The Evolution of RomCom: From Ordinary RAT to Versatile Cyberweapon in Global Conflicts
Published on: 2025-12-19
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: How RomCom became a multipurpose cyberweapon
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
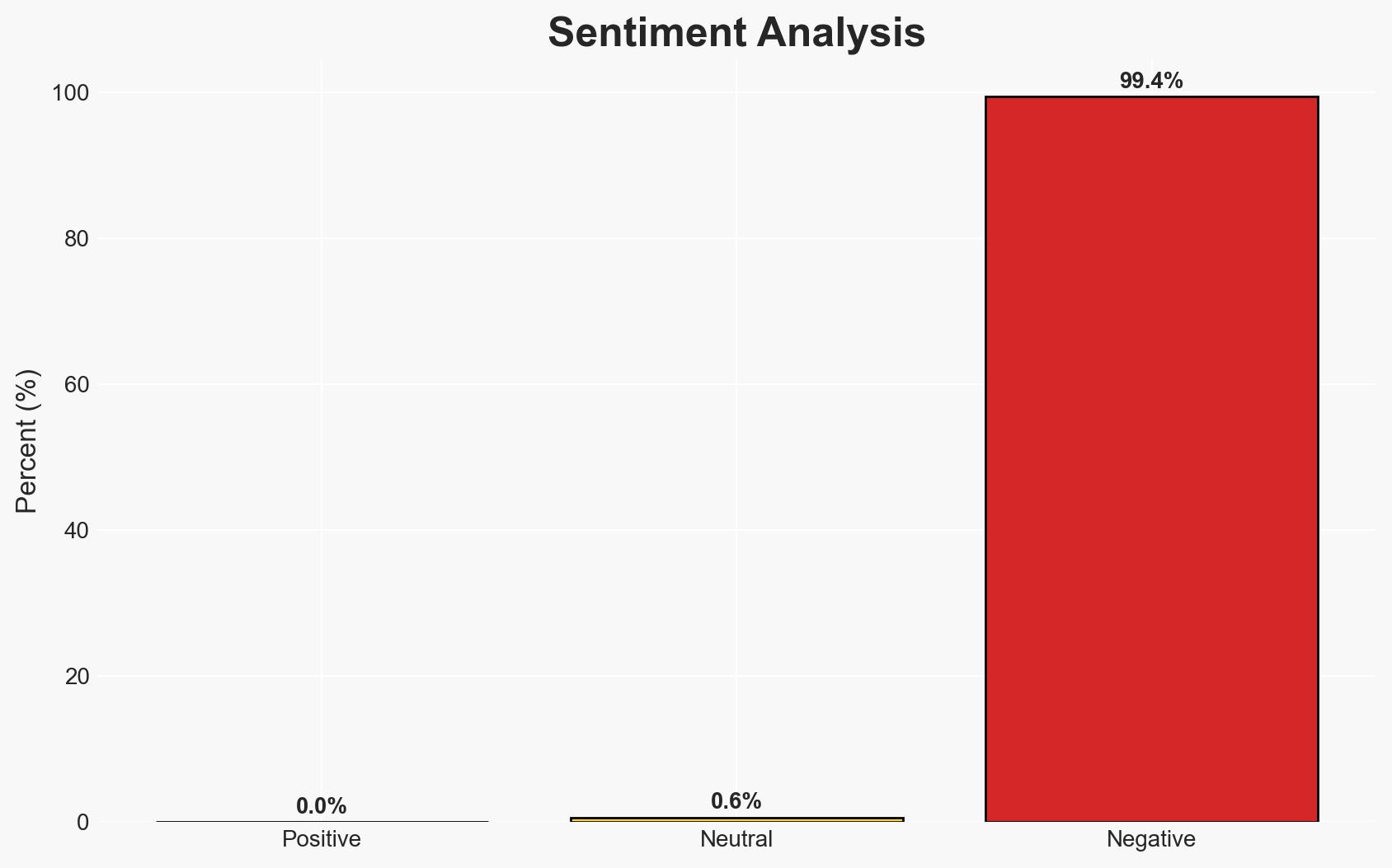
RomCom has evolved from a basic remote access trojan into a sophisticated, modular cyberweapon used by both nation-states and criminal organizations. This development highlights the blurring lines between espionage and organized crime, posing significant threats to geopolitical stability and cybersecurity. The most likely hypothesis is that RomCom is being utilized by a hybrid actor with both political and financial motives. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: RomCom is primarily a tool of nation-state actors who have co-opted it for espionage purposes. Supporting evidence includes its targeting of Ukraine and NATO-aligned nations, suggesting geopolitical motives. However, the overlap with ransomware operations introduces uncertainty about the primary actors involved.
- Hypothesis B: RomCom is a product of a hybrid actor or group that operates at the intersection of organized crime and state-sponsored activities. The modularity and dual-use nature of the malware support this hypothesis, as does the evidence of shared infrastructure between espionage and ransomware operations.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the evidence of shared infrastructure and the malware’s evolution into a tool capable of both espionage and financial gain. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include new intelligence on actor attribution or changes in targeting patterns.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: RomCom’s development is driven by a single actor or closely linked group; the malware’s modularity is intentional for dual-use purposes; geopolitical targeting aligns with nation-state interests.
