UK Executives Fear Business Collapse Due to Cyber-Attack Risks, Vodafone Survey Reveals
Published on: 2026-01-22
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: UK Executives Warn They May Not Survive a Major Cyber-Attack Vodafone Survey Finds
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
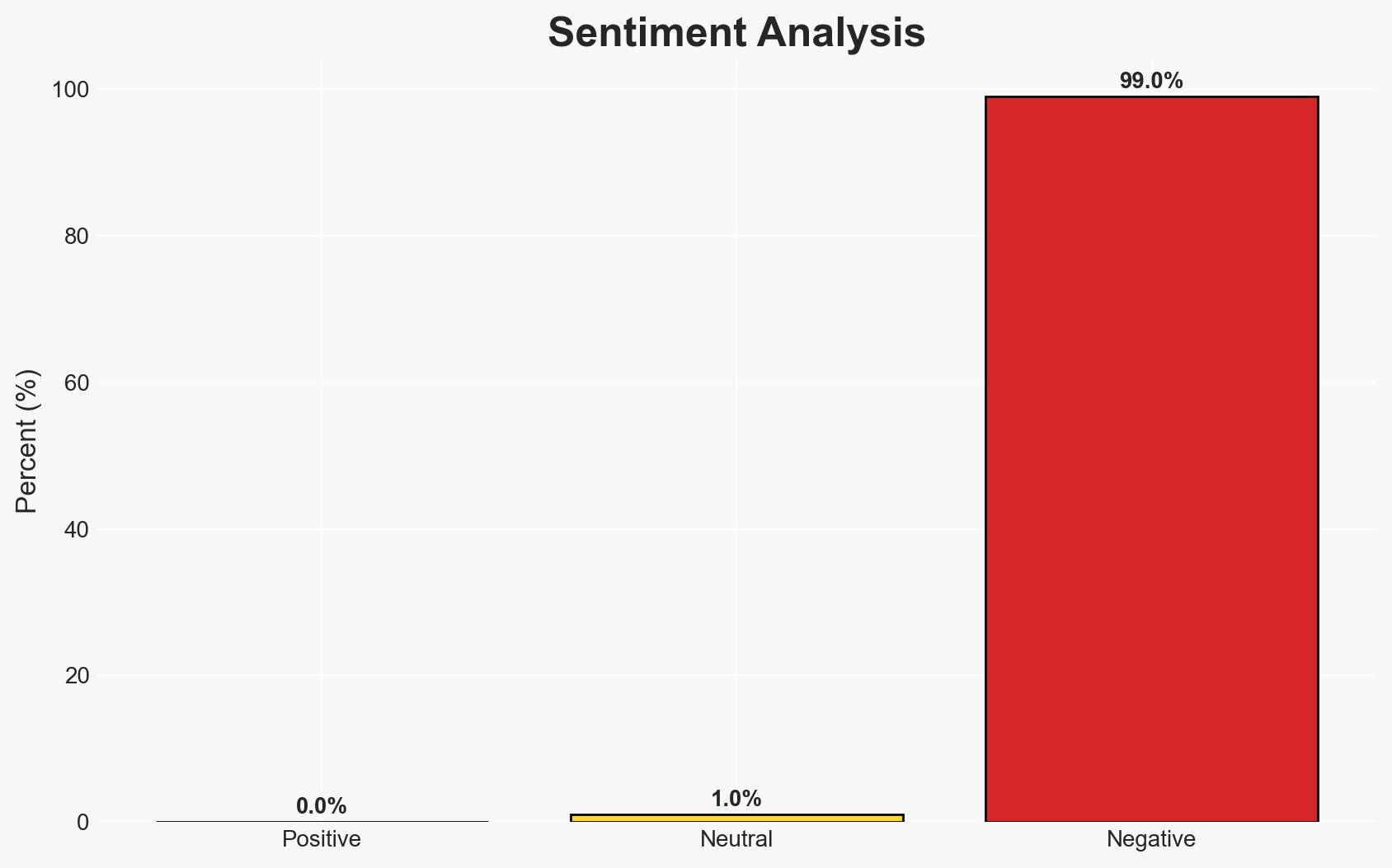
The Vodafone survey indicates that UK businesses are increasingly aware of cyber threats, but many remain inadequately prepared, with some executives fearing insolvency following a major cyber-attack. The most likely hypothesis is that while awareness has increased, actionable preparedness has not kept pace, posing significant risks to business continuity. Confidence in this assessment is moderate due to limited data on actual preparedness measures.
