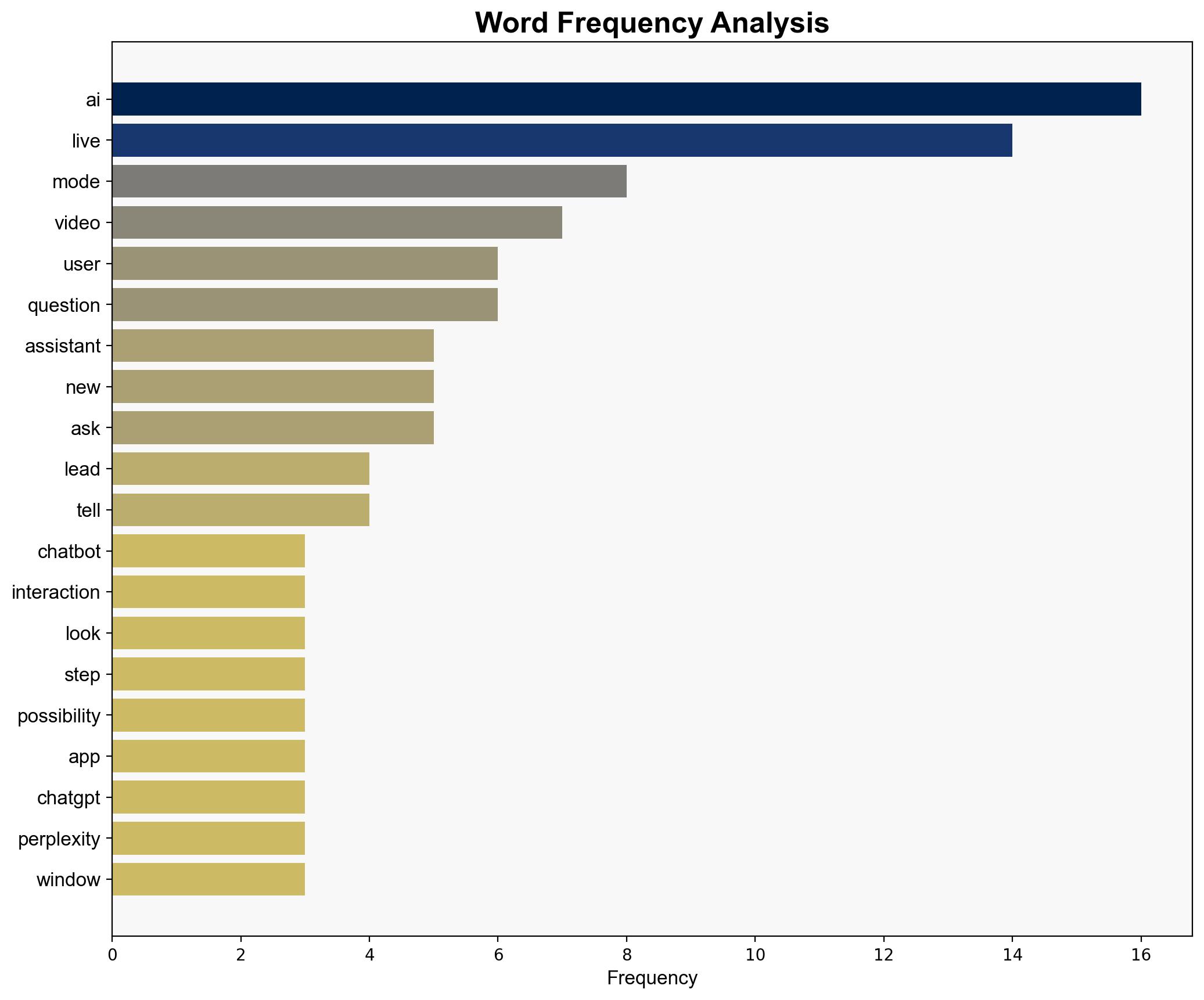
The future of Live AI Ready for Discovery held back by user concerns – Livemint
Published on: 2025-09-13
Intelligence Report: The future of Live AI Ready for Discovery held back by user concerns – Livemint
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
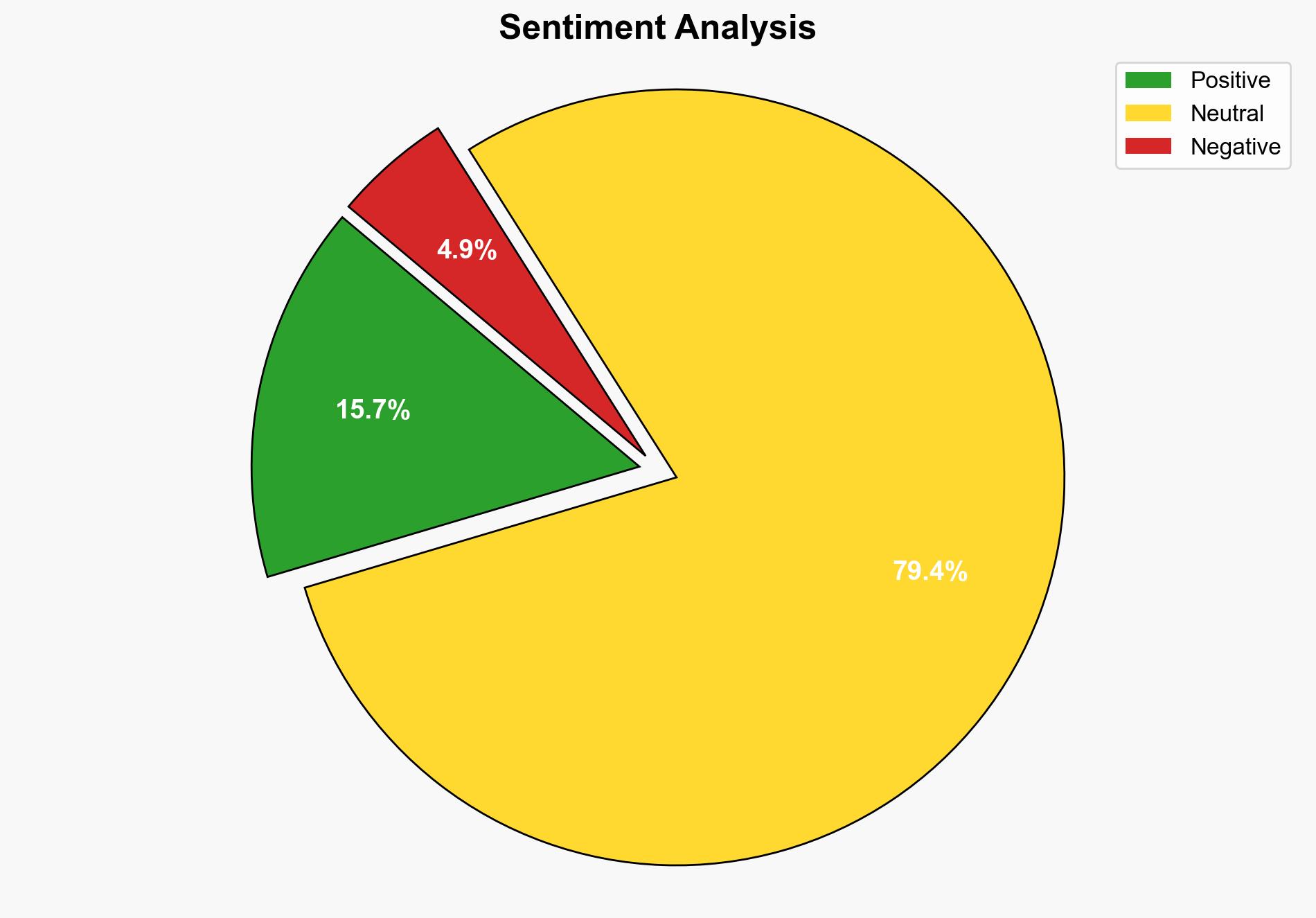
The strategic judgment is that user concerns about privacy and trust are significantly hindering the adoption of live AI technologies. The most supported hypothesis is that these concerns are rooted in a lack of trust and understanding of AI capabilities and limitations. To address this, a strategic focus on transparency, user education, and robust privacy measures is recommended. Confidence Level: Moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **Hypothesis A**: User concerns about privacy and trust are the primary barriers to the adoption of live AI technologies. This is due to a lack of understanding and fear of potential misuse of personal data.
2. **Hypothesis B**: The slow adoption of live AI technologies is primarily due to technical limitations and the current underperformance of AI systems in delivering reliable and context-aware interactions.
Using the Analysis of Competing Hypotheses (ACH) 2.0, Hypothesis A is better supported. The source text emphasizes user concerns and trust deficits, which align more closely with Hypothesis A than with technical limitations.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**: It is assumed that user concerns are primarily about privacy and trust, and not significantly about technical performance.
