Two US Cybersecurity Professionals Plead Guilty to Extorting Victims for ALPHV Ransomware Gang
Published on: 2025-12-31
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: 2 US Cybersecurity Experts Guilty of Extortion Scheme for ALPHV Ransomware
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
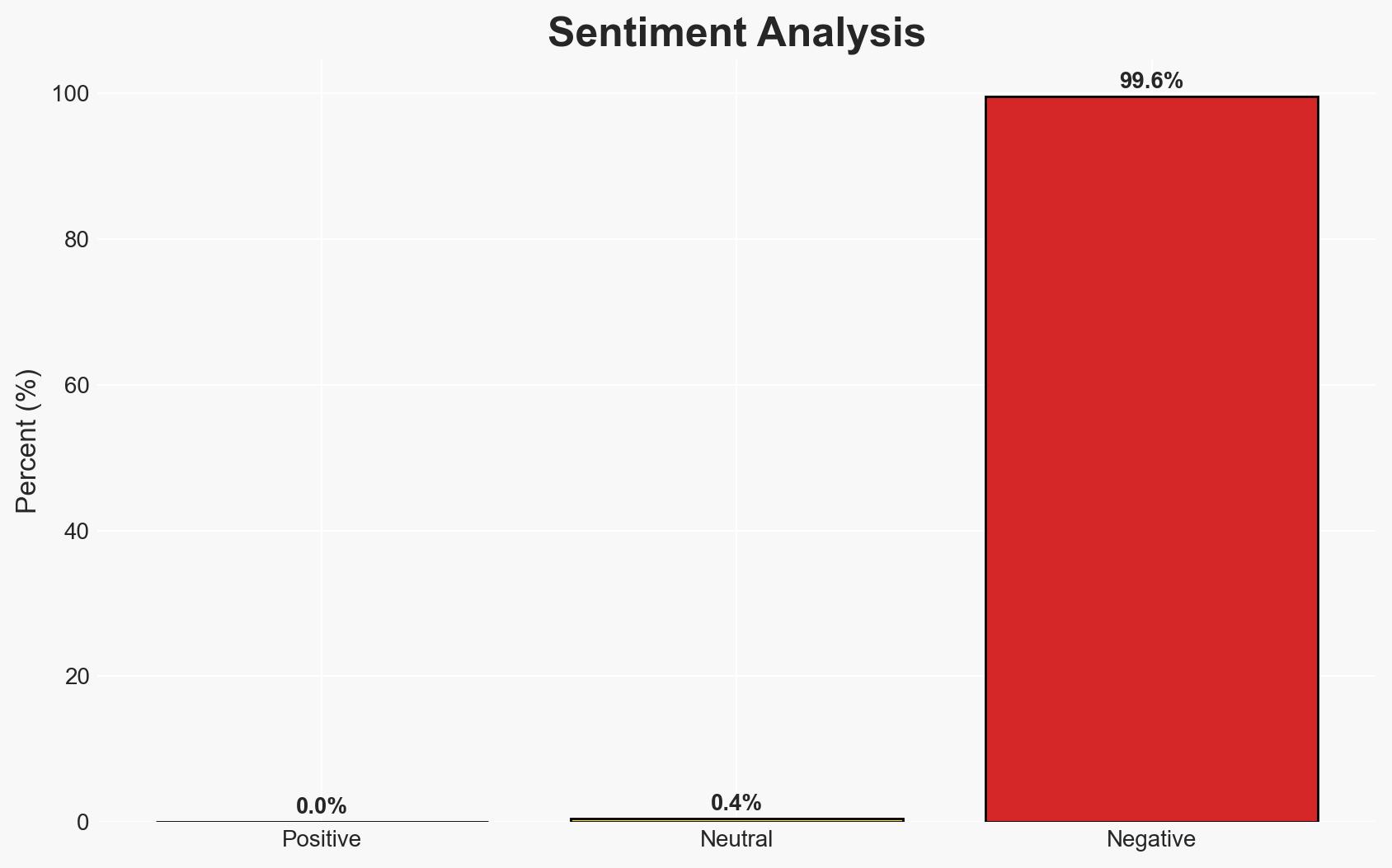
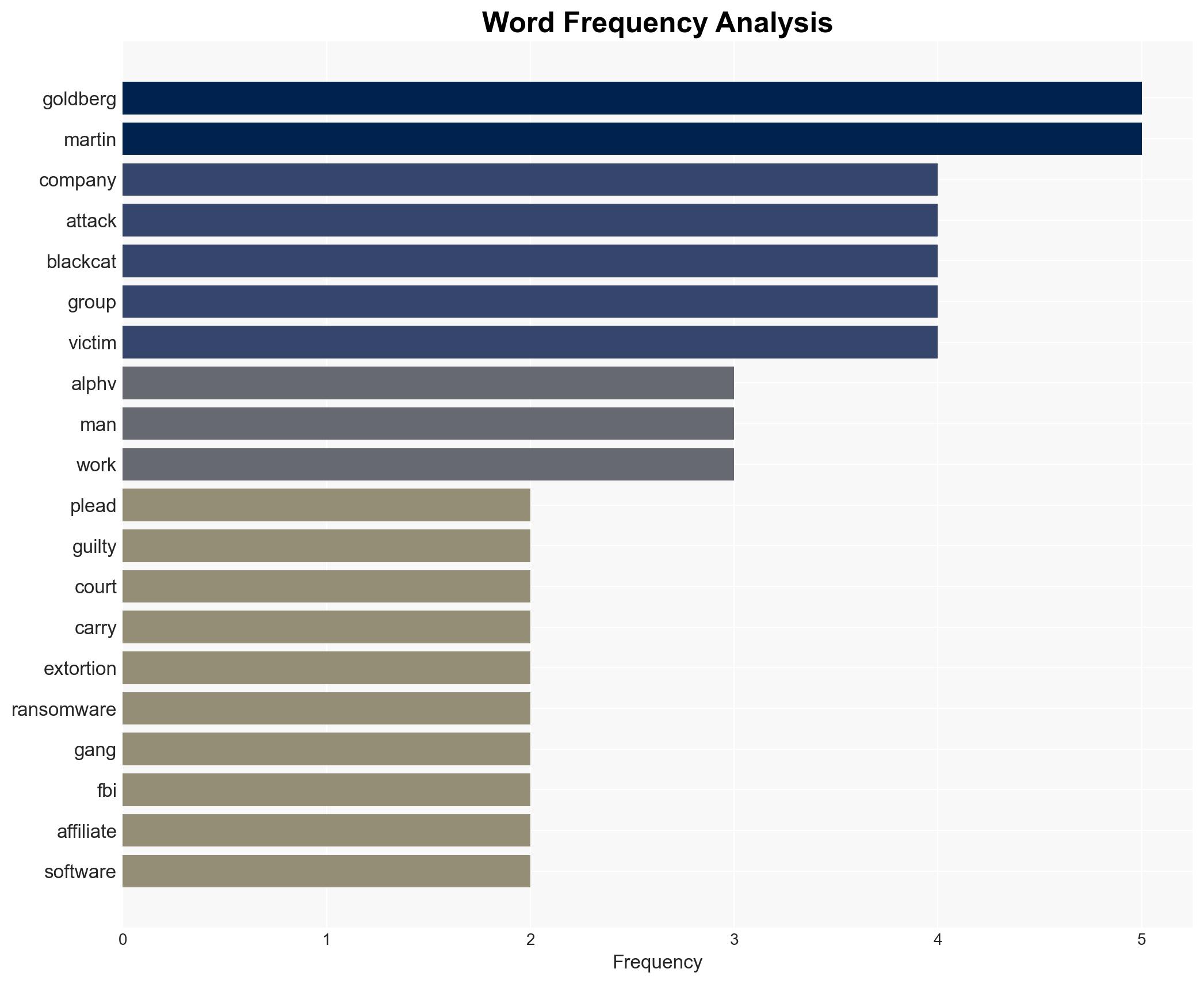
Two US cybersecurity professionals, Ryan Goldberg and Kevin Martin, have been found guilty of participating in an extortion scheme with the ALPHV ransomware group. This case highlights the insider threat risk within cybersecurity sectors, with moderate confidence in the assessment that insider knowledge was leveraged to bypass defenses. The incident affects both national and international cybersecurity landscapes, emphasizing the need for enhanced internal security measures.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Goldberg and Martin exploited their insider knowledge from their cybersecurity roles to effectively conduct extortion attacks for ALPHV. This is supported by their employment at firms focused on cyber defense and their successful execution of attacks. However, the full extent of their internal access and how it was utilized remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The involvement of Goldberg and Martin was opportunistic, with limited direct use of insider knowledge, relying more on the tools and strategies provided by ALPHV. This is contradicted by their professional roles, which likely provided significant insights into defensive measures.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the direct correlation between their professional expertise and the sophistication of the attacks. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include further revelations about their operational methods or additional co-conspirators.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The individuals had significant insider access; ALPHV’s RaaS model was critical to their operations; insider threats are a growing risk in cybersecurity firms.
- Information Gaps: Details on the specific methods used to bypass security defenses; the extent of their network within ALPHV; potential additional insiders.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in underestimating the role of external factors; possible deception by the defendants regarding their level of involvement.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development underscores the vulnerability of organizations to insider threats and the sophistication of modern ransomware operations. It may lead to increased scrutiny and regulatory pressure on cybersecurity firms.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased international cooperation against ransomware threats.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened alertness to insider threats within critical infrastructure sectors.
- Cyber / Information Space: Possible escalation in ransomware sophistication and targeting of cybersecurity professionals.
- Economic / Social: Increased costs for cybersecurity measures and potential loss of trust in cybersecurity firms.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of insider activities within cybersecurity firms; initiate a review of current security protocols.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for intelligence sharing on ransomware threats; invest in employee vetting and training programs.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Improved internal security measures reduce insider threats.
- Worst: Increased insider attacks lead to significant breaches and financial losses.
- Most-Likely: Gradual improvement in detecting and mitigating insider threats with ongoing challenges.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Ryan Goldberg, Kevin Martin, ALPHV (BlackCat) ransomware group, Sygnia, DigitalMint
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, insider threat, ransomware, extortion, cybercrime, law enforcement, information security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us