- Information Gaps: Precise attribution of the actors behind RomCom; detailed understanding of the command and control infrastructure; insights into the decision-making processes of the actors involved.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential confirmation bias in attributing nation-state involvement; source bias from cybersecurity firms with vested interests; possible deception by actors to obscure true motives.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The evolution of RomCom into a multipurpose cyberweapon could lead to increased cyber operations targeting critical infrastructure and governmental entities, potentially escalating geopolitical tensions.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions between nation-states, particularly if RomCom is linked to state-sponsored actors targeting strategic interests.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced threat landscape with increased risks to national security and critical infrastructure from hybrid cyber actors.
- Cyber / Information Space: Growing sophistication in malware development could lead to more widespread and difficult-to-detect cyberattacks.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic disruptions from ransomware attacks and increased costs for cybersecurity defenses; erosion of public trust in digital systems.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of RomCom-related activities; increase information sharing among cybersecurity entities; implement immediate mitigation strategies for identified vulnerabilities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures and partnerships to counter hybrid cyber threats; invest in capability development for detecting and responding to modular malware.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Successful attribution and neutralization of RomCom actors, reducing threat levels.
- Worst: Escalation of cyberattacks leading to significant geopolitical conflicts and economic disruptions.
- Most-Likely: Continued evolution and deployment of RomCom by hybrid actors, necessitating ongoing defensive measures.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
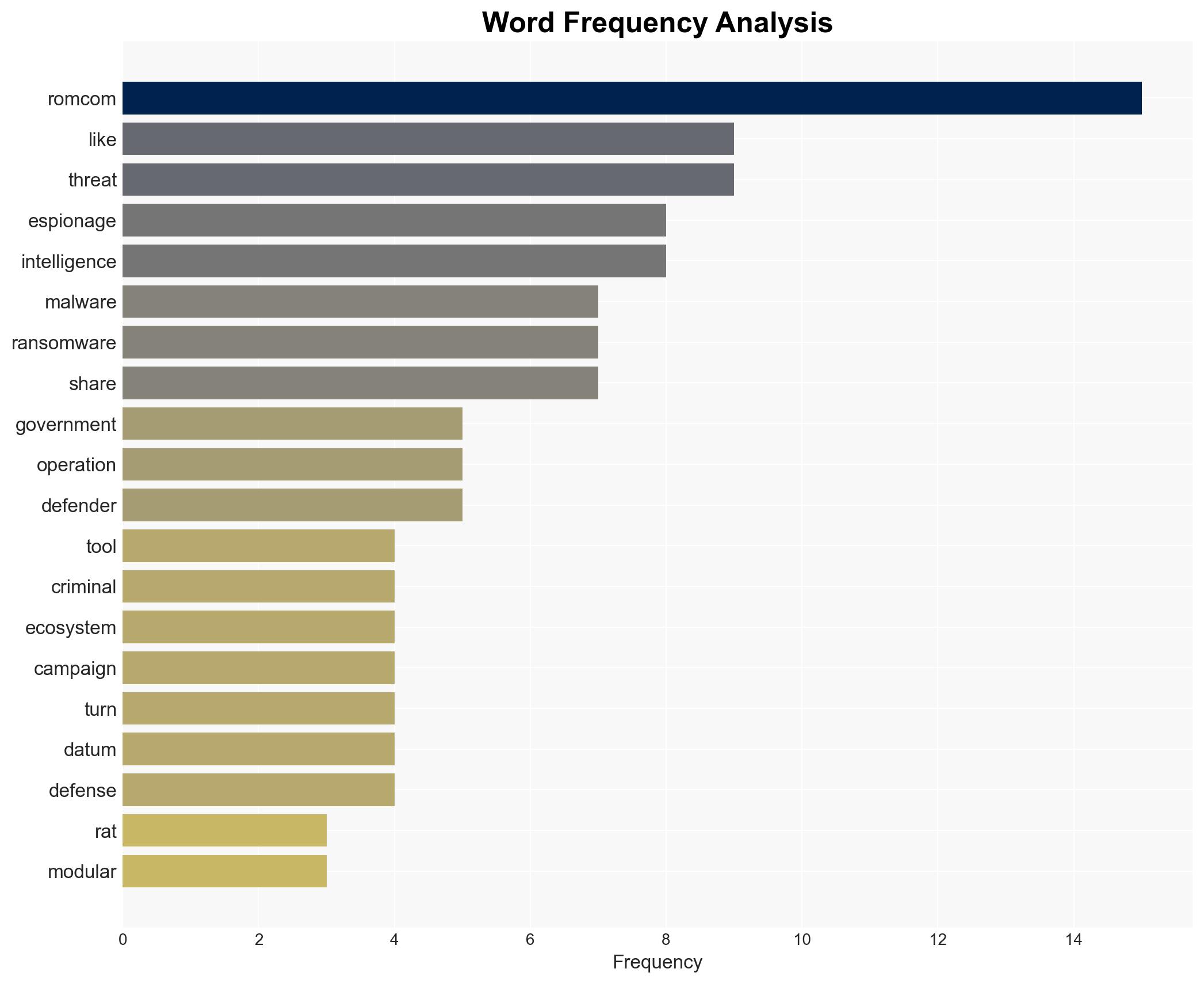
cybersecurity, cyber-espionage, ransomware, nation-state actors, organized crime, malware evolution, geopolitical tensions
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us