– **Red Flags**: There is a potential bias in underestimating the role of technical limitations. The source does not provide detailed evidence on the technical capabilities of current AI systems.
– **Blind Spots**: The analysis may overlook cultural factors influencing user trust and adoption rates in different regions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
– **Economic**: Delayed adoption of live AI could slow down potential economic benefits from increased productivity and innovation.
– **Cyber**: Increased use of live AI could expose users to new cybersecurity threats if privacy concerns are not adequately addressed.
– **Psychological**: Persistent trust deficits could lead to widespread skepticism about AI technologies, affecting future innovations.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- **Mitigation**: Implement robust privacy measures and transparent data handling practices to build user trust.
- **Education**: Develop comprehensive user education programs to demystify AI technologies and their benefits.
- **Projections**:
– **Best Case**: Successful trust-building leads to widespread adoption and integration of live AI, driving innovation.
– **Worst Case**: Continued distrust results in stagnation of AI adoption, limiting technological progress.
– **Most Likely**: Gradual adoption as trust-building measures are implemented, with incremental improvements in AI capabilities.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– **Mala Bhargava**: Contributor to the discussion on AI adoption and user concerns.
– **Entities**: Companies investing in AI technologies, such as Microsoft and Meta, are key players in addressing these concerns.
7. Thematic Tags
technology adoption, privacy concerns, AI trust, user education, innovation barriers