The GAIN AI Act Looks More Like Protectionism Than National Security – Reason
Published on: 2025-09-09
Intelligence Report: The GAIN AI Act Looks More Like Protectionism Than National Security – Reason
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
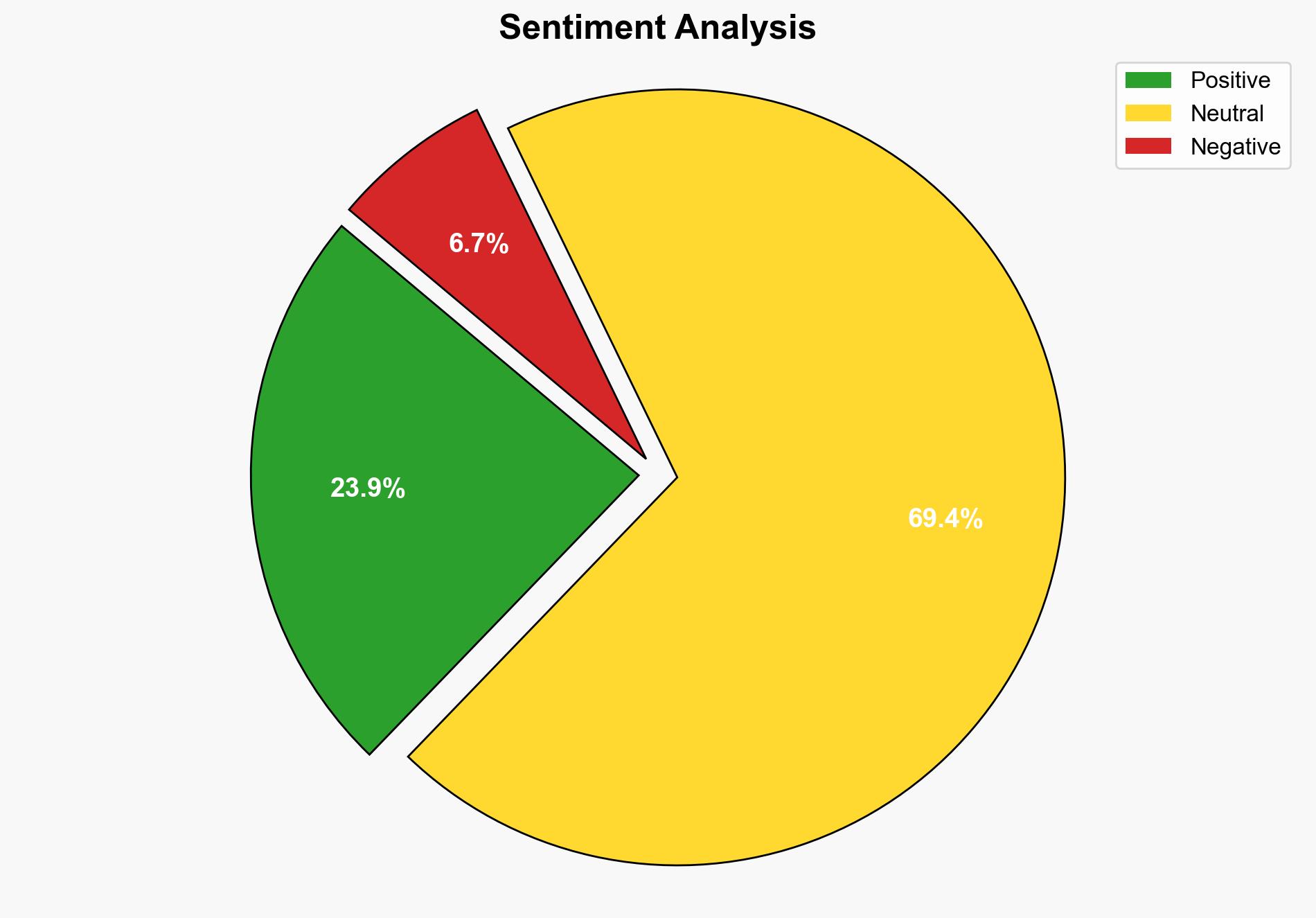
The GAIN AI Act is likely to be more protectionist than a genuine national security measure. This conclusion is supported by evidence that suggests the Act’s primary impact would be to prioritize domestic sales over international competitiveness, potentially harming the U.S. semiconductor industry’s global standing. Confidence Level: Moderate. Recommended action: Re-evaluate the Act’s provisions to balance national security concerns with maintaining global market competitiveness.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **Protectionism Hypothesis**: The GAIN AI Act is primarily a protectionist measure aimed at bolstering domestic semiconductor sales at the expense of global competitiveness. This is supported by the Act’s requirements for companies like Nvidia to prioritize American buyers and obtain export licenses, which could distort supply chains and reduce competitiveness.
2. **National Security Hypothesis**: The GAIN AI Act is genuinely intended to protect national security by restricting the export of advanced AI chips to countries of concern, thereby preventing adversaries from gaining access to critical technologies. This hypothesis is supported by the Act’s alignment with existing export controls and its focus on countries with military ties.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Protectionism Hypothesis Assumptions**: Assumes that the primary motivation is economic rather than security-driven. Assumes that the Act will lead to significant market distortion.
– **National Security Hypothesis Assumptions**: Assumes that the countries targeted by the Act pose a genuine threat to U.S. national security. Assumes that export controls are an effective means of mitigating this threat.
– **Red Flags**: Lack of clear evidence linking the Act’s provisions directly to enhanced national security. Potential bias in interpreting the Act’s economic impact as purely negative.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
– **Economic Risks**: Potential loss of global market share for U.S. semiconductor companies, leading to decreased revenue and innovation capacity.
– **Geopolitical Risks**: Strained relations with allied countries that may view the Act as an overreach or unfair trade practice.
– **Technological Risks**: Slower technological advancement due to reduced competition and collaboration with international partners.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- **Mitigation**: Conduct a thorough impact assessment of the GAIN AI Act on both national security and economic competitiveness. Engage with industry stakeholders to refine the Act’s provisions.
- **Best Case Scenario**: The Act is revised to effectively balance national security and economic interests, maintaining U.S. leadership in the semiconductor industry.
- **Worst Case Scenario**: The Act leads to significant market disruptions and loss of competitiveness, with minimal national security benefits.
- **Most Likely Scenario**: The Act results in moderate market disruption, with some national security benefits but also economic drawbacks.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– Jim Banks: Introduced the GAIN AI Act.
– Nvidia, AMD, Intel: Major semiconductor companies affected by the Act.
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, economic policy, semiconductor industry, protectionism