UK Businesses Face Rising Costs Due to Uncontrollable Supply Chain Cyberattacks
Published on: 2025-11-28
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Supply chain cyberattacks are becoming unmanageable – and UK businesses are paying the price
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
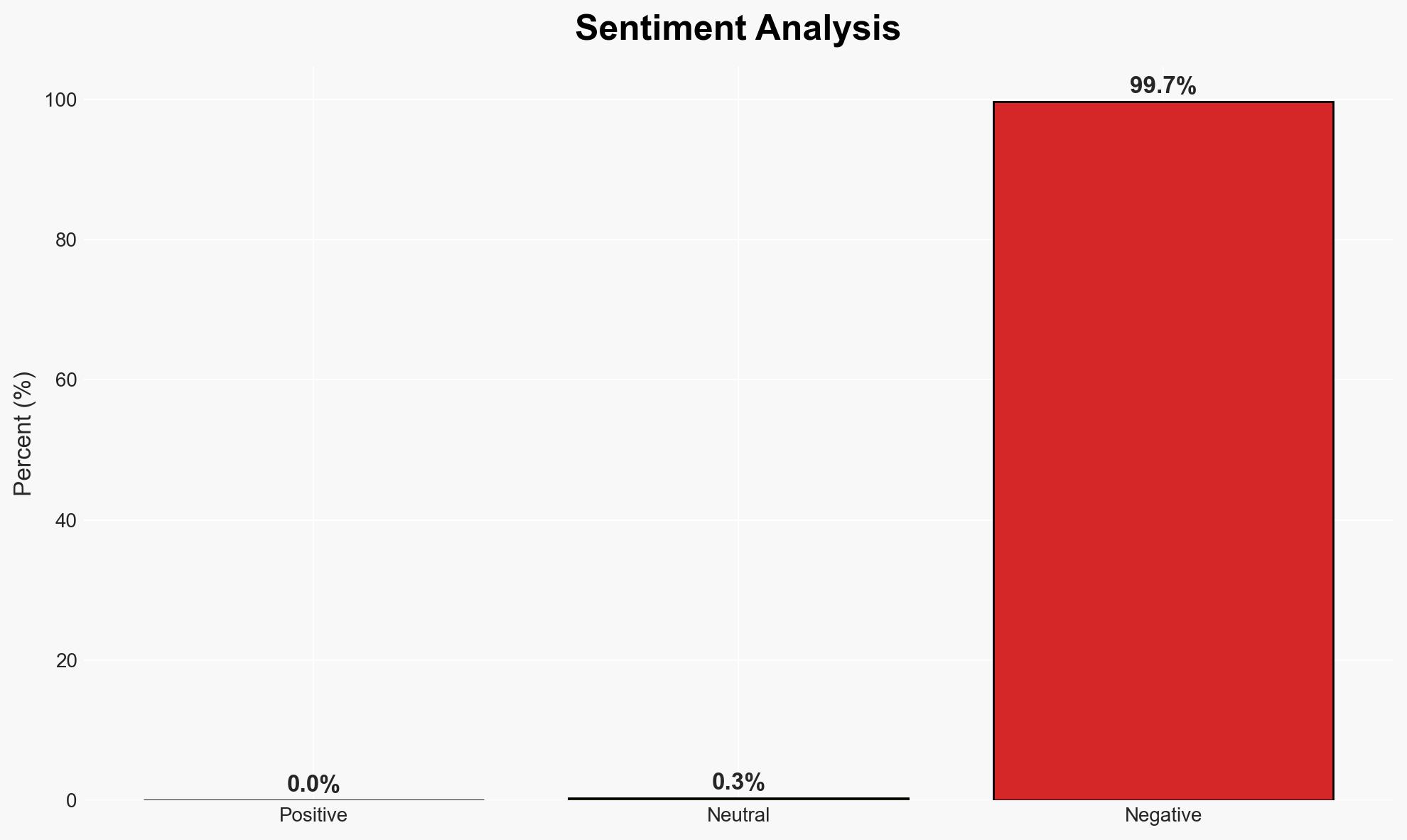
Supply chain cyberattacks are increasingly impacting UK businesses, leading to operational disruptions and financial losses. The most likely hypothesis is that attackers are exploiting vulnerabilities in smaller suppliers to access larger networks. This situation poses a significant risk to national economic stability and security. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to existing information gaps and potential biases in source reporting.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Cybercriminals are primarily targeting smaller suppliers within the supply chain to exploit their weaker cybersecurity measures, thereby gaining access to larger, more secure organizations. This is supported by evidence of recent breaches involving small vendors and the “island hopping” tactic. However, uncertainty remains about the full extent of these vulnerabilities across different sectors.
