The core pillars of cyber resiliency – BetaNews
Published on: 2025-04-02
Intelligence Report: The Core Pillars of Cyber Resiliency – BetaNews
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
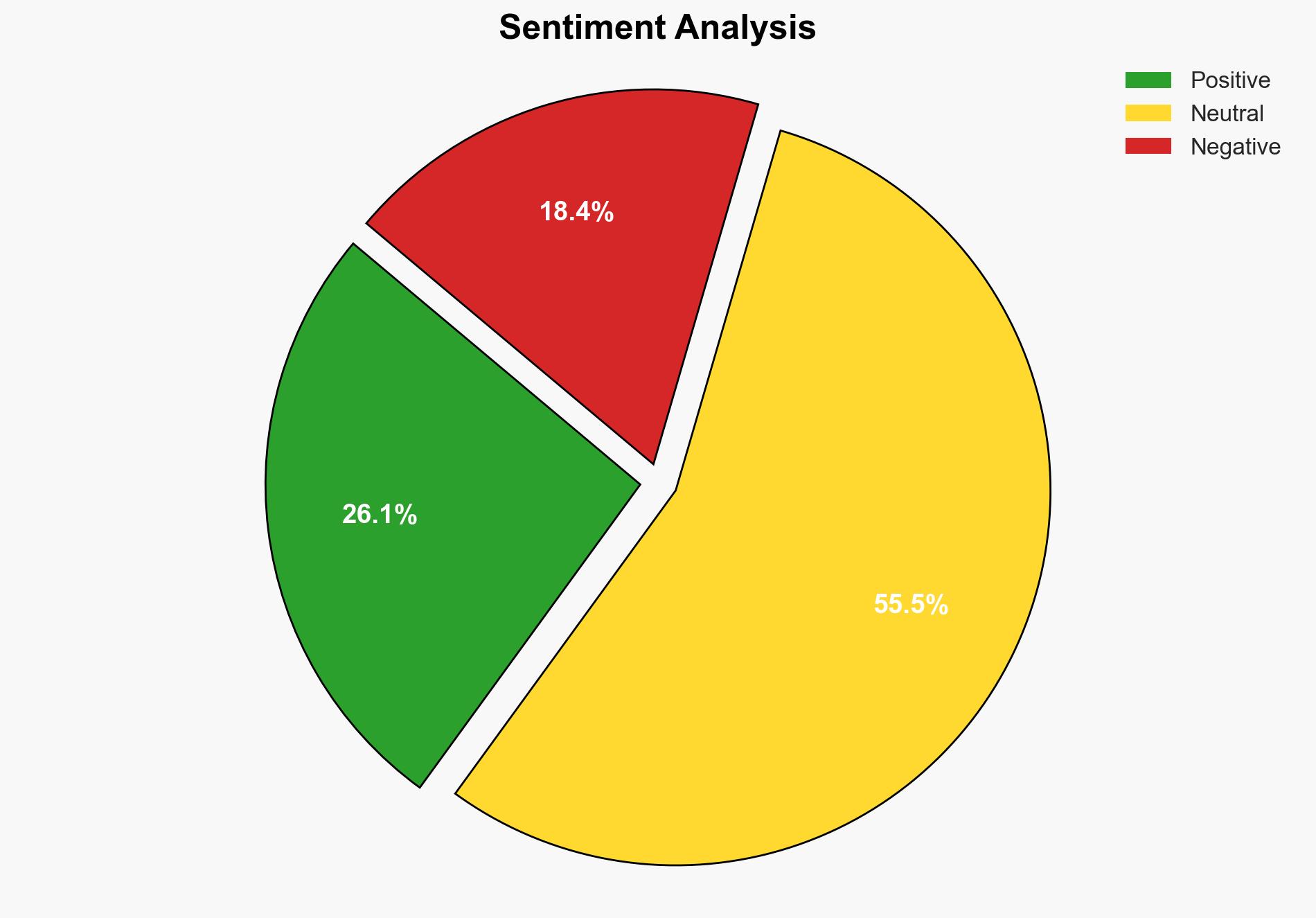
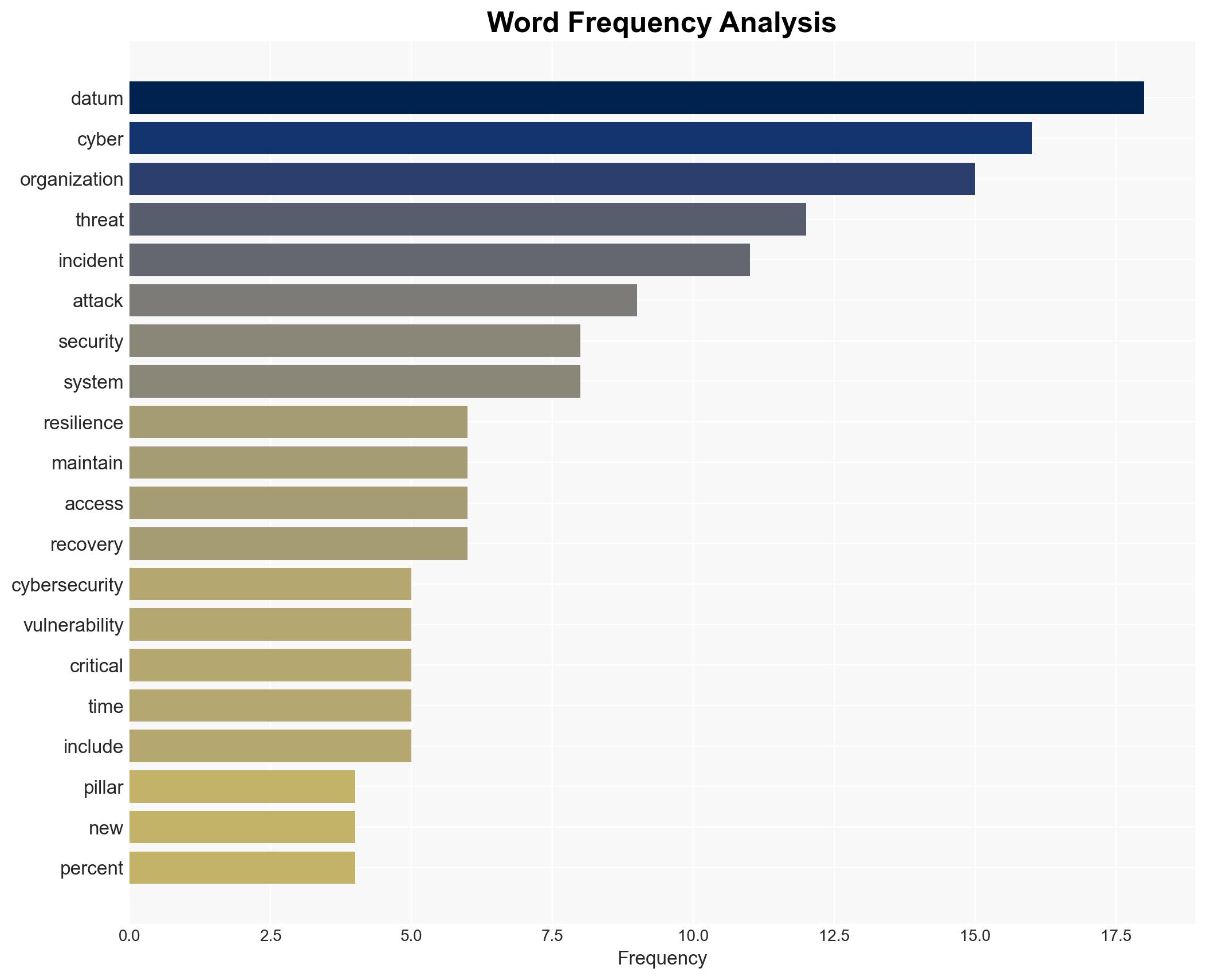
The evolving cybersecurity threat landscape necessitates a comprehensive approach to cyber resiliency. Organizations must enhance their cybersecurity posture by adopting offensive security strategies, improving cyber hygiene, and fostering cybersecurity awareness. The integration of AI and automation is critical to managing the increasing sophistication of cyber threats. Immediate action is required to minimize dwell time and protect critical infrastructure and sensitive data.
2. Detailed Analysis
The following structured analytic techniques have been applied for this analysis:
General Analysis
The report highlights the rapid evolution of cybersecurity threats, driven by advancements in AI and automation. The increase in ransomware attacks and the expansion of the attack surface pose significant challenges. Organizations are urged to implement advanced monitoring systems for real-time insights into network traffic and user behavior. Strong password management and multi-factor authentication are emphasized as critical components of cyber hygiene. Regular software updates and employee training on phishing and social engineering tactics are essential to mitigate risks.
3. Implications and Strategic Risks
The growing complexity of cyber threats poses significant risks to national security, regional stability, and economic interests. The potential for long-term undetected cyber threats increases the likelihood of substantial damage to business operations and customer service. The reliance on outdated software and inadequate cybersecurity practices heightens vulnerability to attacks, impacting critical infrastructure and sensitive data.
4. Recommendations and Outlook
Recommendations:
- Implement advanced monitoring systems to enhance real-time threat detection and response capabilities.
- Adopt strong password policies and enforce multi-factor authentication to reduce unauthorized access risks.
- Conduct regular cybersecurity training for employees to recognize and respond to phishing and social engineering tactics.
- Ensure timely software updates and patch management to protect against known vulnerabilities.
Outlook:
In the best-case scenario, organizations that adopt comprehensive cyber resiliency strategies will significantly reduce the impact of cyber threats. The worst-case scenario involves continued reliance on outdated practices, leading to increased vulnerability and potential widespread damage. The most likely outcome is a gradual improvement in cybersecurity posture as organizations recognize the necessity of proactive measures.
5. Key Individuals and Entities
The report does not mention specific individuals or organizations by name. However, it emphasizes the importance of key stakeholders in implementing and maintaining robust cybersecurity measures to safeguard against evolving threats.