Trump Administration Plans to Collaborate with Private Sector for Offensive Cyber Operations Against Foreign…
Published on: 2025-12-15
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Trump Administration Turning to Private Firms in Cyber Offensive
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
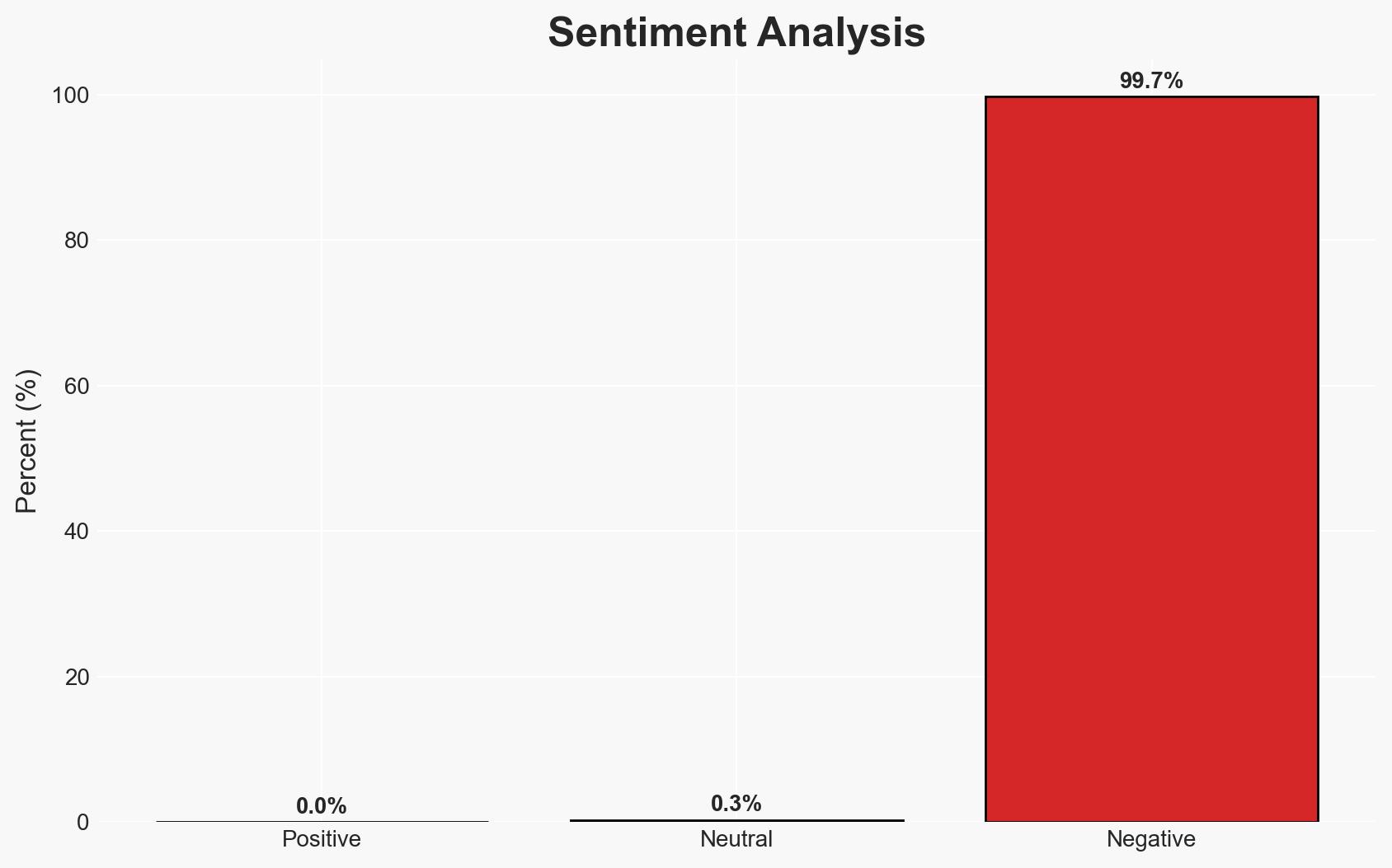
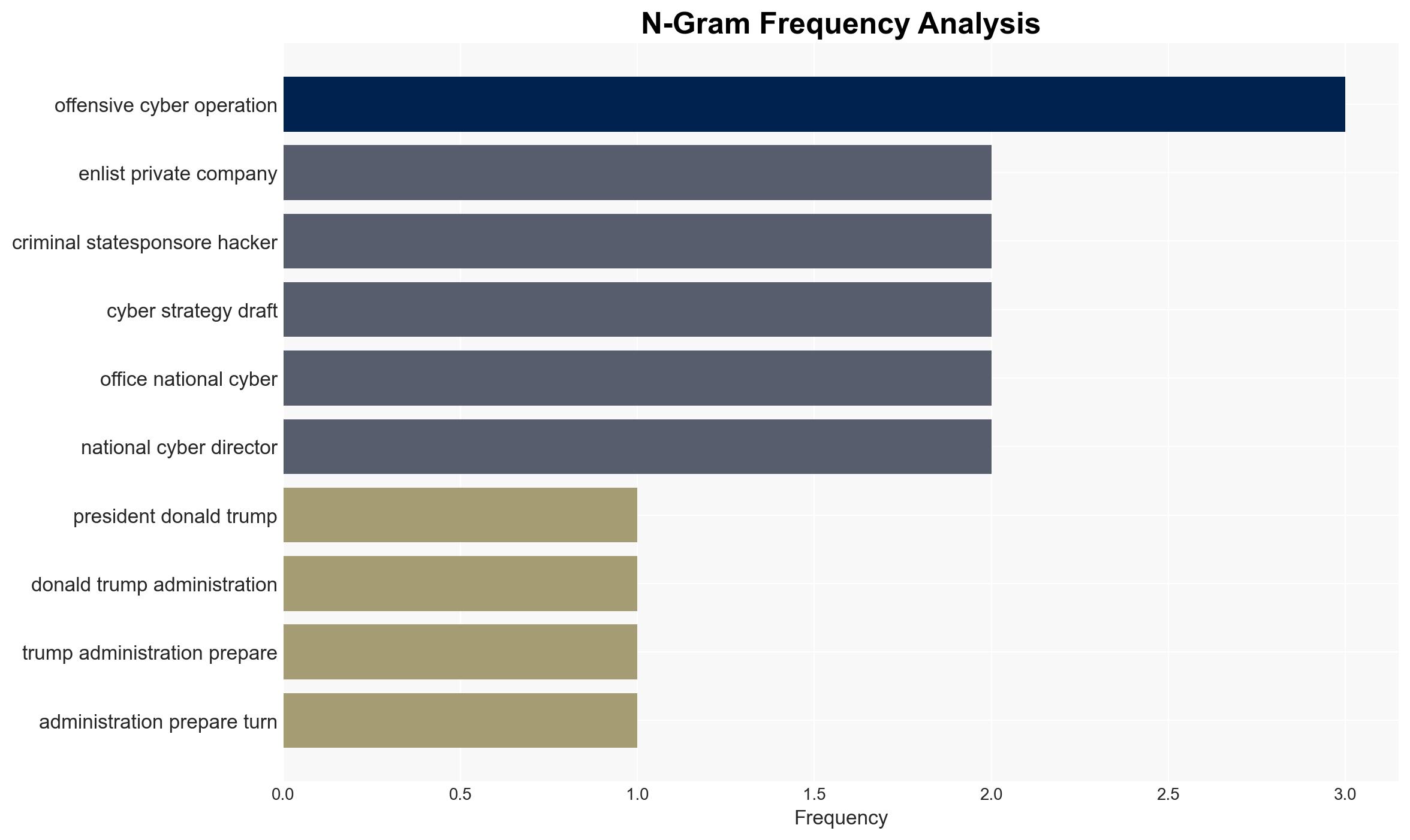
The Trump administration is considering enlisting private companies to conduct offensive cyber operations against foreign adversaries, potentially expanding the U.S. cyber warfare capacity. This move could alter the landscape of cyber conflict and raise legal and operational challenges. Moderate confidence is placed in the hypothesis that this strategy will be pursued, given the draft’s existence and the administration’s stated intentions.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The Trump administration will implement the strategy of using private firms for offensive cyber operations. This is supported by the draft strategy and the administration’s public commitment to enhancing cybersecurity. However, the lack of legal framework and potential international backlash are significant uncertainties.
- Hypothesis B: The strategy will not be implemented due to legal, ethical, and operational challenges. While discussions have occurred, the absence of a finalized policy and potential legislative hurdles could prevent execution.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the administration’s proactive steps and draft strategy, though key indicators such as legal developments and international reactions could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The administration has the political will to pursue this strategy; private firms are willing and capable of conducting offensive operations; legal frameworks can be adapted to support these actions.
- Information Gaps: Specific details on how private firms will be integrated and regulated; the extent of international legal implications; potential reactions from foreign adversaries.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting due to political motivations; risk of deception by adversaries to mislead U.S. cyber strategy development.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could significantly impact the cyber warfare landscape, potentially leading to increased private sector involvement in national security operations and altering international norms.