- Hypothesis B: The increase in supply chain cyberattacks is due to a broader systemic failure in cybersecurity practices across all levels of the supply chain, not just smaller suppliers. This hypothesis is less supported by specific evidence but aligns with general trends of inadequate cybersecurity measures and overconfidence in existing defenses.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to specific incidents involving smaller suppliers being exploited. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of similar breaches in larger, well-protected organizations or systemic vulnerabilities being exploited across the board.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Organizations are not fully aware of the vulnerabilities within their supply chains; smaller suppliers generally have weaker cybersecurity measures; attackers prefer easier targets with indirect access to larger networks.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the cybersecurity posture of smaller suppliers and the specific methods used by attackers to exploit these vulnerabilities.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting from cybersecurity firms aiming to promote their services; lack of independent verification of breach details; possible underreporting by affected organizations.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The trend of increasing supply chain cyberattacks could exacerbate vulnerabilities in critical national infrastructure and economic stability. If unchecked, this could lead to more significant disruptions and a loss of trust in digital supply chains.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regulatory scrutiny and international cooperation on cybersecurity standards.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment as cybercriminals and state actors exploit supply chain vulnerabilities for espionage or sabotage.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased focus on securing digital supply chains and enhancing vendor cybersecurity practices.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic downturn due to operational disruptions and financial losses; erosion of consumer trust in digital transactions.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a comprehensive audit of supply chain cybersecurity practices; enhance monitoring of smaller suppliers; increase awareness and training on supply chain risks.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms for better threat intelligence; invest in advanced cybersecurity technologies; establish clear protocols for breach response.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Enhanced cybersecurity measures lead to a significant reduction in successful supply chain attacks.
- Worst: Continued attacks result in major disruptions to critical infrastructure and economic stability.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in cybersecurity posture reduce but do not eliminate the threat, with ongoing incidents at a manageable level.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
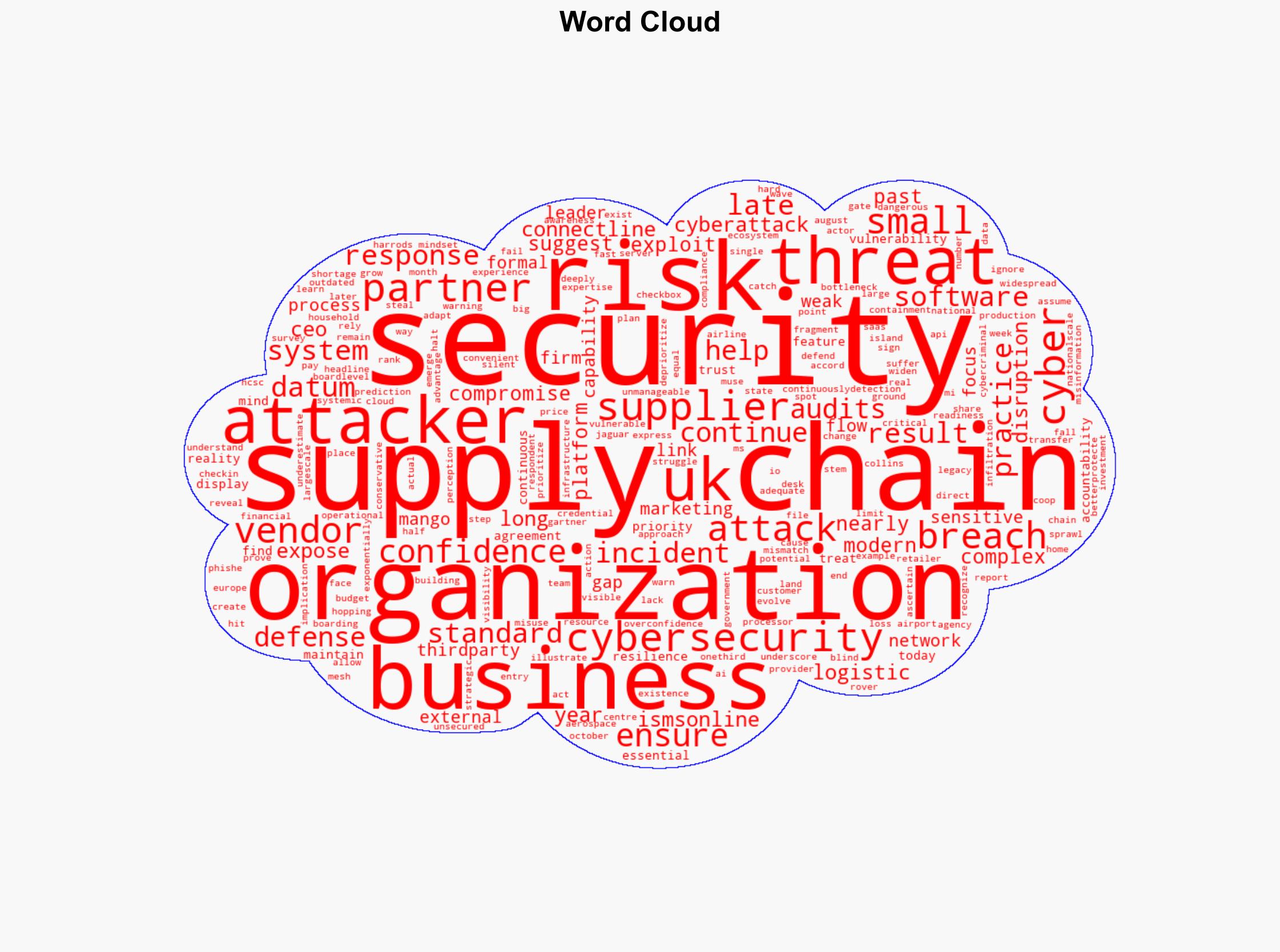
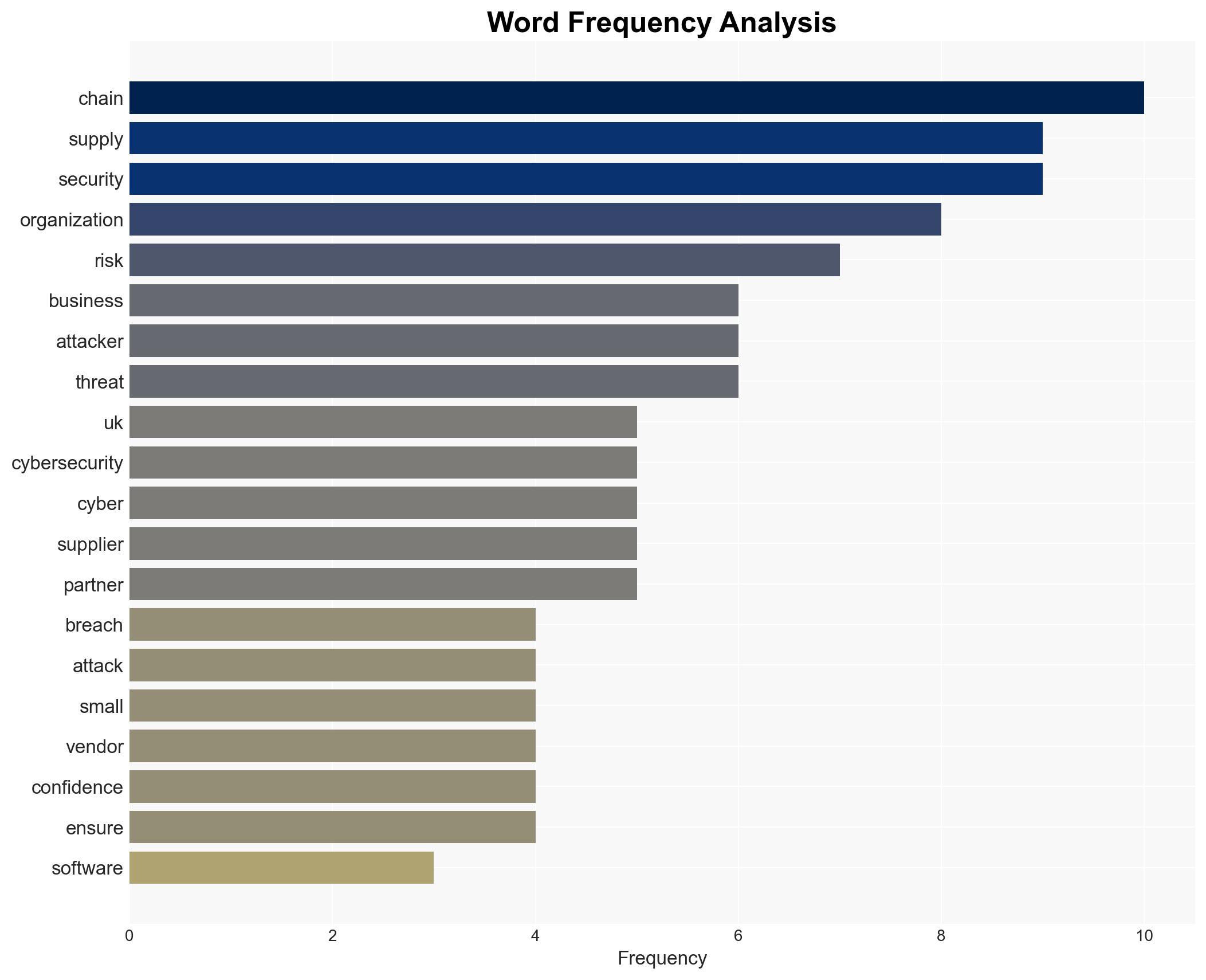
Cybersecurity, supply chain security, cyberattacks, UK businesses, cybersecurity vulnerabilities, economic impact, digital supply chains, national security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us