U.S. Military Action in Venezuela Signals Shift Toward Autocratic Governance on Global Stage
Published on: 2026-01-07
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: 2026 begins with an increasingly autocratic United States rising on the global stage
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
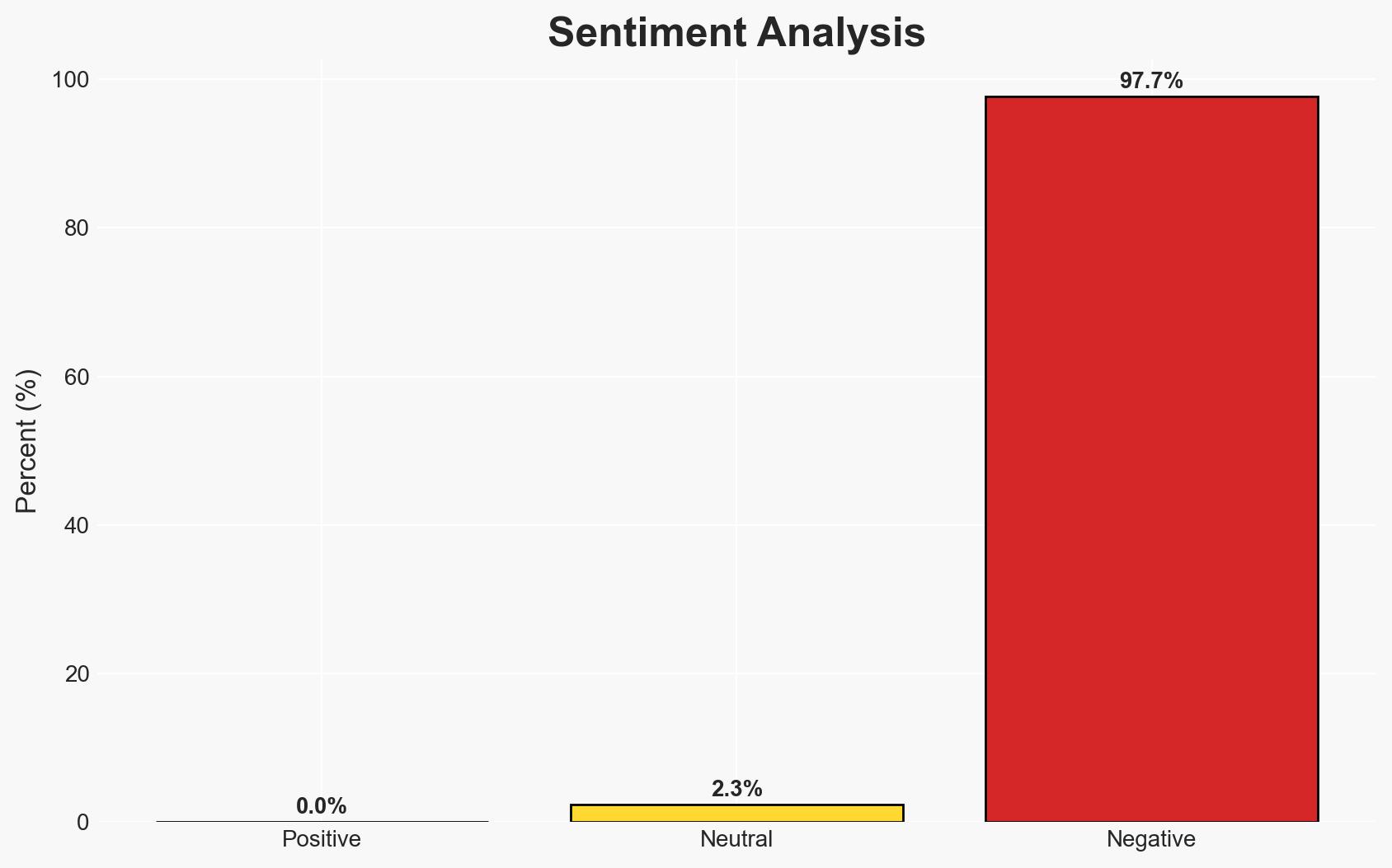
The United States’ military intervention in Venezuela marks a significant shift towards autocratic governance under President Donald Trump, emphasizing unilateral military action over traditional diplomatic engagement. This development could destabilize regional geopolitics and undermine international legal norms. The most likely hypothesis is that this reflects a broader strategic pivot in U.S. foreign policy, prioritizing economic interests and military dominance. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the lack of comprehensive data on internal U.S. decision-making processes.
