U.S. Military Action in Venezuela: A New Chapter in the Ongoing Drug War Narrative
Published on: 2026-01-08
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
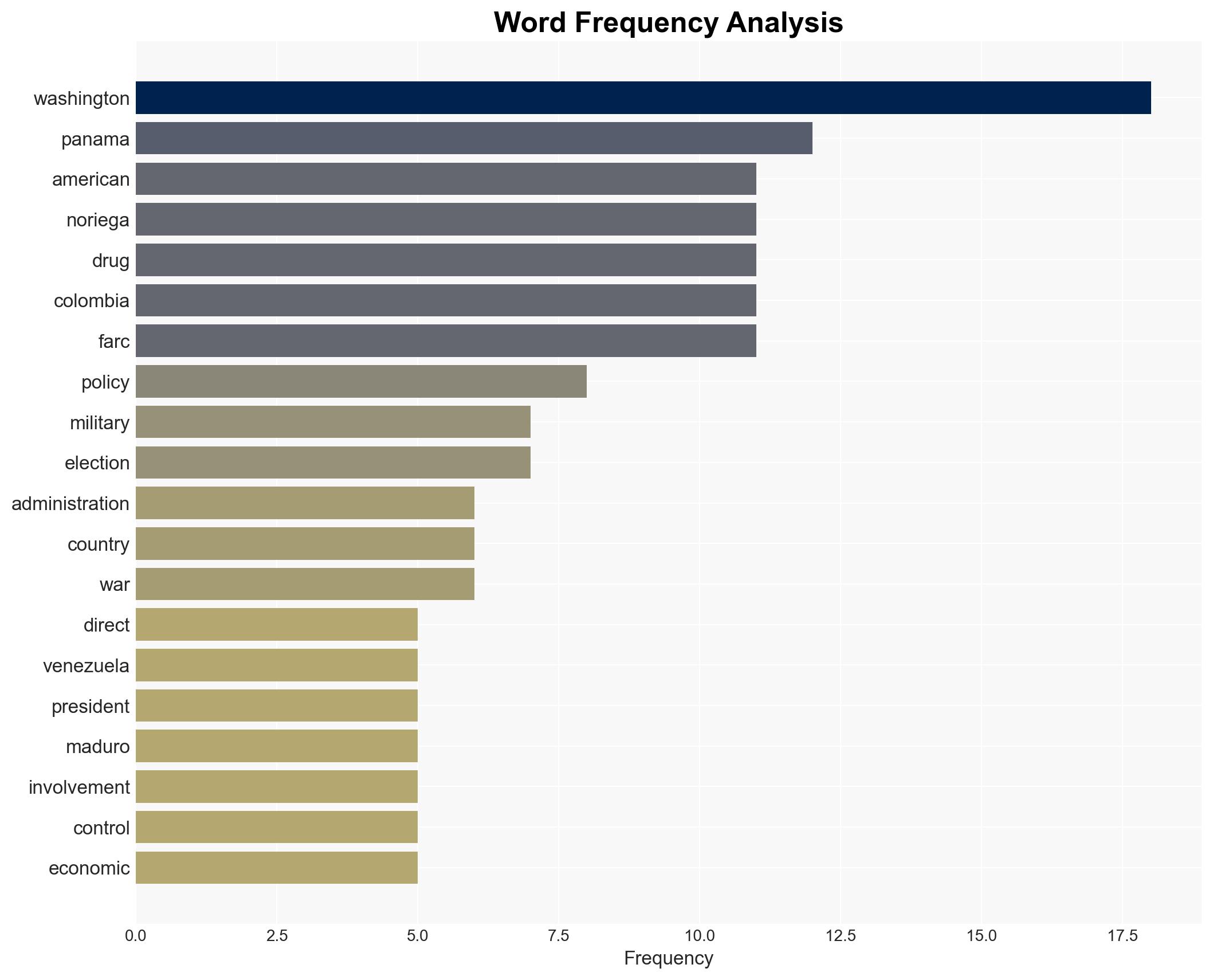
Intelligence Report: Panama Colombia and Venezuela The Perpetual Fraud of the War on Drugs
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
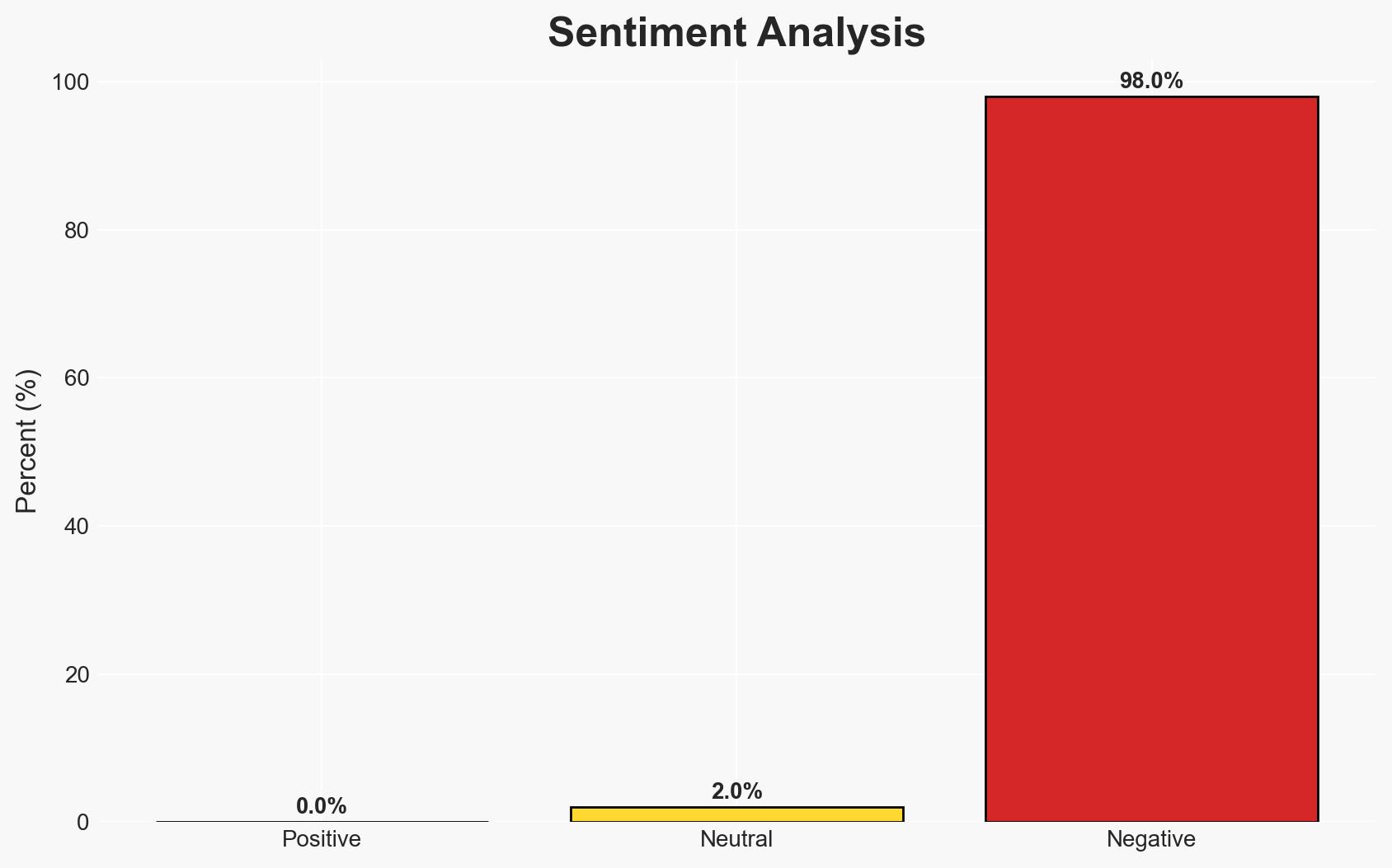
The U.S. military action against Venezuela, justified by claims of combating drug trafficking and restoring democracy, mirrors historical precedents such as the Panama invasion. This operation may be driven by both security concerns and geopolitical interests, particularly Venezuela’s vast oil reserves. The primary hypothesis is that U.S. actions are motivated by a combination of national security and strategic resource acquisition. Confidence in this assessment is moderate due to potential biases and incomplete information.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The U.S. intervention in Venezuela is primarily motivated by national security concerns related to drug trafficking and the desire to restore democracy. Supporting evidence includes official U.S. statements and historical parallels with Panama. Contradicting evidence includes skepticism about the true motivations behind such interventions.
- Hypothesis B: The U.S. intervention is driven by strategic interests in Venezuela’s oil reserves, using drug trafficking and democratic restoration as pretexts. This is supported by the timing of the intervention and the economic value of Venezuelan resources. Contradicting evidence includes the potential genuine security threats posed by drug networks.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the historical pattern of U.S. interventions aligning with strategic resource interests. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include new evidence of direct security threats from Venezuela or changes in U.S. policy rhetoric.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The U.S. has the capability and intent to act on both security and strategic resource motivations; Venezuela’s government is significantly involved in drug trafficking; U.S. public statements reflect true intentions.
