Trust Wallet Chrome Extension Compromised, $8.5 Million Stolen in Shai-Hulud Supply Chain Attack
Published on: 2025-12-31
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Trust Wallet Chrome Extension Hack Drains 85M via Shai-Hulud Supply Chain Attack
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
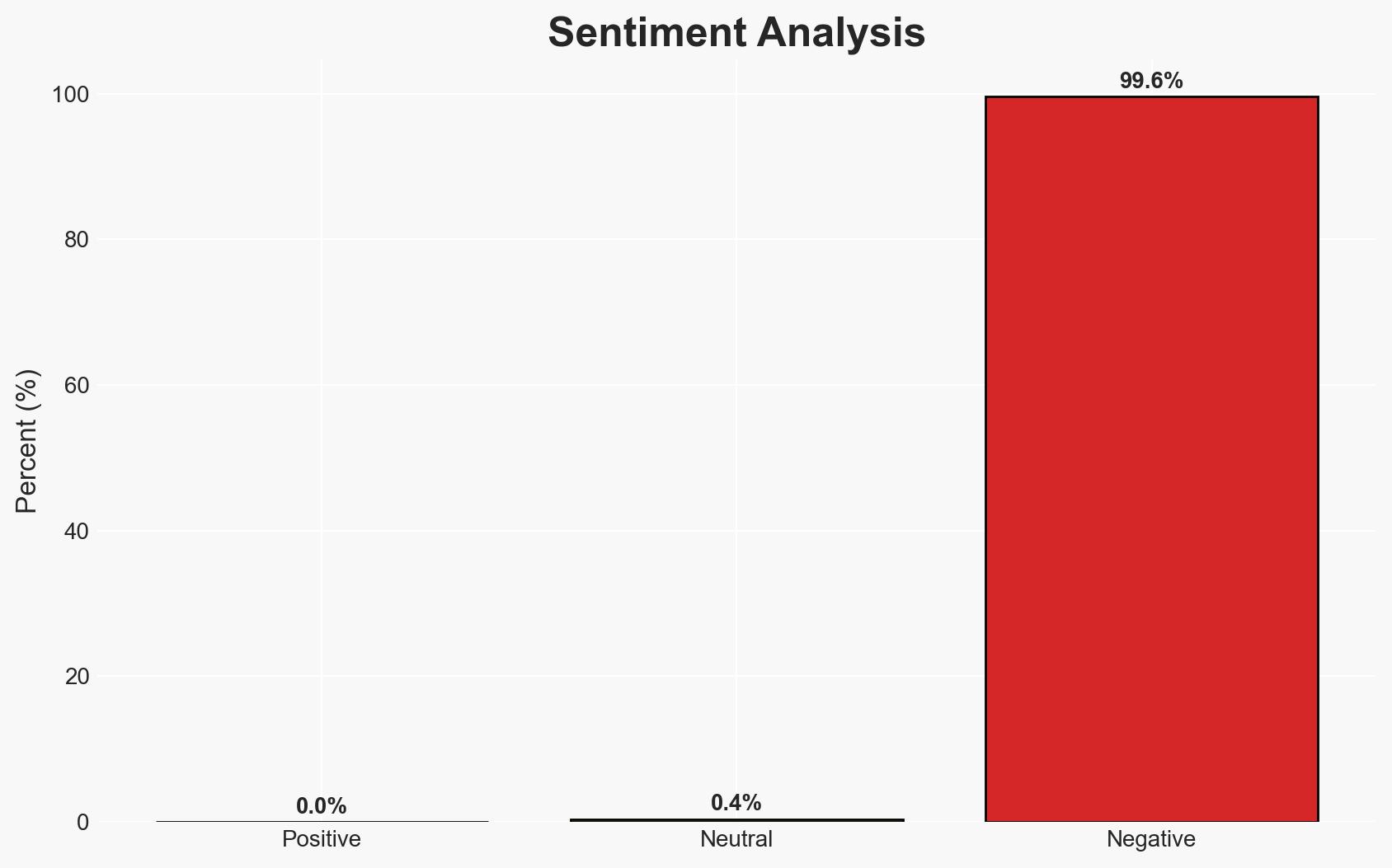
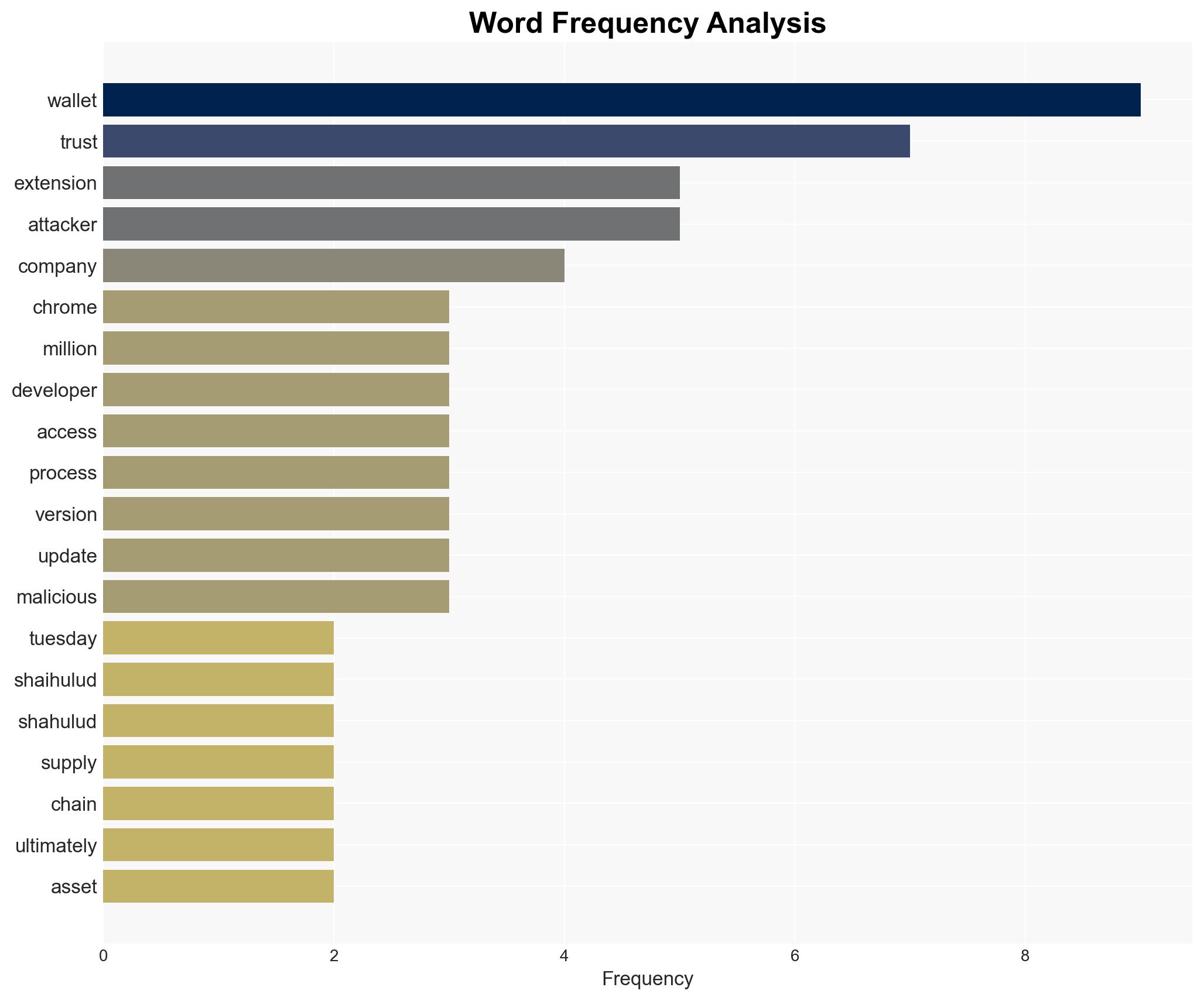
The Shai-Hulud supply chain attack has compromised Trust Wallet’s Chrome extension, resulting in the theft of $8.5 million in cryptocurrency assets. This incident highlights significant vulnerabilities in software supply chains, affecting approximately one million users. The attack underscores the need for enhanced security measures in digital asset management platforms. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The attack was primarily facilitated by the exposure of Trust Wallet’s GitHub secrets, allowing unauthorized access to the Chrome Web Store API and subsequent distribution of a trojanized extension. This hypothesis is supported by the direct evidence of leaked keys and the attacker’s ability to bypass standard release processes. Key uncertainties include the initial method of obtaining the GitHub secrets.
- Hypothesis B: The attack was part of a broader, coordinated campaign targeting multiple organizations through the Shai-Hulud supply chain attack, exploiting common developer tools. While this hypothesis aligns with the industry’s acknowledgment of widespread impact, specific evidence linking the broader campaign directly to this incident is less clear.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to direct evidence of compromised GitHub secrets and API keys. Indicators that could shift this judgment include new evidence of simultaneous attacks on other organizations using similar methods.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Trust Wallet’s internal security protocols were insufficient to prevent the exposure of sensitive credentials; the attack was financially motivated; the attacker had prior knowledge of Trust Wallet’s release processes.
- Information Gaps: The precise method used to initially compromise Trust Wallet’s GitHub secrets; the identity and motivations of the attackers.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in Trust Wallet’s reporting to minimize perceived negligence; possible deception by attackers in masking their true objectives or affiliations.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased scrutiny and regulation of digital asset platforms, influencing industry standards for security. It may also prompt other organizations to reassess their supply chain security measures.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regulatory actions targeting digital asset management and cybersecurity practices.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment for digital financial platforms; potential for similar attacks on other sectors.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased focus on securing software supply chains and enhancing monitoring of developer tools.
- Economic / Social: Loss of user trust in digital wallets; potential financial instability for affected users.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of software supply chains; conduct a comprehensive audit of security protocols; engage with affected users to restore trust.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms for threat intelligence sharing; invest in advanced security technologies for credential protection.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid implementation of security measures restores user confidence and prevents further breaches.
- Worst: Continued vulnerabilities lead to additional attacks and significant financial losses.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in security posture reduce risk but require ongoing vigilance and adaptation.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Trust Wallet
- Google Chrome Web Store
- Upwind researchers Guy Gilad and Moshe Hassan
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, supply chain attack, cryptocurrency, digital wallets, software vulnerabilities, cyber-espionage, threat intelligence
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us