2. Competing Hypotheses
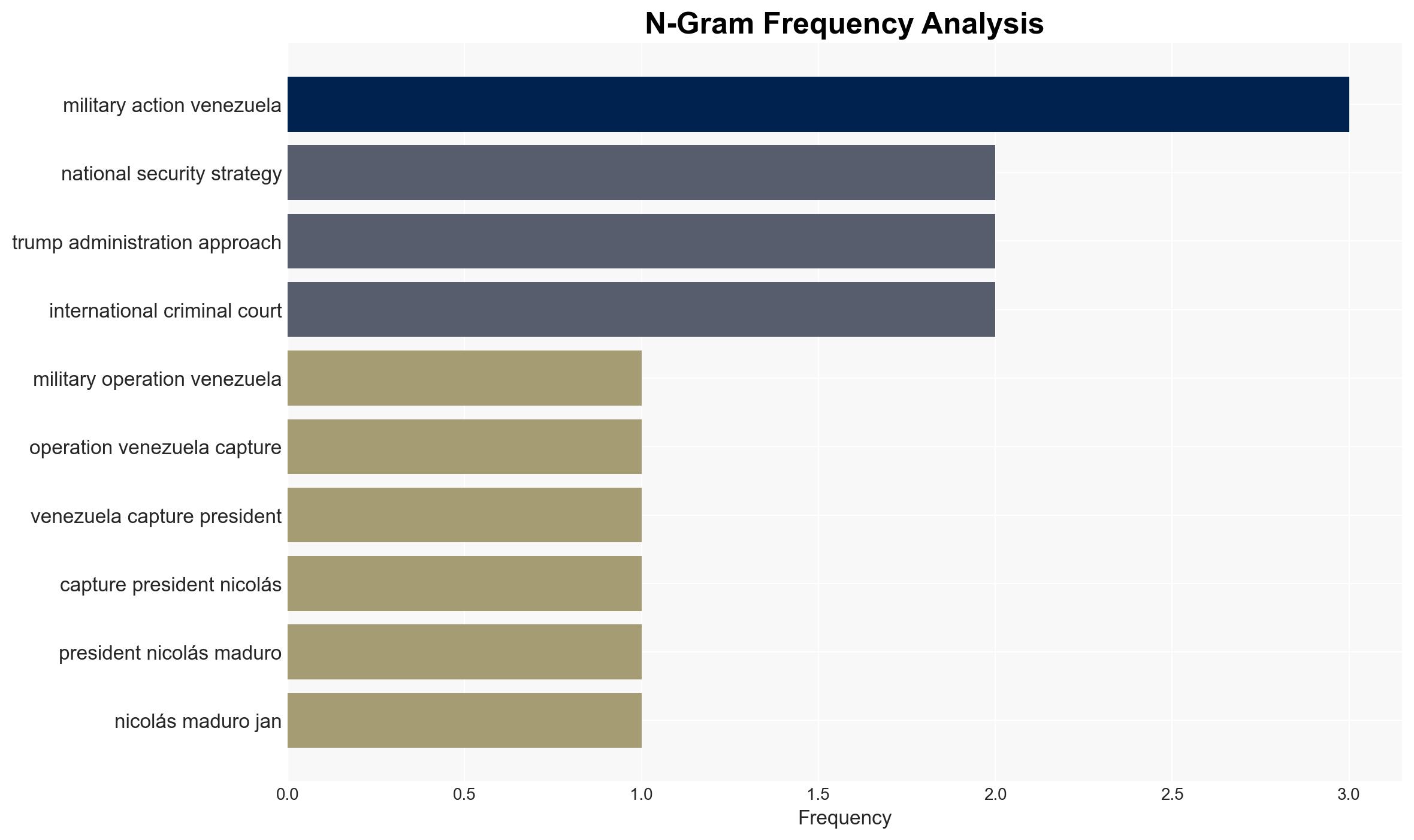
- Hypothesis A: The U.S. intervention in Venezuela is part of a deliberate strategy to assert control over the Western Hemisphere, driven by economic interests, particularly oil. This is supported by the military buildup and the explicit mention of oil interests. However, the lack of congressional or U.N. approval raises legal and ethical questions.
- Hypothesis B: The intervention is a tactical move to distract from domestic issues or consolidate political power internally. This is less supported by the available evidence, as the focus on economic interests and military strategy is more consistent with broader policy shifts.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the alignment with stated policy goals and military actions. Indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in domestic U.S. political dynamics or new information on internal decision-making processes.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The U.S. prioritizes economic interests over international norms; military actions are primarily driven by strategic resource acquisition; the Trump administration will continue to bypass traditional diplomatic channels.
- Information Gaps: Detailed insights into internal U.S. decision-making processes; comprehensive data on regional responses and alliances; clarity on long-term U.S. strategic objectives.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in interpreting U.S. actions as purely economically driven; risk of underestimating domestic political motivations; possible manipulation of public narratives to justify military actions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased regional instability and a shift in global power dynamics, challenging existing alliances and international norms.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for strained relations with traditional allies; increased influence of autocratic regimes globally.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of regional conflicts and insurgencies; potential for retaliatory actions against U.S. interests.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased cyber operations targeting U.S. infrastructure; potential for misinformation campaigns to shape public perception.