2. Competing Hypotheses
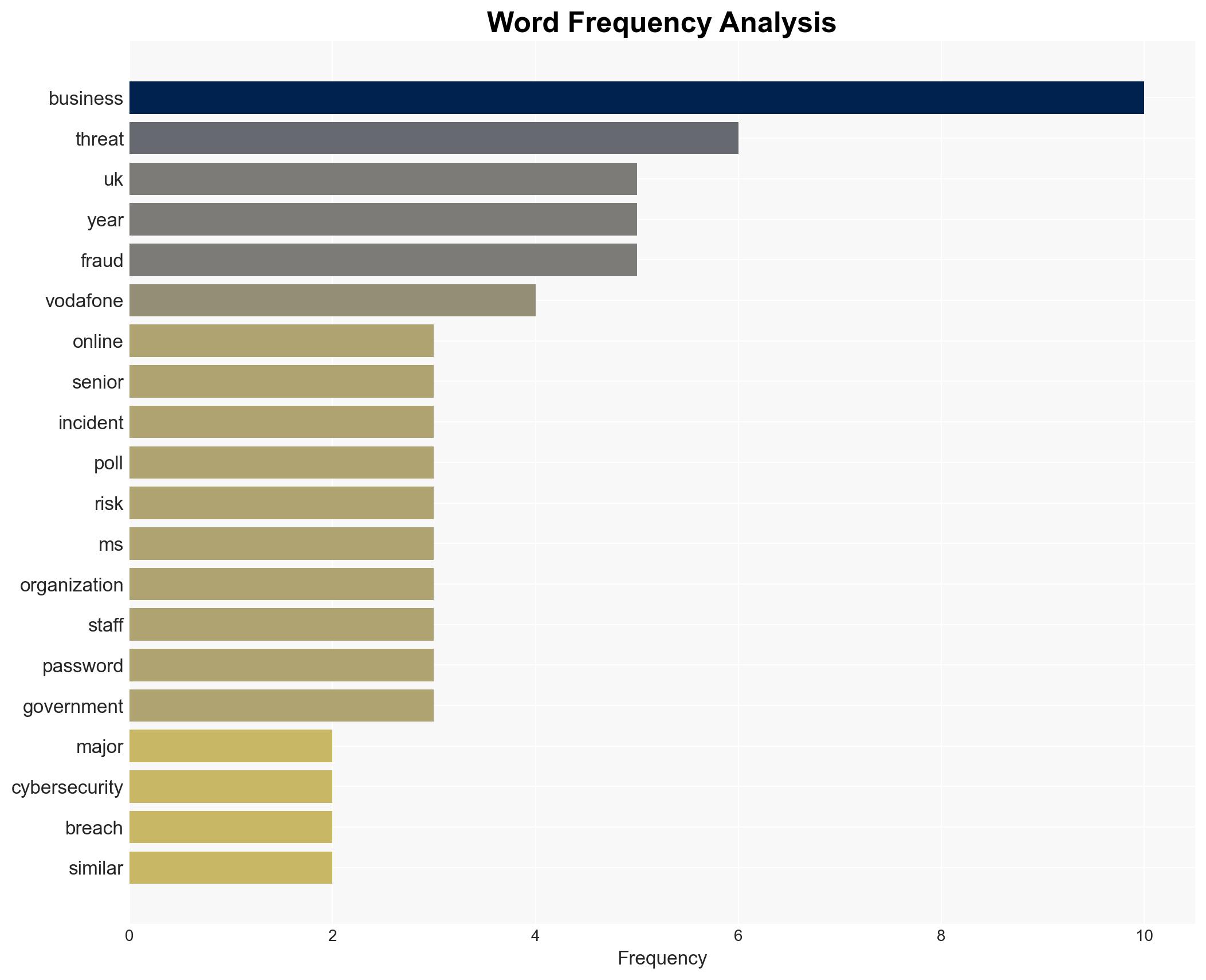
- Hypothesis A: UK businesses are aware of cyber threats and are actively improving their defenses. Evidence includes increased awareness from past breaches and government initiatives like the Fraud Sector Charter. However, the lack of widespread cyber-awareness training and password security practices contradicts this.
- Hypothesis B: Despite increased awareness, UK businesses are not significantly improving their cybersecurity measures. Supporting evidence includes the high percentage of businesses at risk and poor password practices. Contradicting evidence includes government initiatives aimed at improving cybersecurity.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the evidence of inadequate preparedness and poor security practices. Indicators that could shift this judgment include widespread implementation of government-recommended security measures and improved training statistics.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Businesses are accurately reporting their cybersecurity practices; government initiatives will be effectively implemented; the survey sample is representative of the broader business landscape.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on specific cybersecurity measures implemented by businesses; metrics on the effectiveness of government initiatives.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in self-reported survey data; over-reliance on high-profile breaches to gauge overall risk; possible underreporting of successful cybersecurity improvements.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The current state of cybersecurity preparedness in UK businesses could lead to significant economic disruptions if major attacks occur. The interaction between increased awareness and inadequate action may exacerbate vulnerabilities.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased pressure on the government to enforce stricter cybersecurity regulations and support businesses in enhancing defenses.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of cyber-attacks being used as tools for economic disruption or political leverage.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential increase in cybercrime targeting poorly secured businesses; proliferation of AI-driven threats like deepfakes.
- Economic / Social: Potential for significant financial losses and business closures, leading to job losses and economic instability.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Encourage businesses to conduct cybersecurity audits; promote government resources and initiatives; increase awareness of password security practices.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop public-private partnerships to enhance cybersecurity resilience; invest in training programs; monitor the implementation of the Fraud Sector Charter.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid improvement in cybersecurity practices, leading to reduced vulnerability.
- Worst: Major cyber-attack causing widespread business failures and economic impact.
- Most-Likely: Gradual improvement with ongoing risks due to slow adoption of best practices.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Nick Gliddon, Vodafone Business Director
- UK Government
- Vodafone Business
- MSP Six Degrees
- Major UK Retailers and Carmakers (e.g., M&S, Jaguar Land Rover)
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, business resilience, economic impact, government policy, cyber threats, AI-driven threats, public-private partnerships
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us