- Information Gaps: Detailed intelligence on the scale of Venezuela’s drug trafficking operations and internal U.S. decision-making processes.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential cognitive bias in interpreting U.S. actions as purely self-serving; source bias from official U.S. statements; possible manipulation in the portrayal of Venezuela’s government.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development may exacerbate regional tensions and influence U.S.-Latin America relations. It could lead to increased instability in Venezuela and impact global oil markets.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for strained diplomatic relations with countries opposing U.S. actions; risk of regional alliances forming against U.S. influence.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Possible escalation of retaliatory actions by Venezuelan or allied groups; changes in regional security dynamics.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased propaganda and misinformation campaigns by both state and non-state actors; potential cyber operations targeting U.S. interests.
- Economic / Social: Disruption in oil markets; potential humanitarian crisis in Venezuela due to political instability and economic sanctions.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance intelligence collection on Venezuelan networks; engage diplomatically with regional allies to mitigate tensions; monitor oil market fluctuations.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for potential cyber threats; strengthen partnerships with Latin American countries; assess long-term impacts on U.S. strategic interests.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Stabilization and democratic transition in Venezuela; Worst: Escalation of conflict and regional destabilization; Most-Likely: Prolonged tension with intermittent diplomatic engagements. Triggers include shifts in Venezuelan governance or U.S. policy changes.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
Counter-Terrorism, drug trafficking, U.S. foreign policy, Venezuela, oil reserves, regional stability, geopolitical strategy
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- ACH 2.0: Reconstruct likely threat actor intentions via hypothesis testing and structured refutation.
- Indicators Development: Track radicalization signals and propaganda patterns to anticipate operational planning.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Analyze spread/adaptation of ideological narratives for recruitment/incitement signals.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Counter-Terrorism Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us