- Economic / Social: Disruption in global oil markets; potential economic sanctions or trade disruptions affecting U.S. economy.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor regional military movements and diplomatic communications; assess potential for retaliatory actions; engage with allies to mitigate geopolitical tensions.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen alliances and partnerships to counterbalance U.S. unilateral actions; develop resilience measures for potential economic disruptions.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: U.S. actions lead to a stable geopolitical realignment with minimal conflict.
- Worst: Escalation into broader regional conflicts with significant global economic impact.
- Most-Likely: Continued U.S. assertiveness with periodic regional tensions and economic fluctuations.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- President Donald Trump
- President Nicolás Maduro
- U.S. Department of State
- U.S. Military
- National Security Experts
7. Thematic Tags
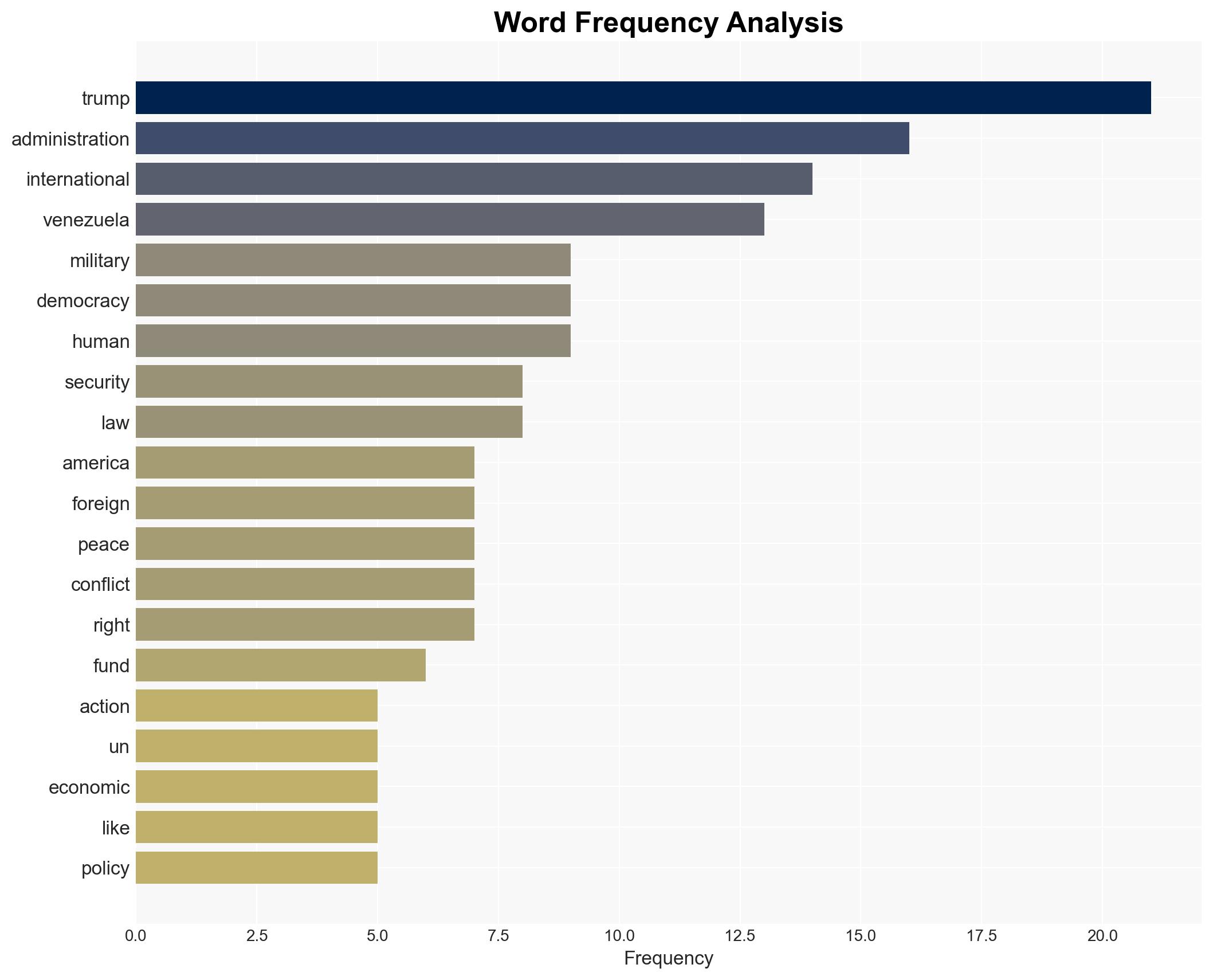
national security threats, autocracy, military intervention, U.S. foreign policy, Venezuela, international law, geopolitical strategy, economic interests
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us