- Political / Geopolitical: Could escalate tensions with foreign governments and lead to retaliatory cyber actions.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: May enhance U.S. capabilities against state-sponsored cyber threats but could also expose private firms to new security risks.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased complexity in cyber operations and potential challenges in maintaining operational security and oversight.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic opportunities for private firms but also risks of reputational damage and legal liabilities.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor legal developments and international reactions; assess private sector readiness and capability.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop legal frameworks and partnerships; enhance oversight mechanisms to ensure accountability and compliance.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Successful integration of private firms enhances U.S. cyber capabilities without significant backlash.
- Worst: Legal and operational failures lead to international incidents and domestic legal challenges.
- Most-Likely: Gradual implementation with ongoing legal and operational adjustments.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- President Donald Trump
- Office of the National Cyber Director
- Private cybersecurity firms (not specifically identified)
7. Thematic Tags
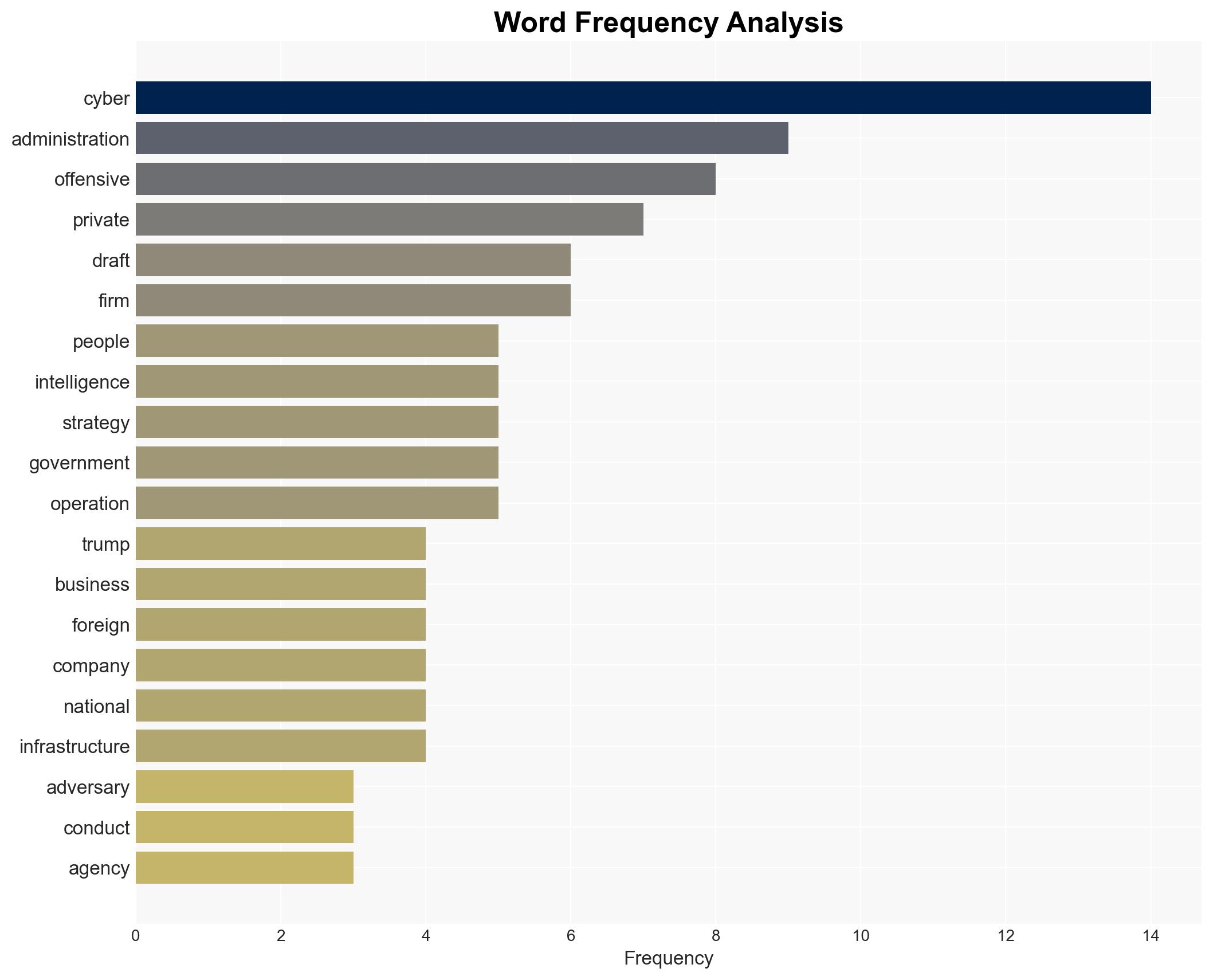
cybersecurity, cyber warfare, private sector involvement, national security, legal frameworks, international relations, cybersecurity strategy, offensive cyber operations
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us