The open source advantage Faster bugs better builds wider buy-in – VentureBeat
Published on: 2025-04-19
Intelligence Report: The Open Source Advantage – Faster Bugs, Better Builds, Wider Buy-In
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
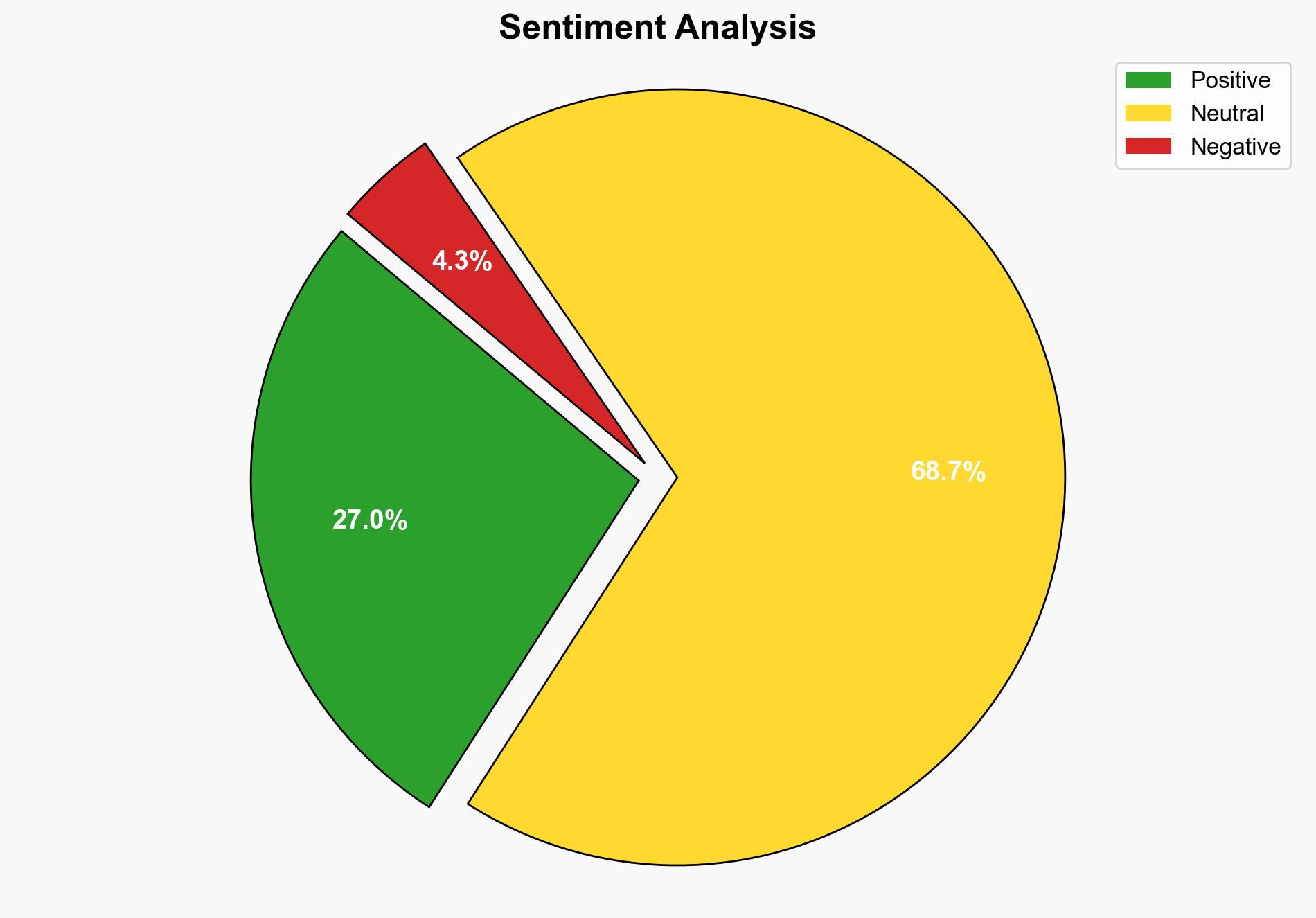
The adoption of open source technology offers significant advantages, including rapid bug resolution, accelerated development cycles, and increased community engagement. However, it also presents challenges such as potential security vulnerabilities and loss of control over proprietary features. Strategic recommendations include leveraging open source for transparency and innovation while maintaining a balance with proprietary solutions to safeguard competitive advantages.
2. Detailed Analysis
The following structured analytic techniques have been applied:
Analysis of Competing Hypotheses (ACH)
Open source adoption can be driven by the need for transparency and community collaboration. Conversely, security breaches may arise from inadequate vetting of open source contributions or insufficient integration with existing security protocols.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths: Community-driven innovation, cost-effectiveness, and rapid deployment.
Weaknesses: Potential security risks, dependency on community support.
Opportunities: Enhanced collaboration, faster time-to-market for new features.
Threats: Intellectual property concerns, reduced control over product evolution.
Indicators Development
Key indicators of emerging cyber threats include increased frequency of unvetted code contributions, heightened activity in open source community forums, and reports of security vulnerabilities in widely-used open source projects.
3. Implications and Strategic Risks
The shift towards open source can disrupt traditional business models, impacting economic stability and competitive positioning. Security vulnerabilities inherent in open source projects pose risks to national infrastructure and corporate data integrity. Politically, open source can democratize technology access, but may also lead to geopolitical tensions over control and influence in tech development.
4. Recommendations and Outlook
- Encourage the adoption of open source for non-critical systems to leverage community innovation while maintaining proprietary control over core technologies.
- Implement robust security protocols for integrating open source solutions to mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
- Consider scenario-based planning to anticipate and respond to shifts in the open source landscape, such as increased regulatory scrutiny or changes in community dynamics.
5. Key Individuals and Entities
Notable figures in the open source community include individuals from HashiCorp and Elastic, who have navigated licensing challenges. The Linux Foundation and the Cloud Native Computing Foundation are pivotal entities promoting open source adoption.