysis:
General Analysis
The civil war in Sudan, ongoing since April, has resulted in significant loss of life and displacement. Foreign powers, notably the UAE and Saudi Arabia, are backing opposing factions, contributing to the conflict’s intensity. The UAE is accused of supplying weapons to the Rapid Support Forces (RSF), while Saudi Arabia supports the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF). This rivalry is driven by ambitions for access to Sudan’s resources and strategic positioning in the region. The involvement of these powers complicates peace efforts and risks further destabilizing the region.
3. Implications and Strategic Risks
The foreign involvement in Sudan’s civil war poses several risks:
- Increased regional instability due to the militarization of the conflict.
- Escalation of violence leading to further humanitarian crises and displacement.
- Potential for broader regional conflicts as alliances shift and tensions rise.
- Economic impacts on Sudan and neighboring countries due to disrupted trade and investment.
4. Recommendations and Outlook
Recommendations:
- Encourage diplomatic efforts to mediate between conflicting parties and foreign backers.
- Implement international sanctions on entities supplying weapons to factions in Sudan.
- Increase humanitarian aid and support for displaced populations.
- Promote transparency and accountability in foreign involvement in Sudan.
Outlook:
Best-case scenario: Successful diplomatic interventions lead to a ceasefire and peace negotiations, reducing violence and allowing for humanitarian aid distribution.
Worst-case scenario: Continued foreign intervention escalates the conflict, leading to widespread destruction and regional destabilization.
Most likely outcome: Prolonged conflict with intermittent peace talks, influenced by foreign powers’ strategic interests, resulting in ongoing humanitarian challenges.
5. Key Individuals and Entities
The report mentions significant individuals and organizations involved in the conflict:
- UAE – Accused of supporting the RSF with weapons.
- Saudi Arabia – Supporting the SAF for strategic and economic benefits.
- RSF – Rapid Support Forces, a faction in the conflict.
- SAF – Sudanese Armed Forces, another faction in the conflict.