The Largest Human Project Ever Just Entered Its Final Reactor Phase – BGR
Published on: 2025-10-21
Intelligence Report: The Largest Human Project Ever Just Entered Its Final Reactor Phase – BGR
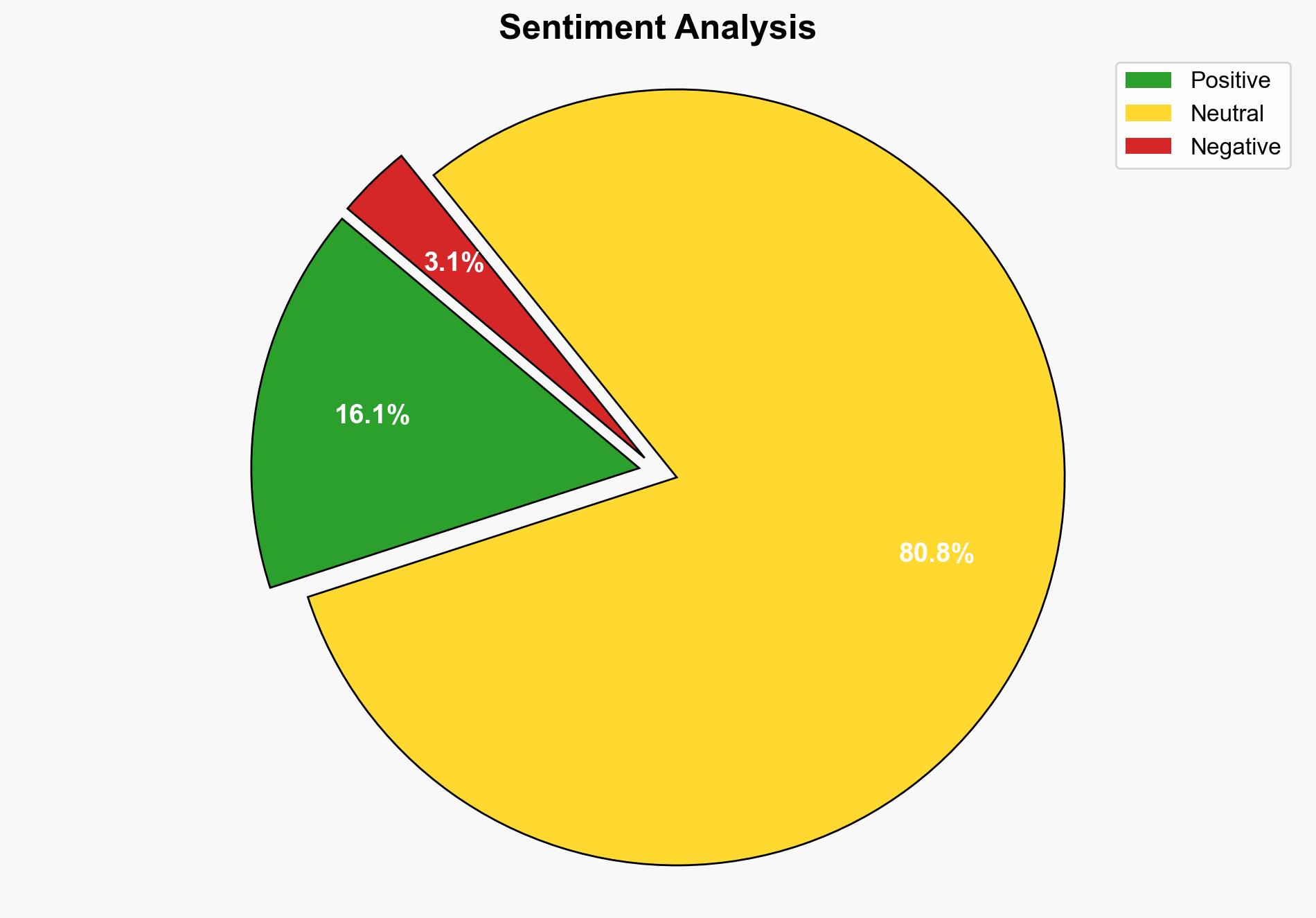
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The ITER project, a significant international fusion energy experiment, has entered its final reactor phase, marking a critical milestone in the quest for sustainable energy. The most supported hypothesis suggests that ITER will successfully demonstrate the feasibility of fusion energy, leading to advancements in commercial fusion projects. Confidence level: Moderate. Recommended action: Monitor technological developments and international collaboration dynamics closely.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **Hypothesis A**: ITER will successfully demonstrate the feasibility of fusion energy, paving the way for commercial fusion power plants.
2. **Hypothesis B**: Technical and geopolitical challenges will hinder ITER’s progress, delaying or preventing the demonstration of fusion feasibility.
Using ACH 2.0, Hypothesis A is better supported due to the project’s advancement to the final reactor phase and the successful completion of critical components like the central solenoid magnet. However, Hypothesis B remains plausible due to potential technical challenges and geopolitical tensions among member countries.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**: The assumption that all technical components will function as expected and that international collaboration will remain stable.
– **Red Flags**: Potential delays in component integration, geopolitical tensions affecting collaboration, and unforeseen technical failures.
– **Blind Spots**: Over-reliance on current technological capabilities and underestimation of geopolitical risks.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
Successful demonstration of fusion energy could revolutionize global energy markets, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and impacting geopolitical power dynamics. However, failure or significant delays could lead to increased skepticism about fusion energy’s viability, affecting future funding and international cooperation. Geopolitical tensions among member countries could also escalate, impacting global stability.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Monitor technological advancements and international collaboration closely to identify potential risks early.
- Engage in diplomatic efforts to ensure stable international cooperation and mitigate geopolitical tensions.
- Scenario-based projections:
- Best Case: Successful demonstration leads to rapid development of commercial fusion plants, transforming energy markets.
- Worst Case: Technical failures and geopolitical tensions cause significant delays or project failure, undermining future fusion energy initiatives.
- Most Likely: Gradual progress with some delays, leading to eventual demonstration of fusion feasibility.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– ITER Organization
– Westinghouse Electric Company
– European Union, China, India, Japan, Korea, Russia, United States (as member countries)
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, energy security, international collaboration, technological innovation, geopolitical dynamics